J Bacteriol Virol.
2020 Dec;50(4):227-234. 10.4167/jbv.2020.50.4.227.
Proteins in Outer Membrane Vesicles Produced by Burkholderia cepacia are Responsible for Pro-inflammatory Responses in Epithelial Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 41944, Republic of Korea
- 2Drug & Disease Target Team, Korea Basic Science Institute, Ochang 28119, Republic of Korea
- 3Department of Bio-Analytical Science, University of Science and Technology (UST), Daejeon 34116, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2512142
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2020.50.4.227
Abstract
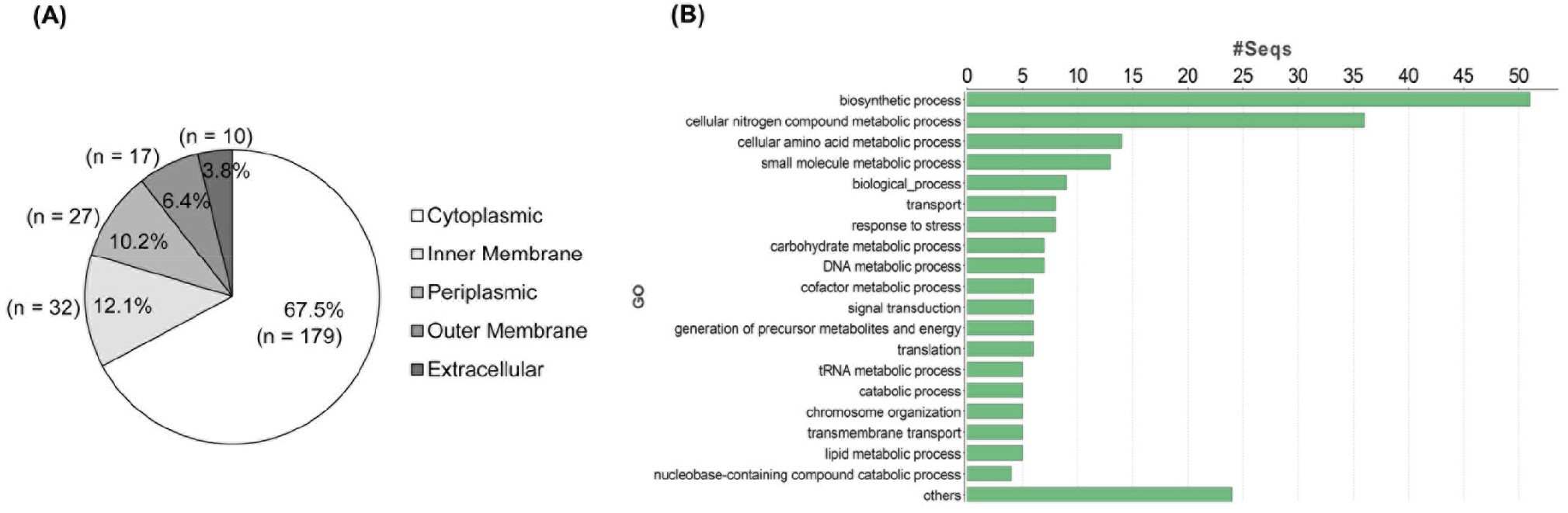
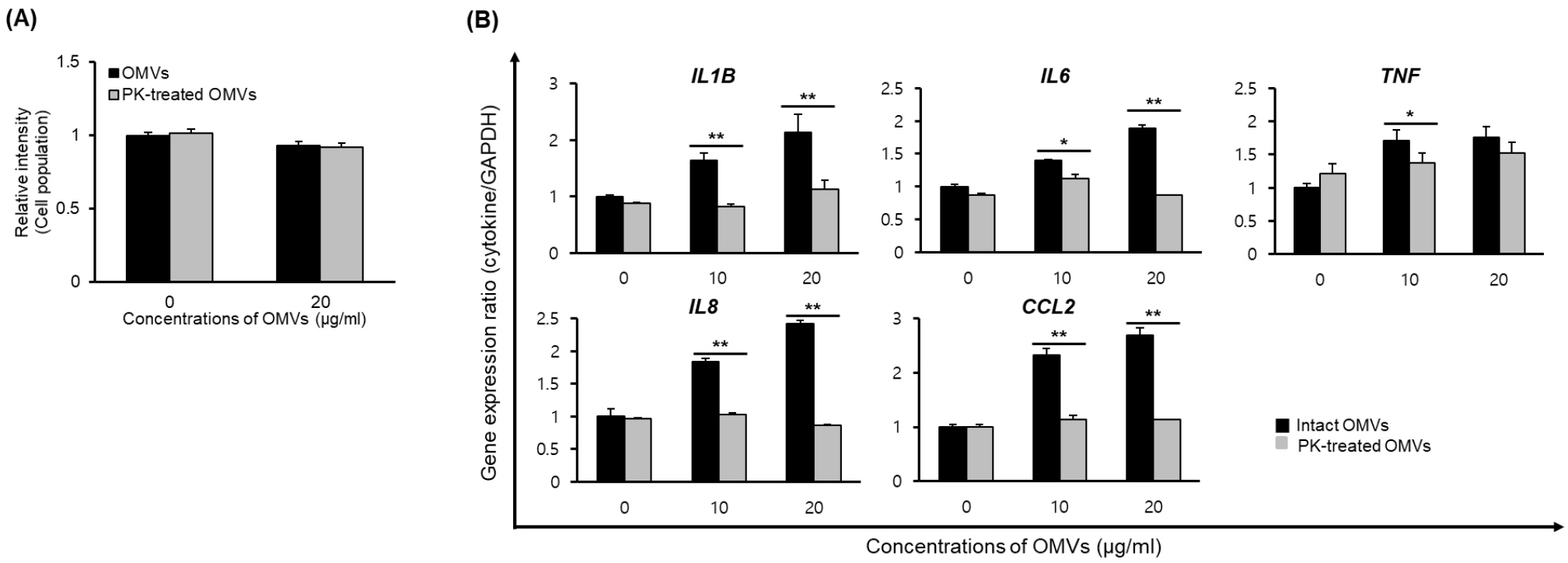
- Gram-negative bacterial pathogens produce outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) and this secreted cargo plays a role in host-pathogen interactions. OMVs isolated from Burkholderia cepacia induce the cytotoxicity and pro-inflammatory responses both in vitro and in vivo, but OMV components associated with host pathology have not been characterized. This study analyzed the proteomes of OMVs produced by B. cepacia ATCC 25416 and investigated whether proteins in B. cepacia OMVs were responsible for host pathology in vitro. Proteomic analysis revealed that a total of 265 proteins were identified in B. cepacia OMVs. Of the 265 OMV proteins, 179 (67.5%), 32 (12.1%), 27 (10.2%), 17 (6.4%), and 10 (3.8%) were predicted to be located in the cytoplasm, inner membrane, periplasmic space, outer membrane, and extracellular compartment, respectively. Several putative virulence factors were also identified in B. cepacia OMVs. B. cepacia OMVs slightly induced the cytotoxicity in lung epithelial A549 cells, but there was no difference in cytotoxic activity between intact OMVs and proteinase K-treated OMVs. B. cepacia OMVs stimulated the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine genes in A549 cells, but the expression of these cytokine genes was significantly inhibited in A549 cells incubated with proteinase K-treated OMVs. In conclusion, our results suggest that proteins in B. cepaciaOMVs are directly responsible for pro-inflammatory responses in lung epithelial cells.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lipuma JJ. Update on the Burkholderia cepacia complex. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2005;11:528-33.DOI: 10.1097/01.mcp.0000181475.85187.ed. PMID: 16217180.2. Bach E, Sant’Anna FH, Magrich dos Passos JF, Balsanelli E, de Baura VA, Pedrosa FO, et al. Detection of misidentifications of species from the Burkholderia cepacia complex and description of a new member, the soil bacterium Burkholderia catarinensis sp nov. Pathog Dis 2017;75.DOI: 10.1093/femspd/ftx076. PMID: 28859310.3. Kidd TJ, Douglas JM, Bergh HA, Coulter C, Bell SC. Burkholderia cepacia complex epidemiology in persons with cystic fibrosis from Australia and New Zealand. Res Microbiol 2008;159:194-9.DOI: 10.1016/j.resmic.2008.01.001. PMID: 18356026.4. Kenna DTD, Lilley D, Coward A, Martin K, Perry C, Pike R, et al. Prevalence of Burkholderia species, including members of Burkholderia cepacia complex, among UK cystic and non-cystic fibrosis patients. J Med Microbiol 2017;66:490-501.DOI: 10.1099/jmm.0.000458. PMID: 28463663.5. Burkholder WH. Sour skin, a bacterial rot of onion bulbs. Phytopathology 1950;40:115-7.6. Abdelfattah R, Al-Jumaah S, Al-Qahtani A, Al-Thawadi S, Barron I, Al-Mofada S, et al. Outbreak of Burkholderia cepacia bacteraemia in a tertiary care centre due to contaminated ultrasound probe gel. J Hosp Infect 2018; 98:289-94.DOI: 10.1016/j.jhin.2017.09.010. PMID: 28923373.7. Abdallah M, Abdallah HA, Memish ZA. Burkholderia cepacia complex outbreaks among non-cystic fibrosis patients in the intensive care units: A review of adult and pediatric literature. Infez Med 2018;26:299-307.8. Tegos GP, Haynes MK, Schweizer HP. Dissecting novel virulent determinants in the Burkholderia cepacia complex. Virulence 2012;3:234-7.DOI: 10.4161/viru.19844. PMID: 22546904. PMCID: PMC3442833.9. Thomson ELS, Dennis JJ. A Burkholderia cepacia complex non-ribosomal peptide- synthesized toxin is hemolytic and required for full virulence. Virulence 2012;3:286-98.DOI: 10.4161/viru.19355. PMID: 22546908. PMCID: PMC3442841.10. Lagatolla C, Skerlavaj S, Dolzani L, Tonin EA, Bragadin CM, Bosco M, et al. Microbiological characterization of Burkholderia cepacia isolates from cystic fibrosis patients: investigation of the exopolysaccharides produced. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2002;209:99-106.DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2002.tb11116.x. PMID: 12007661.11. Jan AT. Outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) of gram-negative bacteria: a perspective update. Front Microbiol 2017;8:1053.DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01053. PMID: 28649237. PMCID: PMC5465292.12. Kulp A, Kuehn MJ. Biological functions and biogenesis of secreted bacterial outer membrane vesicles. Ann Rev Microbiol 2010;64:163-84.DOI: 10.1146/annurev.micro.091208.073413. PMID: 20825345. PMCID: PMC3525469.13. Ellis TN, Kuehn MJ. Virulence and immunomodulatory roles of bacterial outer membrane vesicles. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2010;74:81-94.DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.00031-09. PMID: 20197500. PMCID: PMC2832350.14. Lee EY, Bang JY, Park GW, Choi DS, Kang JS, Kim HJ, et al. Global proteomic profiling of native outer membrane vesicles derived from Escherichia coli. Proteomics 2007;7:3143-53.DOI: 10.1002/pmic.200700196. PMID: 17787032.15. Bomberger JM, Maceachran DP, Coutermarsh BA, Ye S, O’Toole GA, Stanton BA. Long-distance delivery of bacterial virulence factors by Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane vesicles. PLoS Pathog 2009;5:e1000382.DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000382. PMID: 19360133. PMCID: PMC2661024.16. Jin JS, Kwon SO, Moon DC, Gurung M, Lee JH, Kim SI, et al. Acinetobacter baumannii secretes cytotoxic outer membrane protein A via outer membrane vesicles. PLoS One 2011;6:e17027.DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017027. PMID: 21386968. PMCID: PMC3046175.17. Nho JS, Jun SH, Oh MH, Park TI, Choi CW, Kim SI, et al. Acinetobacter nosocomialis secretes outer membrane vesicles that induce epithelial cell death and host inflammatory responses. Microb Pathog 2015;81:39-45.DOI: 10.1016/j.micpath.2015.03.012. PMID: 25778390.18. Kim YJ, Jeon H, Na SH, Kwon HI, Selasi GN, Nicholas A, et al. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia outer membrane vesicles elicit a potent inflammatory response in vitro and in vivo. Pathog Dis 2016;74:ftw104.19. Allan ND, Kooi C, Sokol PA, Beveridge TJ. Putative virulence factors are released in association with membrane vesicles from Burkholderia cepacia. Can J Microbiol 2003;49:613-24.DOI: 10.1139/w03-078. PMID: 14663495.20. Kim SY, Kim MH, Son JH, Kim SI, Yun SH, Kim K, et al. Outer membrane vesicles produced by Burkholderia cepacia cultured with subinhibitory concentrations of ceftazidime enhance pro-inflammatory responses. Virulence 2020; 11:995-1005.DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1802193. PMID: 32799627. PMCID: PMC7567438.21. Yun SH, Park EC, Lee SY, Lee H, Choi CW, Yi YS, et al. Antibiotic treatment modulates protein components of cytotoxic outer membrane vesicles of multidrug-resistant clinical strain, Acinetobacter baumannii DU202. Clin Proteomics 2018;15:28.DOI: 10.1186/s12014-018-9204-2. PMID: 30186054. PMCID: PMC6118003.22. Jeon H, Oh MH, Jun SH, Kim SI, Choi CW, Kwon HI, et al. Variation among Staphylococcus aureus membrane vesicle proteomes affects cytotoxicity of host cells. Microb Pathog 2016;93:185-93.DOI: 10.1016/j.micpath.2016.02.014. PMID: 26924795.23. Kwon SO, Gho YS, Lee JC, Kim SI. Proteome analysis of outer membrane vesicles from a clinical Acinetobacter baumannii isolate. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2009;297:150-6.DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01669.x. PMID: 19548894.24. Choi CW, Park EC, Yun SH, Lee SY, Lee YG, Hong Y, et al. Proteomic characterization of the outer membrane vesicle of Pseudomonas putida KT2440. J Proteome Res 2014;13:4298-309.DOI: 10.1021/pr500411d. PMID: 25198519.25. Ishihama Y, Oda Y, Tabata T, Sato T, Nagasu T, Rappsilber J, et al. Exponentially modified protein abundance index (emPAI) for estimation of absolute protein amount in proteomics by the number of sequenced peptides per protein. Mol Cell Proteomics 2005;4:1265-72.DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M500061-MCP200. PMID: 15958392.26. Van Faassen H, KuoLee R, Harris G, Zhao X, Conlan JW, Chen W. Neutrophils play an important role in host resistance to respiratory infection with Acinetobacter baumannii in mice. Infect Immun 2007;75:5597-608.DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00762-07. PMID: 17908807. PMCID: PMC2168347.27. Jun SH, Lee JH, Kim BR, Kim SI, Park TI, Lee JC, et al. Acinetobacter baumannii outer membrane vesicles elicit a potent innate immune response via membrane proteins. PLoS One 2013;8:e71751.DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071751. PMID: 23977136. PMCID: PMC3743744.28. Nieves W, Petersen H, Judy BM, Blumentritt CA, Russell-Lodrigue K, Roy CJ, et al. A Burkholderia pseudomallei outer membrane vesicle vaccine provides protection against lethal sepsis. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2014;21:747-54.DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00119-14. PMID: 24671550. PMCID: PMC4018892.29. Norris MH, Khan MSR, Chirakul S, Schweizer HP, Tuanyok A. Outer membrane vesicle vaccines from biosafe surrogates prevent acute lethal glanders in mice. Vaccines 2018;6:5.DOI: 10.3390/vaccines6010005. PMID: 29320408. PMCID: PMC5874646.30. Punj V, Sharma R, Zaborina O, Chakrabarty AM. Energy-generating enzymes of Burkholderia cepacia and their interactions with macrophages. J Bacteriol 2003;185:3167-78.DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.10.3167-3178.2003. PMID: 12730177. PMCID: PMC154058.31. Hutchison ML, Poxton IR, Govan JR. Burkholderia cepacia produces a hemolysin that is capable of inducing apoptosis and degranulation of mammalian phagocytes. Infect Immun 1998;66:2033-9.DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.5.2033-2039.1998. PMID: 9573086. PMCID: PMC108160.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Skin Infection with Burkholderia cepacia
- A case of lung abscess caused by Burkholderia cepacia in healthy child
- Pseudoinfections Due to Benzalconium-chloride Solution Contaminated with Burkholderia cepacia
- A case of Burkholderia cepacia peritonitis in a patient on CAPD
- Vertebral Osteomyelitis caused by Burkholderia cepacia in an Immunocompetent Elderly Patient After Acupuncture