Prog Med Phys.
2020 Dec;31(4):194-204. 10.14316/pmp.2020.31.4.194.
Trend Analysis on Korean and International Management for Activated Material Waste from Medical Linear Accelerator
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Accelerator Science, Korea University, Sejong, Korea
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 4Research Team of Radiological Physics & Engineering, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2510481
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2020.31.4.194
Abstract
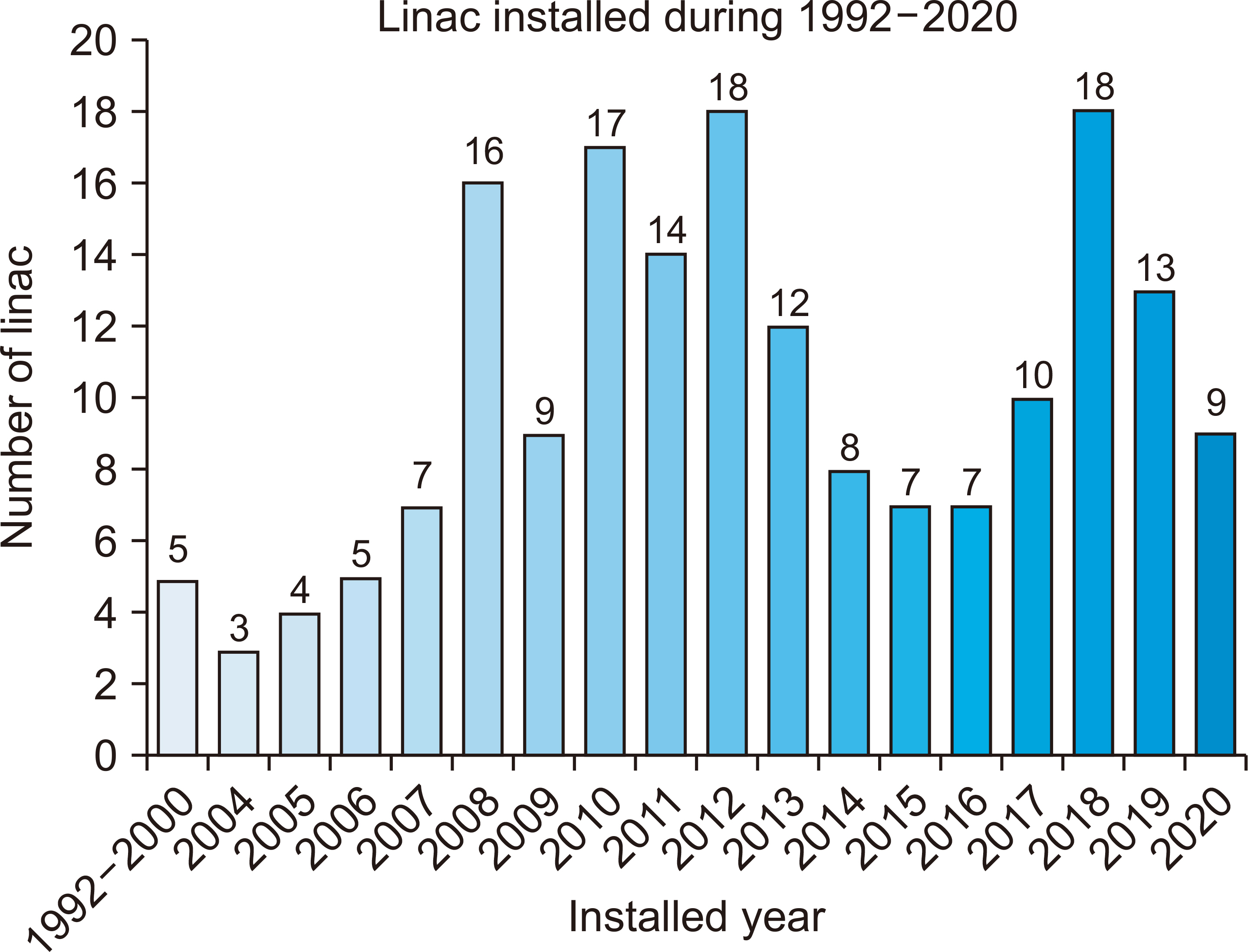
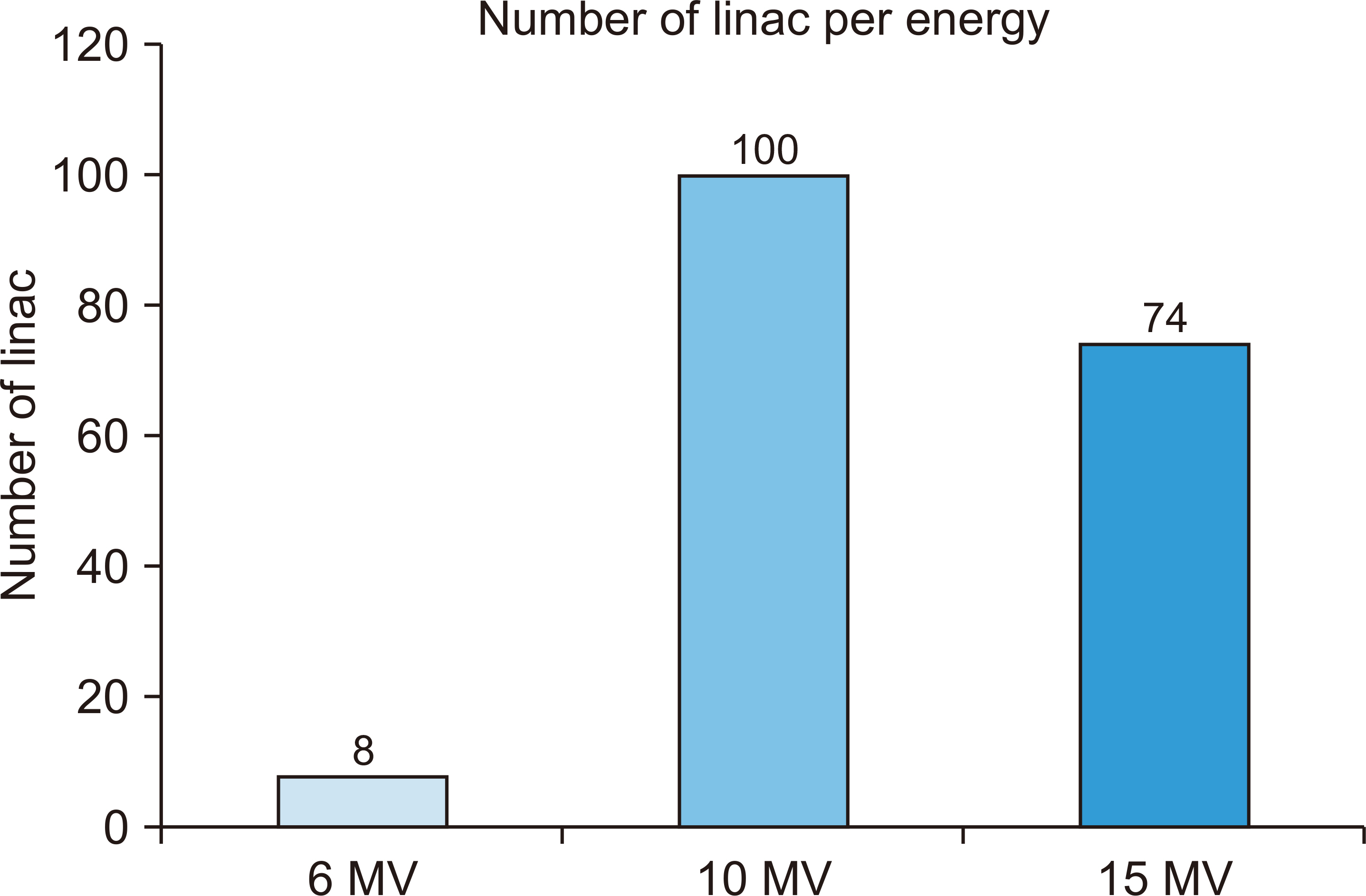
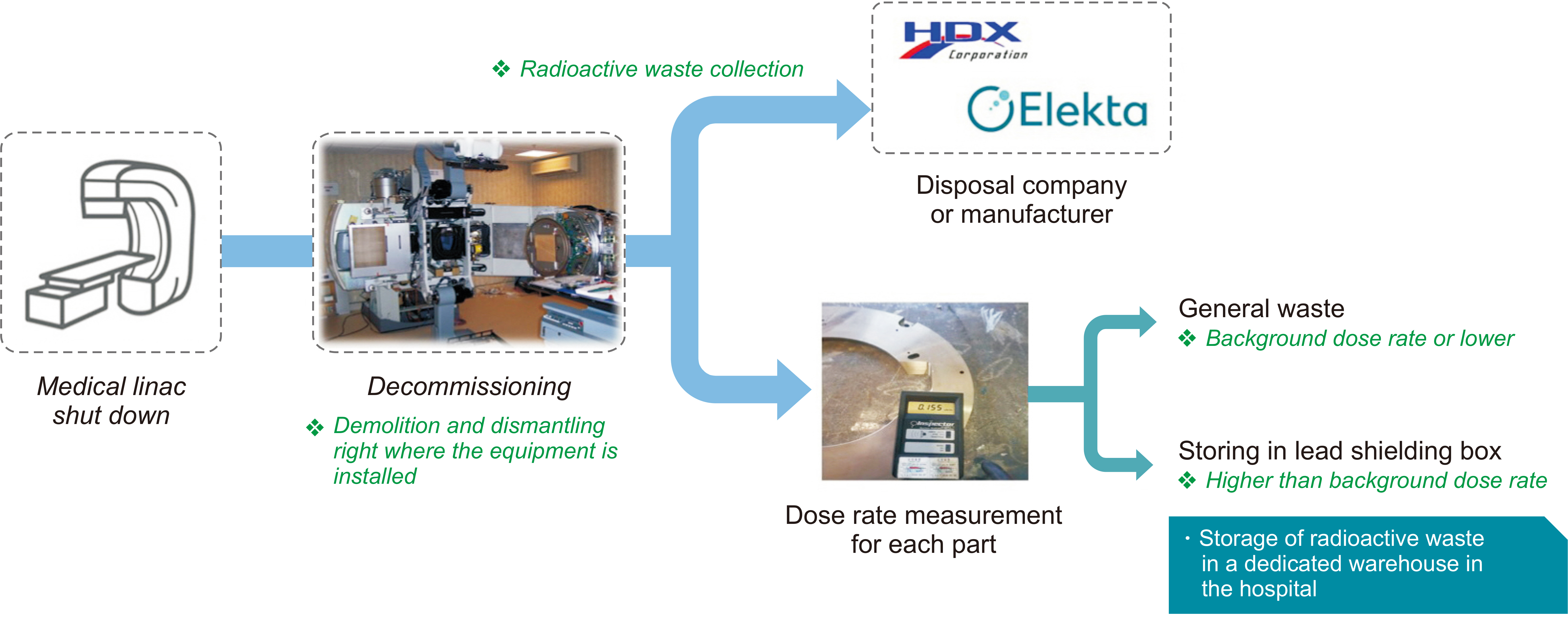
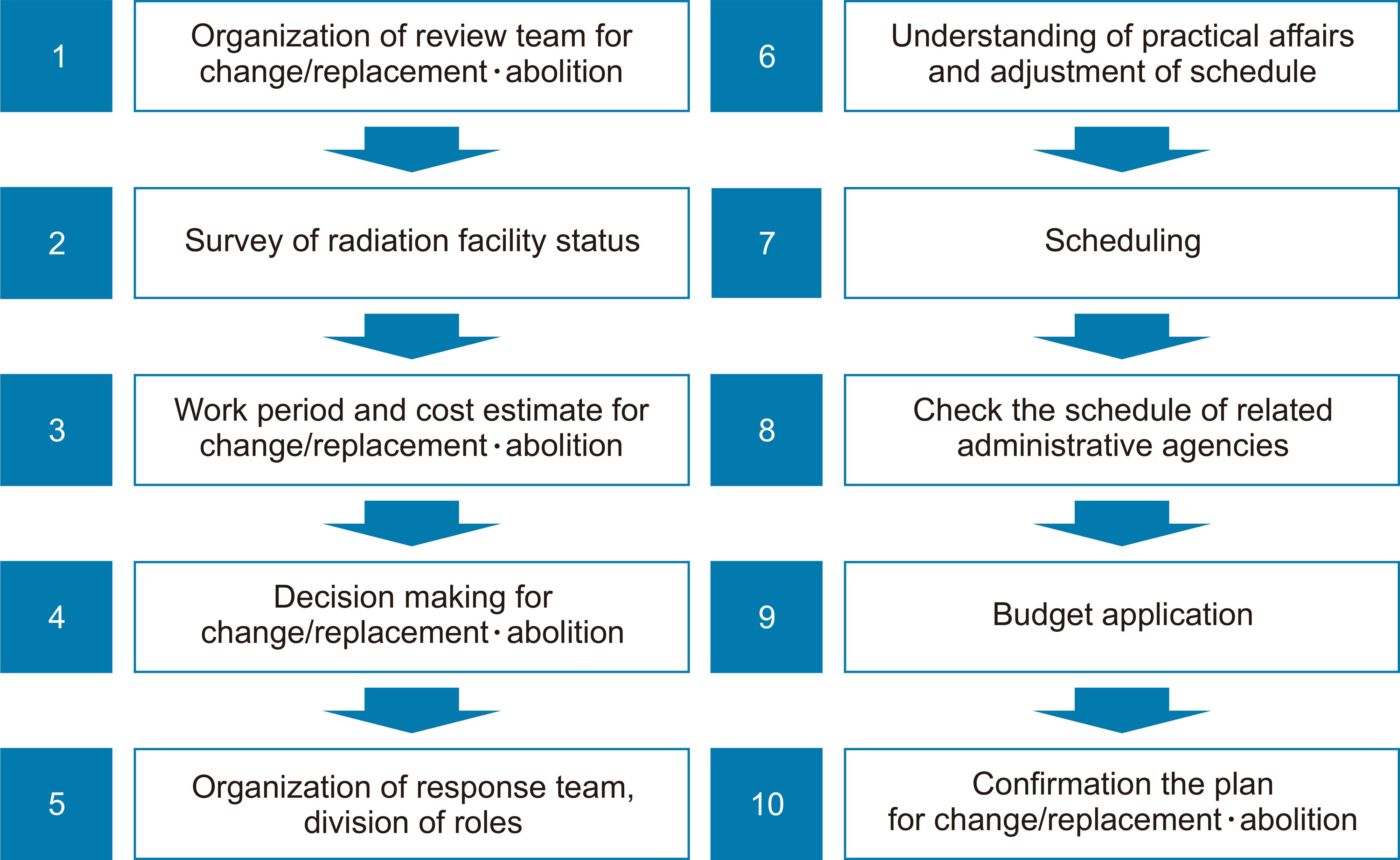
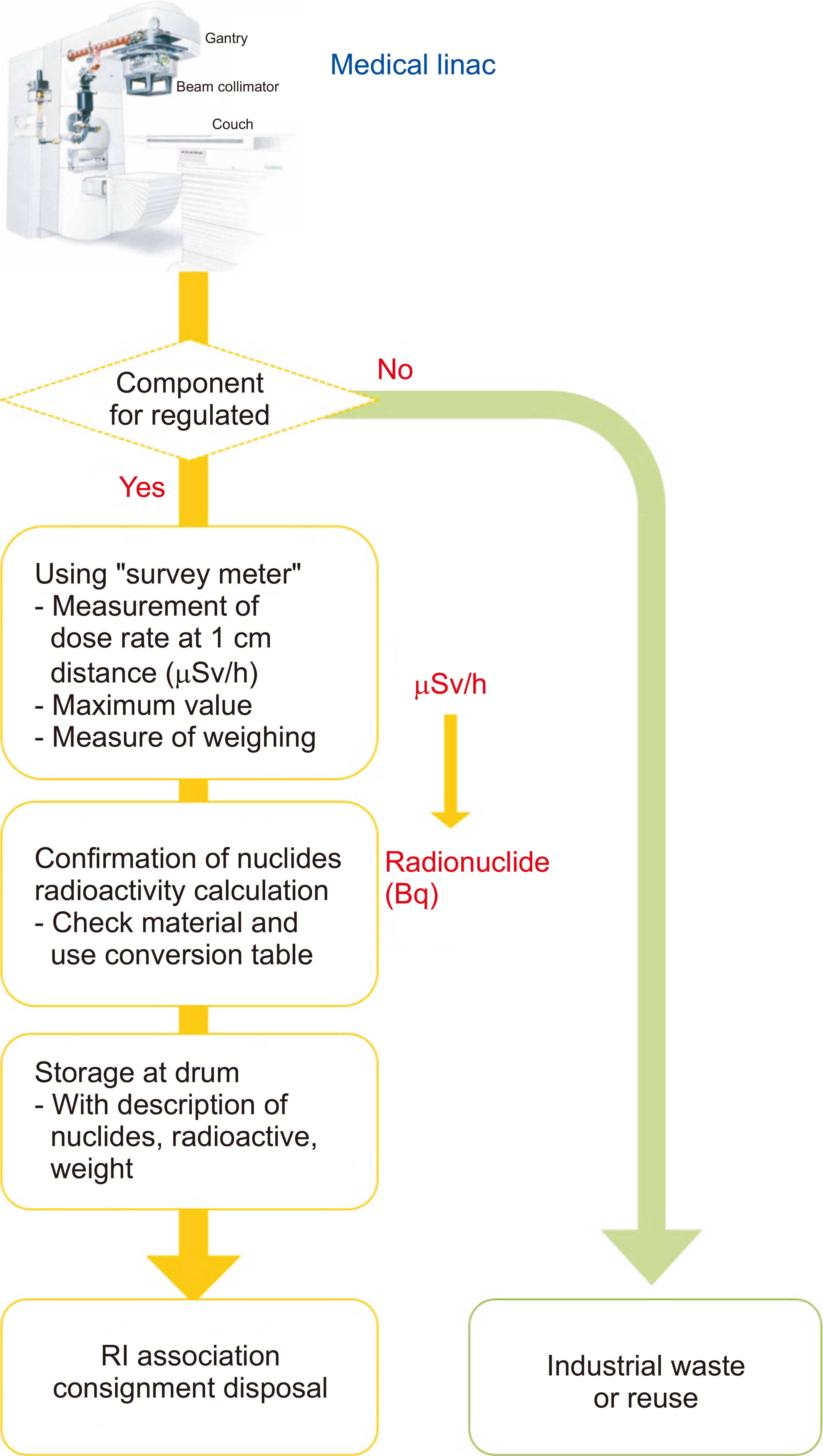
- This study investigated and analyzed the Korean and international status of radioactive waste management for medical linear accelerators (linacs) and proceed prior research to suggest radiation safety regulations and guidelines for the safe use of radiation. We analyzed the number of linacs installed in the radiation oncology departments of 103 institutions. In addition, we analyzed the procedures and standards for disposal in Korea and foreign countries. For foreign countries, we analyzed the status based on reports from the United States, Japan, Europe, and Canada. A total of 182 linacs are installed in Korea and 95% of them use more than 10 MV of energy. In Korea, standards for managing radioactive waste from a linac, disposal procedures, and clearance criteria have yet to be established. Therefore, radioactive waste is disposed of in different ways depending on the hospitals where they originate. Japan, the US, and Canada have recommended clearance levels and procedures for linacs. Other countries have provided management guidelines for research or large-scale accelerators, but not for medical purposes. In this study, we investigated the management of radioactive waste from medical linacs in Korea and abroad. Several foreign countries have suggested a clearance level and criteria for disposing of waste storage drums. For the safe management of medical linacs, it is necessary to establish safety management regulations. In Korea, standards for disposal, such as radiation or dose limits, are required for medical linacs. A system for clearance when disposing at a medical institution should be created.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Measurements of Neutron Activation and Dose Rate Induced by High-Energy Medical Linear Accelerator
Na Hye Kwon, Young Jae Jang, Jinsung Kim, Kum Bae Kim, Jaeryong Yoo, So Hyun Ahn, Dong Wook Kim, Sang Hyoun Choi
Prog Med Phys. 2021;32(4):145-152. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2021.32.4.145.
Reference
-
References
1. International Atomic Energy Agency. 2000. Management of radioactive waste from the use of radionuclides in medicine. International Atomic Energy Agency;Vienna: IAEA-TECDOC 1183.2. National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurement. 1984. Neutron contamination from medical electron accelerators. National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurement;Washington, DC: NCRP Report No. 79.3. National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurement. 2005. Structural shielding design and evaluation for megavoltage X- and gamma-ray radiotherapy facilities. National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurement;Washington, DC: NCRP Report No. 151.4. Lee J, Kim H, Kim M, Song M, Cho D, Yoon H, et al. 2017. Nov. 22-24. Management plan for radioactive waste generated when dismantling the medical linear accelerator. Paper presented at: Workshop for Improving Safety Management in Medical Field. p. 408–409.5. Nuclear Safety and Security Commission Notice 2017-65. 2017. Regulations on radioactive waste classification and clearance standards. Radioactive Waste Safety Division, Nuclear Safety and Security Commission;Sejong:6. Health Physics Society. 2013. Surface and volume radioactivity standards for clearance. McLean: Health Physics Society. ANSI N13.12.7. U.S. Department of Energy. 2016. Clearance and release of personal property from accelerator facilities. U.S. Department of Energy;Washington, DC:8. U.S. Department of Energy. 2013. Radiation protection of the public and the environment. U.S. Department of Energy;Washington, DC:9. U.S. Department of Energy. 2011. Department of Energy. Occupational radiation protection program. U.S. Department of Energy;Washington, DC: DOE-STD-6004-2016.10. Varian Medical Systems. 2014. HE clinic Gantry Head Hazardous Substances and Material Removal and Disposal. Varian Medical Systems, Inc.;Palo Alto:11. Japanese Society of Radiation Oncology. 2014. Society standard for the management of radioactive substances in radiotherapy equipment. Japanese Society of Radiation Oncology.12. European Commission. 2000. Practical use of the concepts of clearance and exemption- part 1. European Commission. Radiation protection 122.13. International Atomic Energy Agency. 1988. Principles for the exemption of radiation sources and practices from regulatory control. International Atomic Energy Agency;Vienna: IAEA 89.14. Strahlenschutzkommission. 2009. Clearance of accelerators and the removal of accelerator parts from radiation protection areas. Strahlenschutzkommission.15. European Union. 2016. Official Journal of the European Union. Consolidated version of the Treaty establishing the European Atomic Energy Community. European Union;2016/C 203/01.16. European Union. 2015. Relating to the plan for the disposal of radioactive waste arising from the European Spallation Source Facility (Linear Accelerator). European Union;2015/C 72/01.17. Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission. 2015. Nuclear substances and radiation devices regulations. Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission;Ottawa: 2000–207.18. Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission. 2018. Conditional clearance levels for the disposal, recycling and reuse of activated medical accelerator components. Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission;Ottawa:
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Calculation of Energy Spectra for Electron Beam of Medical Linear Accelerator Using GEANT4
- Influencing Factors on the Practice of Medical Waste Management of Nurses in Tertiary General Hospitals after COVID-19
- Generation, types and impacts of biomedical waste during COVID-19: Indian context
- Status of Domestic and International Recommendations for Protection Design and Evaluation of Medical Linear Accelerator Facilities
- Linear Accelerator Radiosurgery for Trigeminal Neuralgia: Case Report