J Stroke.
2021 Jan;23(1):139-143. 10.5853/jos.2020.05043.
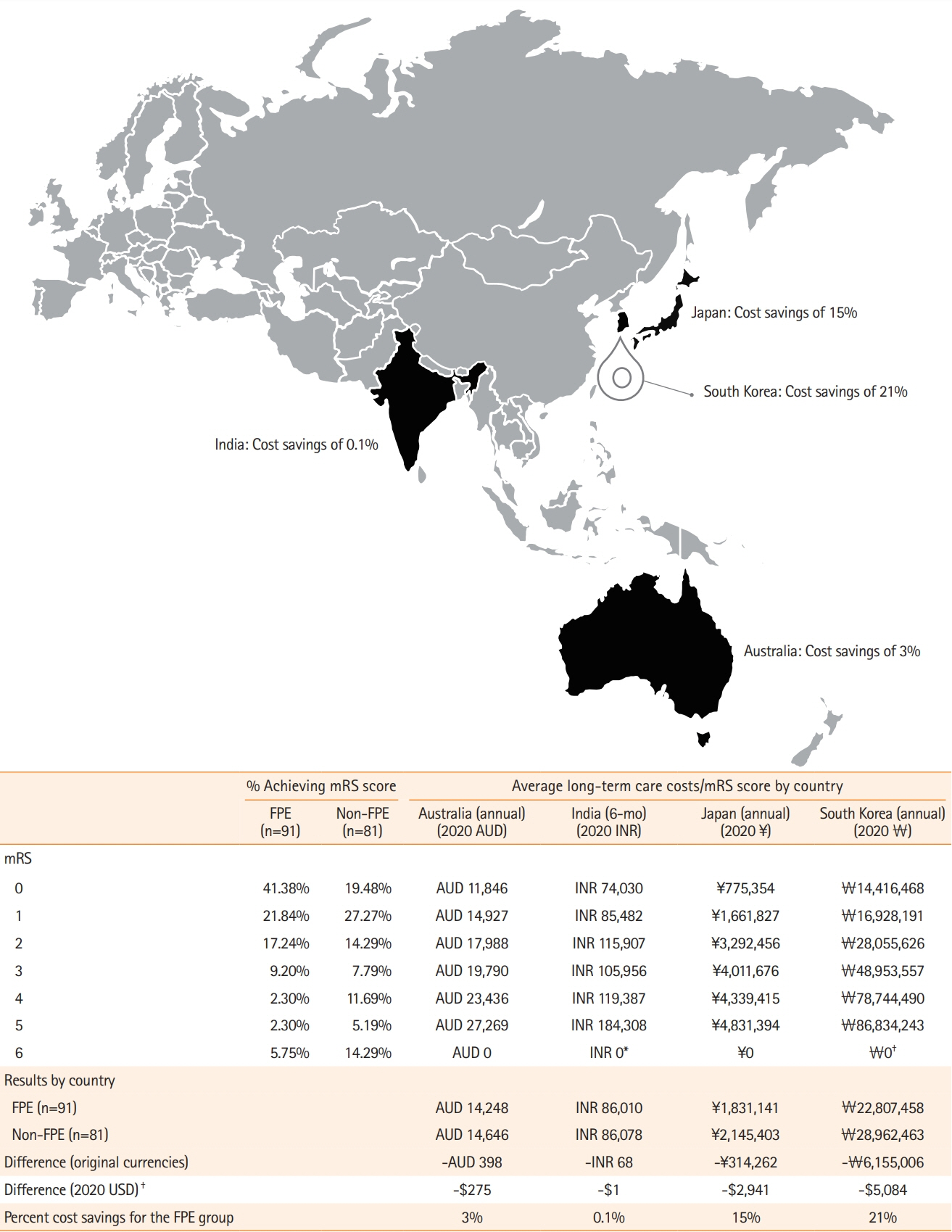
Health Economic Impact of First Pass Success: An Asia-Pacific Cost Analysis of the ARISE II Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Neurology, National University Health System, Singapore
- 2Department of Medicine, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore
- 3Department of Neuroscience, Mercy Health St. Vincent Mercy Hospital, Toledo, OH, USA
- 4Department of Neurology, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, USA
- 5Department of Neurology, Inselspital, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
- 6Johnson & Johnson Medical Asia Pacific, Singapore
- 7Cerenovus, Johnson & Johnson, Irvine, CA, USA
- 8EVERSANA, Burlington, ON, Canada
- 9Departments of Neuroradiology, Karolinska University Hospital and Clinical Neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden
- 10Department of Medical Imaging, AZ Groeninge, Kortrijk, Belgium
- KMID: 2512365
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2020.05043
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Zaidat OO, Castonguay AC, Linfante I, Gupta R, Martin CO, Holloway WE, et al. First pass effect: a new measure for stroke thrombectomy devices. Stroke. 2018; 49:660–666.2. Zaidat OO, Bozorgchami H, Ribó M, Saver JL, Mattle HP, Chapot R, et al. Primary results of the multicenter ARISE II study (Analysis of Revascularization in Ischemic Stroke With EmboTrap). Stroke. 2018; 49:1107–1115.3. Dawson J, Lees JS, Chang TP, Walters MR, Ali M, Davis SM, et al. Association between disability measures and healthcare costs after initial treatment for acute stroke. Stroke. 2007; 38:1893–1898.
Article4. Lobotesis K, Veltkamp R, Carpenter IH, Claxton LM, Saver JL, Hodgson R. Cost-effectiveness of stent-retriever thrombectomy in combination with IV t-PA compared with IV t-PA alone for acute ischemic stroke in the UK. J Med Econ. 2016; 19:785–794.
Article5. Kunz WG, Almekhlafi MA, Menon BK, Saver JL, Hunink MG, Dippel DWJ, et al. Public health and cost benefits of successful reperfusion after thrombectomy for stroke. Stroke. 2020; 51:899–907.
Article6. Maegerlein C, Berndt MT, Mönch S, Kreiser K, Boeckh-Behrens T, Lehm M, et al. Further development of combined techniques using stent retrievers, aspiration catheters and BGC: The PROTECTPLUS Technique. Clin Neuroradiol. 2020; 30:59–65.7. Delgado Almandoz JE, Kayan Y, Young ML, Fease JL, Scholz JM, Milner AM, et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes in patients with acute ischemic strokes treated with mechanical thrombectomy using either Solumbra or ADAPT techniques. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016; 8:1123–1128.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Health Informatics in the Asia Pacific
- Allergic rhinitis, chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis in Asia Pacific: impact on quality of life and sleep
- Allergic diseases in the Asia Pacific: path into the future
- Climate change, air pollution, and biodiversity in Asia Pacific: impact on allergic diseases
- "Asia Pacific Allergy": A new leap forward