J Stroke.
2021 Jan;23(1):1-11. 10.5853/jos.2020.02698.
Role of Blood Pressure Management in Stroke Prevention: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of 93 Randomized Controlled Trials
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Qingdao Central Hospital, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
- 2Department of Neurology and Institute of Neurology, Huashan Hospital, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 3Department of Neurology, Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
- 4Department of Chinese Traditional Medicine, Jing’an District Center Hospital of Shanghai, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- KMID: 2512351
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2020.02698
Abstract
- Background and Purpose
The present study aimed to compare the efficacy and tolerability of different blood pressure (BP)-lowering strategies.
Methods
Randomized controlled trials that compared various antihypertensive treatments and stroke outcomes were included. Eligible trials were categorized into three scenarios: single or combination antihypertensive agents against placebos; single or combination agents against other agents; and different BP-lowering targets. The primary efficacy outcome was the risk reduction pertaining to strokes. The tolerability outcome was the withdrawal of drugs, owing to drug-related side effects (PROSPERO registration number CRD42018118454 [20/12/2018]).
Results
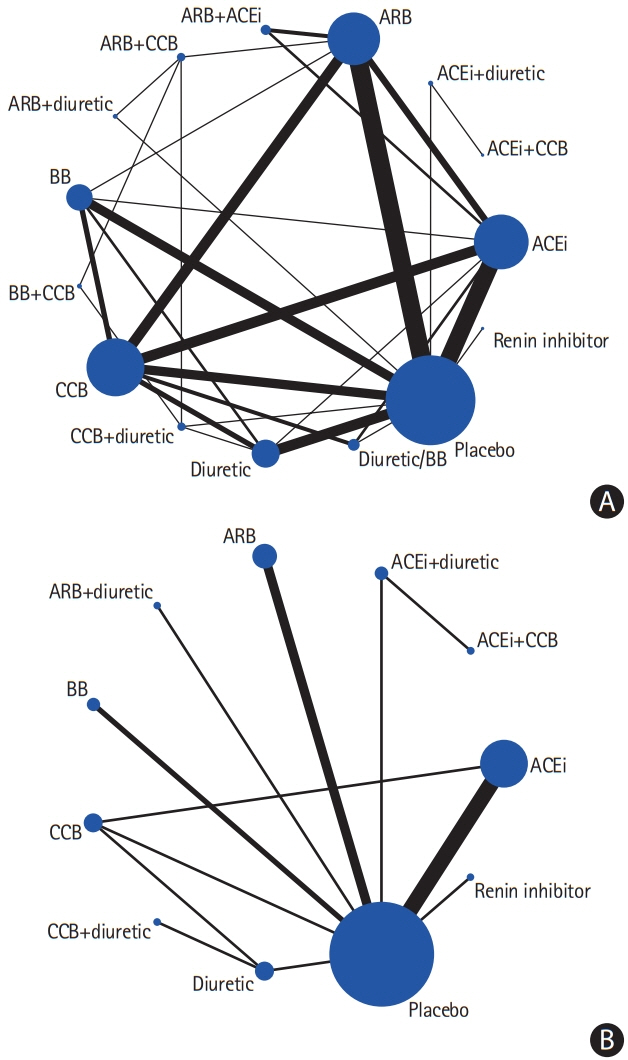
The present study included 93 trials (average follow-up duration, 3.3 years). In the pairwise analysis, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEis) and beta-blockers (BBs) were inferior to calcium channel blockers (CCBs) (odds ratio [OR], 1.123; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.008 to 1.252) (OR, 1.261; 95% CI, 1.116 to 1.425) for stroke prevention, BB was inferior to angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARB) (OR, 1.361; 95% CI, 1.142 to 1.622), and diuretics were superior to ACEi (OR, 0.871; 95% CI, 0.771 to 0.984). The combination of ACEi+CCB was superior to ACEi+diuretic (OR, 0.892; 95% CI, 0.823 to 0.966). The network meta-analysis confirmed that diuretics were superior to BB (OR, 1.34; 95% CI, 1.11 to 1.58), ACEi+diuretic (OR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.02 to 2.08), BB+CCB (OR, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.05 to 3.79), and renin inhibitors (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.25 to 2.75) for stroke prevention. Regarding the tolerability profile, the pairwise analysis revealed that ACEi was inferior to CCB and less tolerable, compared to the other treatments.
Conclusions
Monotherapy using diuretics, CCB, or ARB, and their combinations could be employed as first-line treatments for stroke prevention in terms of efficacy and tolerability.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Systolic blood pressure variability within 120 hours of admission predicts the functional outcomes at discharge of patients with acute ischemic stroke
Tiago Pedro, Pedro Pereira, Ana Sofia Costa, Fábio Almeida, Maria Luísa Loureiro, Teresa Alfaiate, Abílio Gonçalves
J Neurocrit Care. 2022;15(1):32-38. doi: 10.18700/jnc.210038.
Reference
-
References
1. Krishnamurthi RV, Ikeda T, Feigin VL. Global, regional and country-specific burden of ischaemic stroke, intracerebral haemorrhage and subarachnoid haemorrhage: a systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2017. Neuroepidemiology. 2020; 54:171–179.
Article2. Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical practice guidelines. Hypertension. 2018; 71:e13–e115.
Article3. Ettehad D, Emdin CA, Kiran A, Anderson SG, Callender T, Emberson J, et al. Blood pressure lowering for prevention of cardiovascular disease and death: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2016; 387:957–967.
Article4. Katsanos AH, Filippatou A, Manios E, Deftereos S, Parissis J, Frogoudaki A, et al. Blood pressure reduction and secondary stroke prevention: a systematic review and metaregression analysis of randomized clinical trials. Hypertension. 2017; 69:171–179.5. Reboussin DM, Allen NB, Griswold ME, Guallar E, Hong Y, Lackland DT, et al. Systematic review for the 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018; 71:2176–2198.6. Jeffers BW, Robbins J, Bhambri R. Efficacy of calcium channel blockers versus other classes of antihypertensive medication in the treatment of hypertensive patients with previous stroke and/or coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Ther. 2017; 24:e68–e80.
Article7. Salanti G. Indirect and mixed-treatment comparison, network, or multiple-treatments meta-analysis: many names, many benefits, many concerns for the next generation evidence synthesis tool. Res Synth Methods. 2012; 3:80–97.
Article8. Jansen JP, Fleurence R, Devine B, Itzler R, Barrett A, Hawkins N, et al. Interpreting indirect treatment comparisons and network meta-analysis for health-care decision making: report of the ISPOR Task Force on Indirect Treatment Comparisons Good Research Practices: part 1. Value Health. 2011; 14:417–428.
Article9. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:e1000097.
Article10. Hutton B, Salanti G, Caldwell DM, Chaimani A, Schmid CH, Cameron C, et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med. 2015; 162:777–784.
Article11. Law MR, Morris JK, Wald NJ. Use of blood pressure lowering drugs in the prevention of cardiovascular disease: meta-analysis of 147 randomised trials in the context of expectations from prospective epidemiological studies. BMJ. 2009; 338:b1665.
Article12. Higgins J, Green SE. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration;https://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org. 2011. Accessed December 1, 2020.13. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315:629–634.
Article14. Dias S, Welton NJ, Sutton AJ, Ades AE. NICE DSU technical support document 2: a generalised linear modelling framework for pairwise and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence;www.nicedsu.org.uk. 2016. Accessed December 1, 2020.15. Biondi-Zoccai G, Abbate A, Benedetto U, Palmerini T, D’Ascenzo F, Frati G. Network meta-analysis for evidence synthesis: what is it and why is it posed to dominate cardiovascular decision making? Int J Cardiol. 2015; 182:309–314.
Article16. Dias S, Welton NJ, Caldwell DM, Ades AE. Checking consistency in mixed treatment comparison meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2010; 29:932–944.
Article17. Lu G, Ades AE. Assessing evidence inconsistency in mixed treatment comparisons. J Am Stat Assoc. 2006; 101:447–459.
Article18. Higgins JP, Jackson D, Barrett JK, Lu G, Ades AE, White IR. Consistency and inconsistency in network meta-analysis: concepts and models for multi-arm studies. Res Synth Methods. 2012; 3:98–110.
Article19. Salanti G, Ades AE, Ioannidis JP. Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: an overview and tutorial. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011; 64:163–171.
Article20. Chaimani A, Higgins JP, Mavridis D, Spyridonos P, Salanti G. Graphical tools for network meta-analysis in STATA. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e76654.
Article21. Mukete BN, Cassidy M, Ferdinand KC, Le Jemtel TH. Longterm anti-hypertensive therapy and stroke prevention: a meta-analysis. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2015; 15:243–257.
Article22. SPS3 Study Group, Benavente OR, Coffey CS, Conwit R, Hart RG, McClure LA, et al. Blood-pressure targets in patients with recent lacunar stroke: the SPS3 randomised trial. Lancet. 2013; 382:507–515.23. Park JM, Kim BJ, Kwon SU, Hwang YH, Heo SH, Rha JH, et al. Intensive blood pressure control may not be safe in subacute ischemic stroke by intracranial atherosclerosis: a result of randomized trial. J Hypertens. 2018; 36:1936–1941.24. James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, Cushman WC, Dennison-Himmelfarb C, Handler J, et al. 2014 Evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA. 2014; 311:507–520.25. Weiss J, Freeman M, Low A, Fu R, Kerfoot A, Paynter R, et al. Benefits and harms of intensive blood pressure treatment in adults aged 60 years or older: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2017; 166:419–429.26. SoRelle R. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute halts part of antihypertensive and lipid-lowering treatment to prevent heart attack trial (ALLHAT). Circulation. 2000; 101:E9025.
Article27. Xie XX, Liu P, Wan FY, Lin SG, Zhong WL, Yuan ZK, et al. Blood pressure lowering and stroke events in type 2 diabetes: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Cardiol. 2016; 208:141–146.
Article28. Rouse B, Chaimani A, Li T. Network meta-analysis: an introduction for clinicians. Intern Emerg Med. 2017; 12:103–111.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Impact of Mental Practice on Motor Function in Patients With Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- The Effects of Aromatherapy on Stroke Symptoms in Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Introduction to systematic review and meta-analysis
- Blood Pressure Management for Stroke Prevention and in Acute Stroke
- The effect of psyllium supplementation on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials