Healthc Inform Res.
2021 Jan;27(1):57-66. 10.4258/hir.2021.27.1.57.
Comprehensive Review of Factors Influencing the Use of Telepractice in Stuttering Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Health Information Management, School of Health Management and Information Sciences, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 2Health Management and Economics Research Center, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- KMID: 2512625
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2021.27.1.57
Abstract
Objectives
Stuttering is a speech disorder characterized by the repetition of sounds, syllables, or words; prolongation of sounds; and interruptions in speech. Telepractice allows speech services to be delivered to patients regardless of their location. This review investigated factors influencing the use of telepractice in stuttering treatment.
Methods
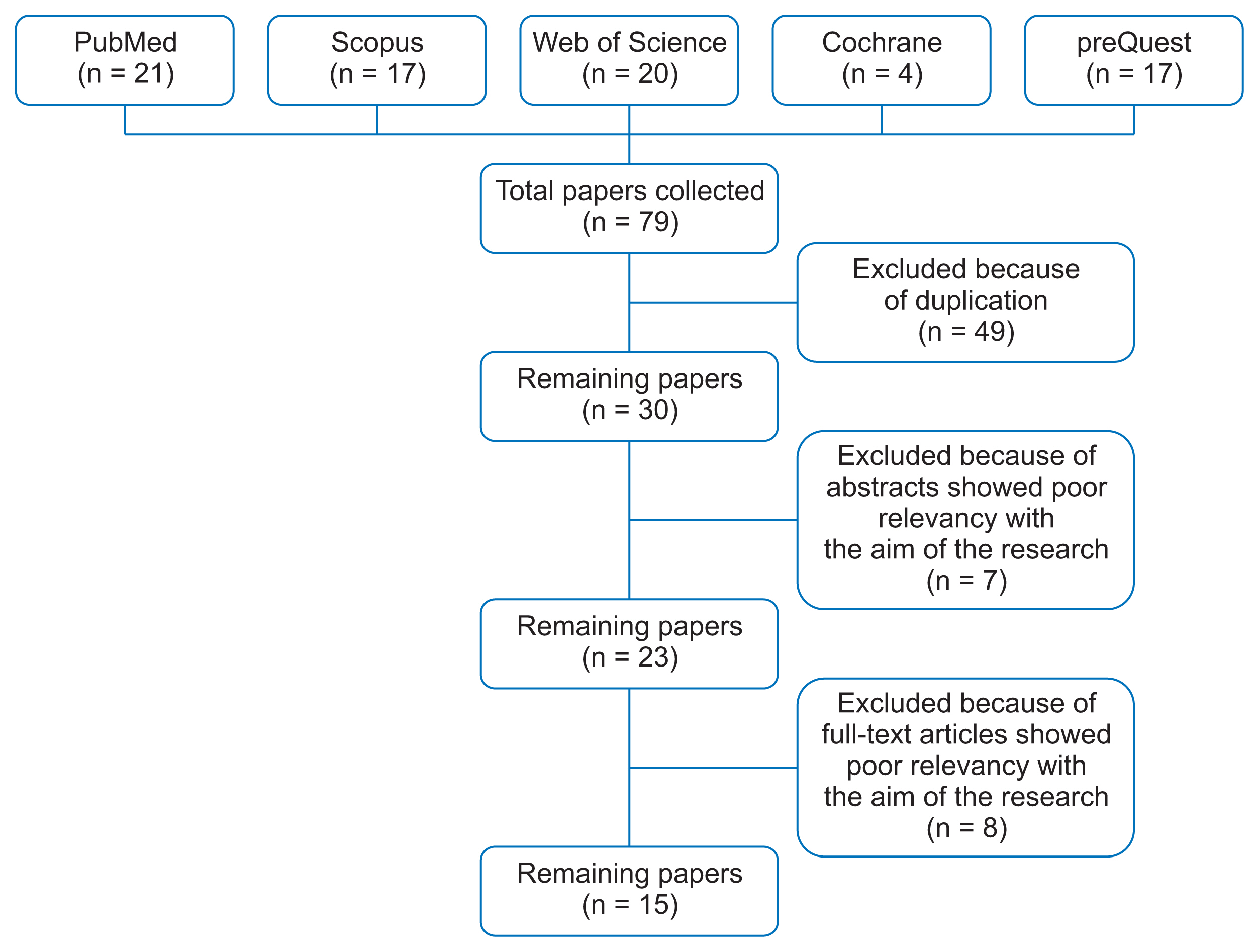
Articles related to the application of telepractice in stuttering were searched using the Scopus, Web of Science, PubMed, Cochrane, and ProQuest databases without consideration of any time limit. Initially, 79 articles were found and after application of the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 15 articles were selected for the review study. Data were analyzed by using the content analysis method and synthesized narratively.
Results
Factors influencing the use of telepractice in stuttering treatment were categorized into individual, technical, clinical, and economic factors. Providing access to healthcare services, maintaining personal privacy, and allowing flexibility in arranging appointments were among individual factors. In terms of the technical factors, technical problems and Internet speed were addressed. Clinical factors were divided into positive and negative outcomes, and economic factors were mainly related to time and cost savings.
Conclusions
Although patients may benefit from using telepractice, the widespread adoption of this technology can be hindered by some technical and non-technical factors. Because telepractice can be employed as a complementary method to treat stuttering, more attention should be paid to the required infrastructure and factors that may negatively impact the use of this technology.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Royal College of Speech and Language Therapists. RC-SLT clinical guidelines. Oxon, UK: Speechmark Publishing;2005.2. Yadegari F, Shirazi TS, Howell P, Nilipour R, Shafiei M, Shafiei B, et al. Persian overall assessment of the speaker’s experience of stuttering for adults: the impact of stuttering on the Persian-speaking adults who stutter. Iran Rehabil J. 2018; 16:131–8.
Article3. Packman A, Onslow M. Investigating optimal intervention intensity with the Lidcombe Program of early stuttering intervention. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2012; 14:467–70.
Article4. Cangi ME, Togram B. Stuttering therapy through telepractice in Turkey: a mixed method study. J Fluency Disord. 2020; 66:105793.
Article5. Beijer LJ, Rietveld AC. Asynchronous telemedicine applications in the rehabilitation of acquired speech-language disorders in neurological patients. Smart Homecare Technol Telehealth. 2015; 3:39–48.6. Bridgman K, Onslow M, O’Brian S, Jones M, Block S. Lidcombe Program webcam treatment for early stuttering: a randomized controlled trial. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2016; 59:932–9.
Article7. Cason J, Cohn ER. Telepractice: an overview and best practices. Perspect Augment Altern Commun. 2014; 23(1):4–17.
Article8. Weidner K, Lowman J. Telepractice for adult speech-language pathology services: a systematic review. Perspect ASHA Spec Interest Groups. 2020; 5:326–38.
Article9. O’Brian S, Packman A, Onslow M. Telehealth delivery of the Camperdown Program for adults who stutter: a phase I trial. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2008; 51:184–95.
Article10. Eslami Jahromi M, Ahmadian L. Evaluating satisfaction of patients with stutter regarding the tele-speech therapy method and infrastructure. Int J Med Inform. 2018; 115:128–33.
Article11. Allen CR. The use of email as a component of adult stammering therapy: a preliminary report. J Telemed Telecare. 2011; 17:163–7.
Article12. Lowe R, O’Brian S, Onslow M. Review of telehealth stuttering management. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2013; 65:223–38.
Article13. McGill M, Noureal N, Siegel J. Telepractice treatment of stuttering: a systematic review. Telemed J E Health. 2019; 25:359–68.
Article14. Wootton R. Telemedicine in low-resource settings. Lausanne, Switzerland: Frontiers Media SA;2015.15. Sicotte C, Lehoux P, Fortier-Blanc J, Leblanc Y. Feasibility and outcome evaluation of a telemedicine application in speech-language pathology. J Telemed Telecare. 2003; 9:253–8.
Article16. Wilson L, Onslow M, Lincoln M. Telehealth adaptation of the Lidcombe Program of early stuttering intervention: five case studies. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2004; 13:81–93.17. Lewis C, Packman A, Onslow M, Simpson JM, Jones M. A phase II trial of telehealth delivery of the Lidcombe Program of early stuttering intervention. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2008; 17:139–49.
Article18. Carey B, O’Brian S, Onslow M, Block S, Jones M, Packman A. Randomized controlled non-inferiority trial of a telehealth treatment for chronic stuttering: the Camperdown Program. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2010; 45:108–20.
Article19. Erickson S, Block S, Menzies R, O’Brian S, Packman A, Onslow M. Standalone Internet speech restructuring treatment for adults who stutter: a phase I study. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2016; 18:329–40.
Article20. Carey B, O’Brian S, Onslow M, Packman A, Menzies R. Webcam delivery of the Camperdown Program for adolescents who stutter: a phase I trial. Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 2012; 43:370–80.
Article21. Carey B, O’Brian S, Lowe R, Onslow M. Webcam delivery of the Camperdown Program for adolescents who stutter: a phase II trial. Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 2014; 45:314–24.
Article22. O’Brian S, Smith K, Onslow M. Webcam delivery of the Lidcombe program for early stuttering: a phase I clinical trial. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2014; 57:825–30.
Article23. Ferdinands B, Bridgman K. An investigation into the relationship between parent satisfaction and child fluency in the Lidcombe Program: clinic versus telehealth delivery. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2019; 21:347–54.
Article24. Vogel AP, Block S, Kefalianos E, Onslow M, Eadie P, Barth B, et al. Feasibility of automated speech sample collection with stuttering children using interactive voice response (IVR) technology. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2015; 17:115–20.
Article25. Kully D. Telehealth in speech pathology: applications to the treatment of stuttering. J Telemed Telecare. 2000; 6(Suppl 2):S39–41.
Article26. Marcin JP, Shaikh U, Steinhorn RH. Addressing health disparities in rural communities using telehealth. Pediatr Res. 2016; 79:169–76.
Article27. Eslami Jahromi M, Ahmadian L, Bahaadinbeigy K. The effect of tele-speech therapy on treatment of stuttering. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2020; 1–6.
Article28. Jafni TI, Bahari M, Ismail W, Radman A. Understanding the implementation of telerehabilitation at pre-implementation stage: a systematic literature review. Procedia Comput Sci. 2017; 124:452–60.
Article29. Constantinescu G, Theodoros D, Russell T, Ward E, Wilson S, Wootton R. Treating disordered speech and voice in Parkinson’s disease online: a randomized controlled non-inferiority trial. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2011; 46:1–16.30. Pitt R, Theodoros D, Hill AJ, Russell T. The impact of the telerehabilitation group aphasia intervention and networking programme on communication, participation, and quality of life in people with aphasia. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2019; 21:513–23.
Article