Korean J Transplant.
2020 Dec;34(4):249-256. 10.4285/kjt.20.0036.
Whole liver deceased donor liver transplantation for pediatric recipients: single-center experience for 20 years
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2510263
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/kjt.20.0036
Abstract
- Background
We investigated the incidence and outcomes of pediatric deceased donor liver transplantation (DDLT) using whole liver grafts in a high-volume liver transplantation (LT) center.
Methods
The study was a retrospective single-center analysis of whole LT in pediatric recipients. The study period was set as 20 years between January 2000 and December 2019. We defined pediatric recipients and donors to be aged ≤18 years.
Results
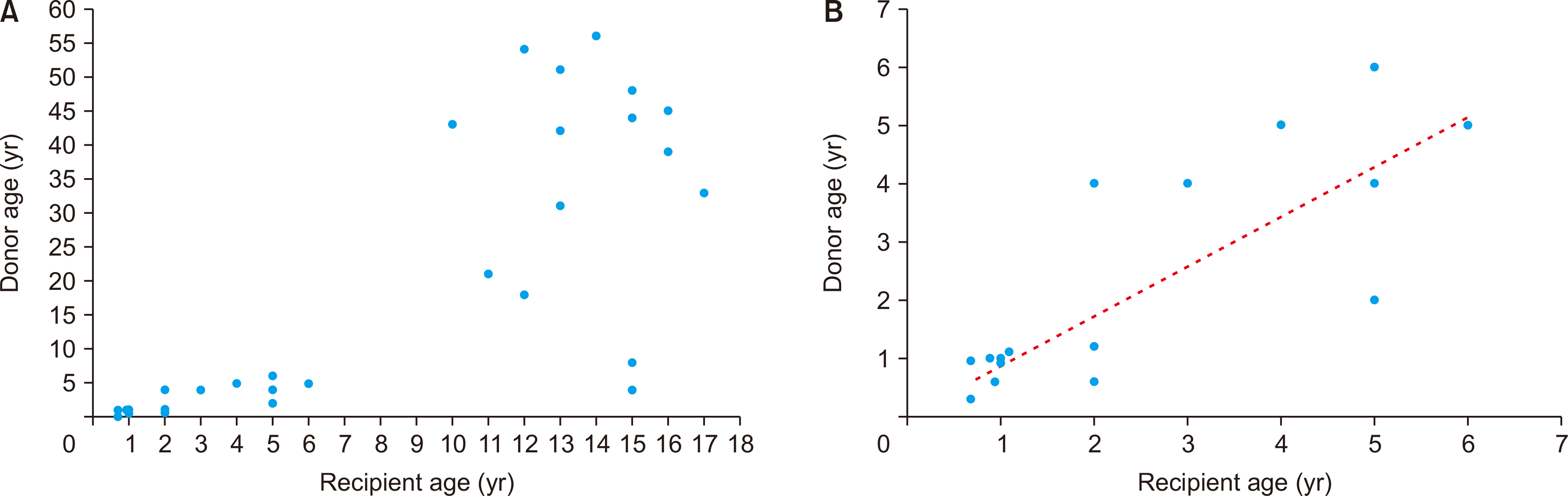
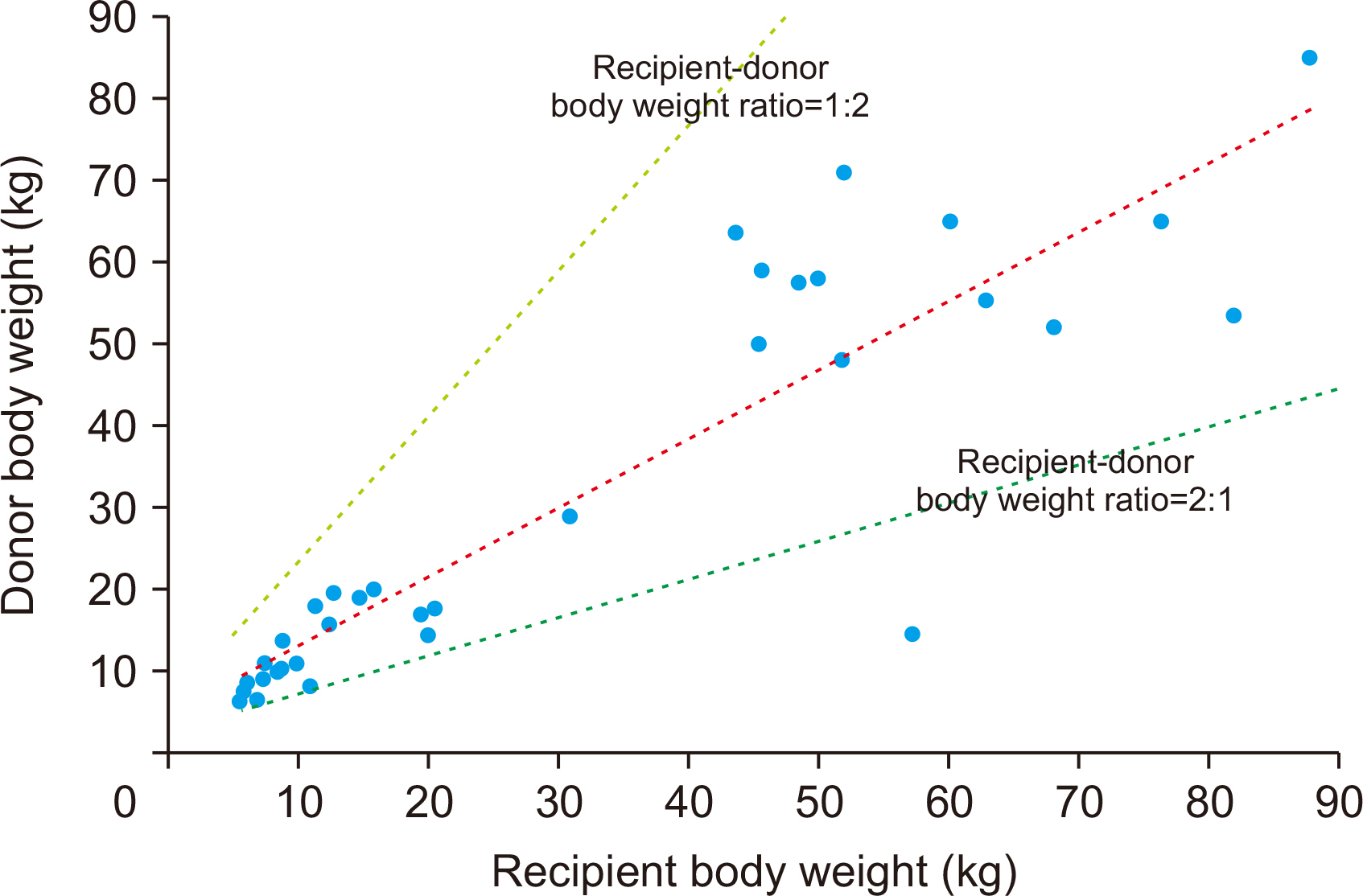
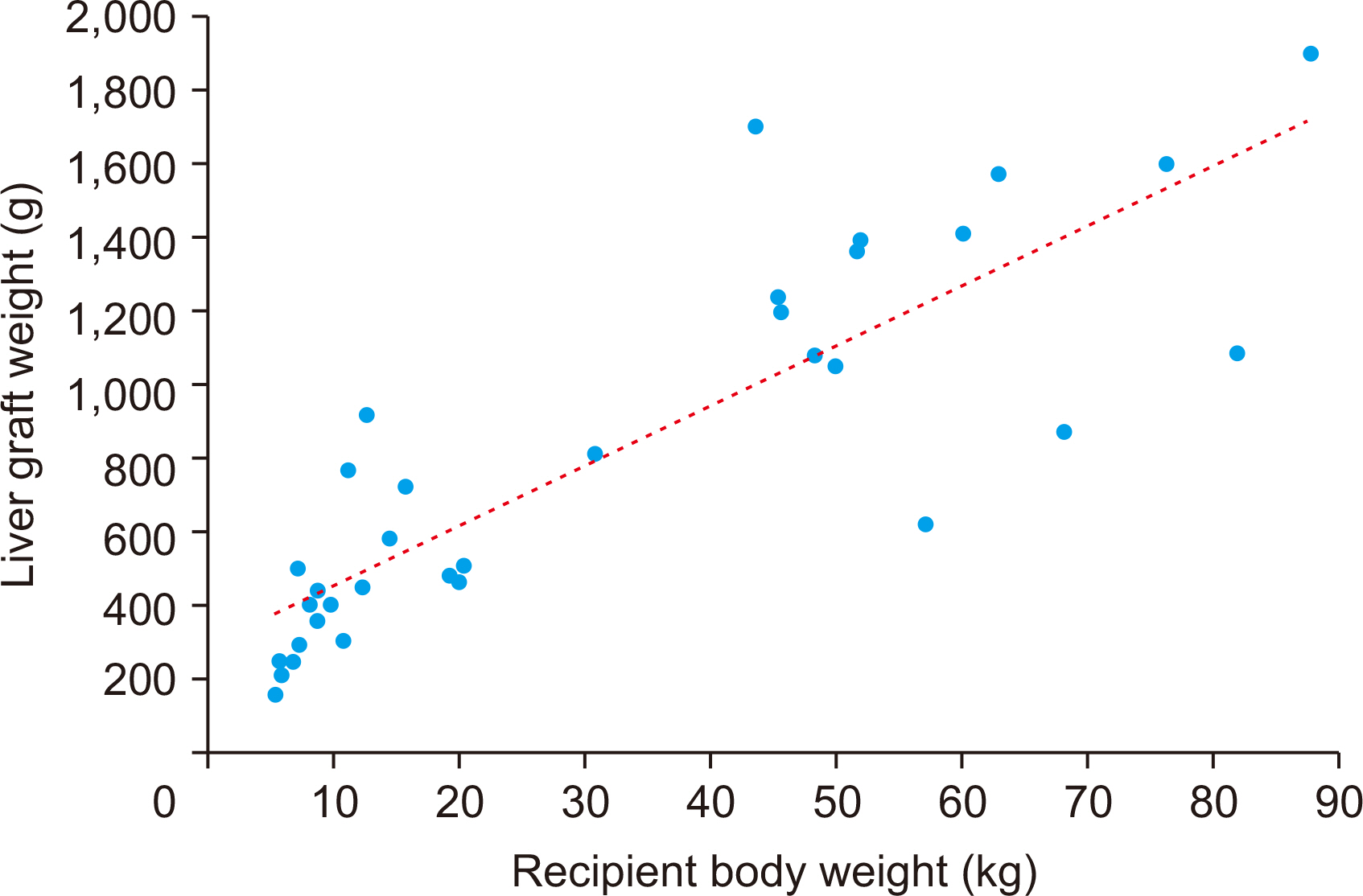
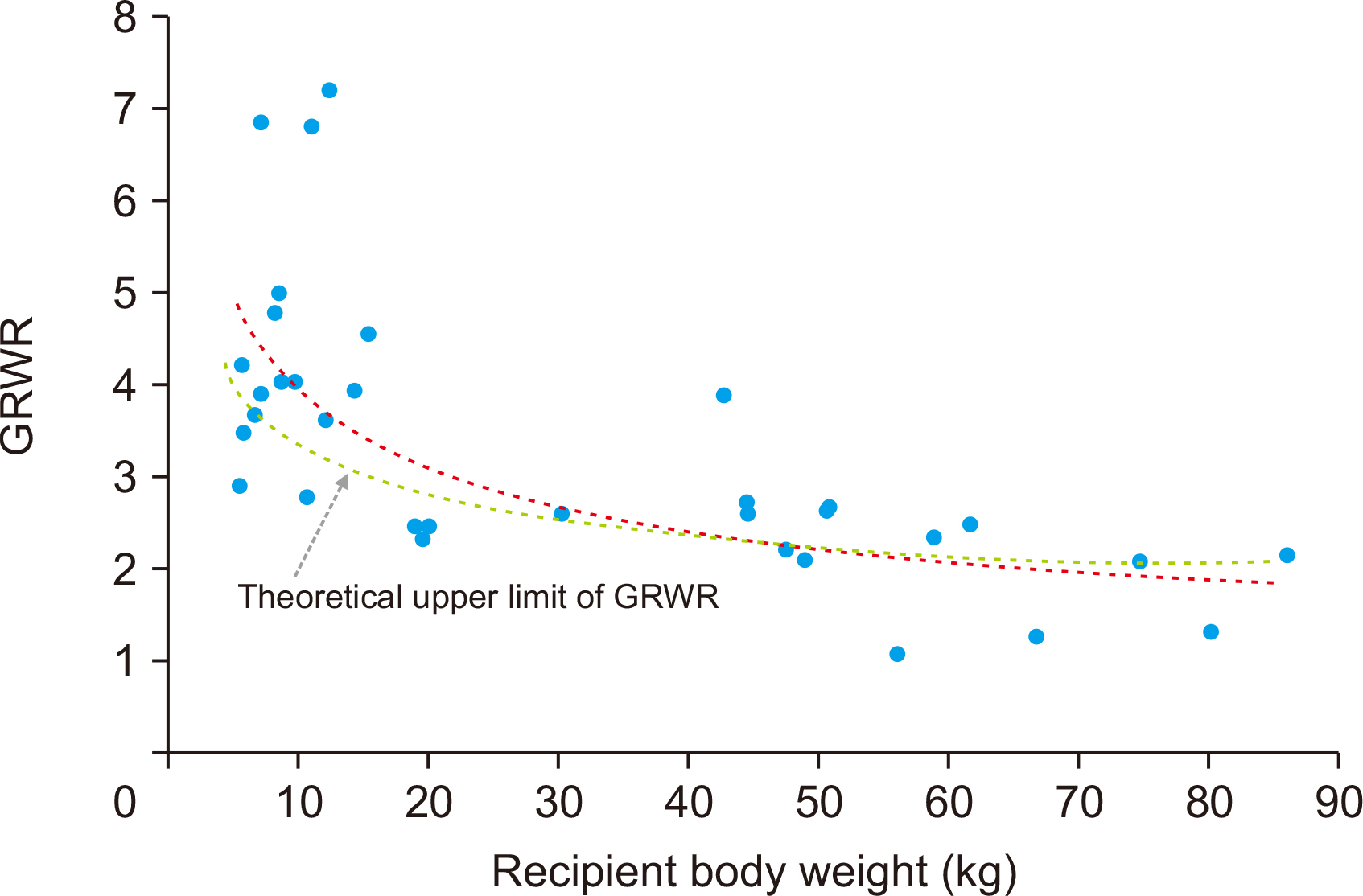
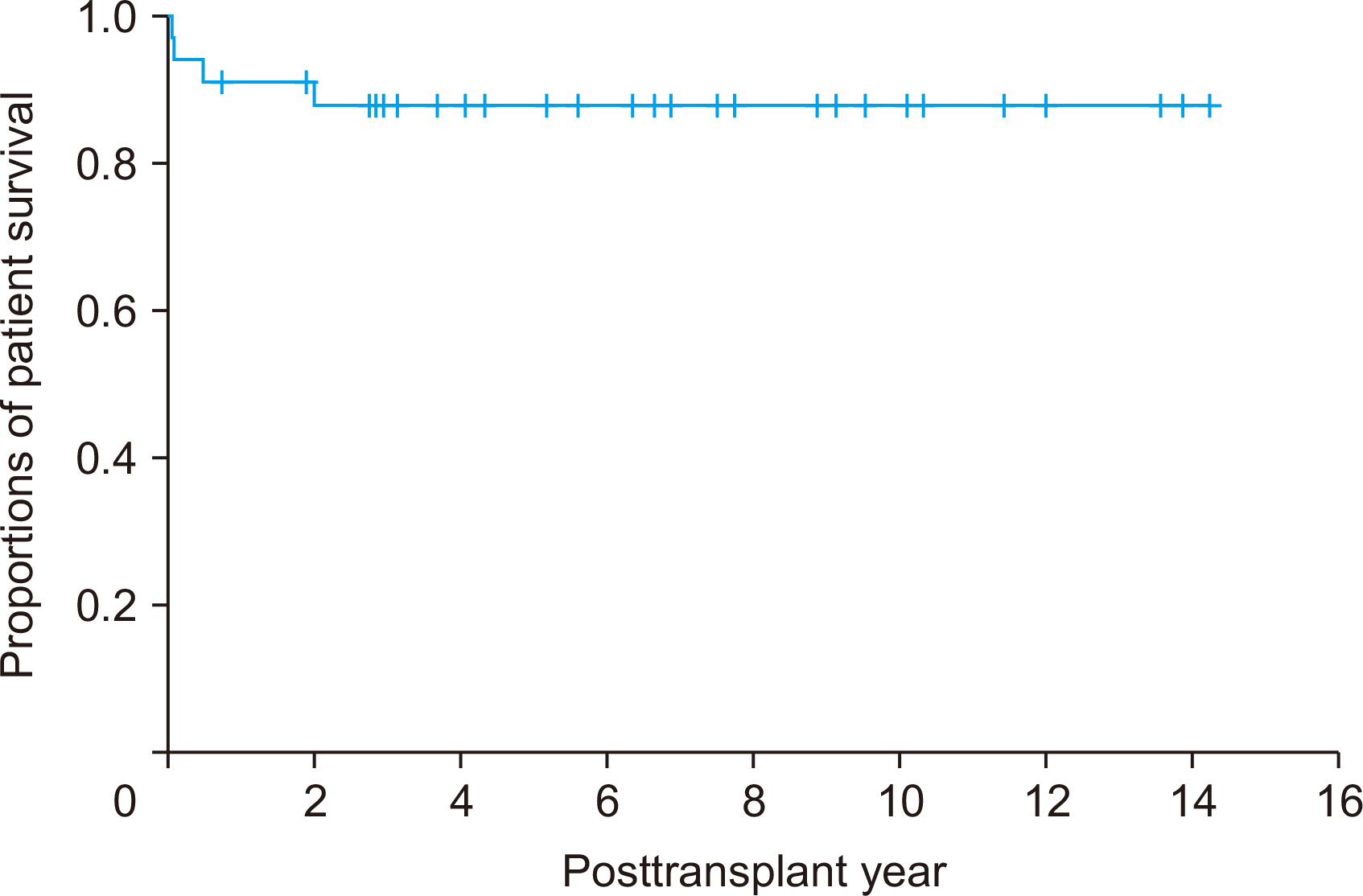
During the study period, there were 98 cases of pediatric DDLT, and 34 pa- tients (34.7%) received whole liver grafts. The age range of the deceased donors was 3 months to 56 years and that of pediatric recipients was 7 months to 17 years. Common primary diseases for LT were biliary atresia in 13, acute liver failure in four, Wilson dis-ease in four, congenital portal vein agenesis in three, and genetic metabolic diseases in three. Pediatric-to-pediatric and adult-to-pediatric whole LTs were 22 (64.7%) and 12 (35.3%), respectively. A good correlation was noted between the donor and the re-cipient’s body weight, and the recipient’s body weight and allograft’s weight. Graft and overall patient survival rates were 91.2% and 91.2% at 1 year, 88.0% and 88.0% at 3 years, and 88.0% and 88.0% at 5 years, respectively.
Conclusions
The results of this study revealed that Korean Network for Organ Sharing (KONOS) regulations with donor-recipient body weight matching exhibited good perfor-mance. Considering the reciprocal trades of liver organs among pediatric and adult donors and recipients, it is necessary to establish a policy for pediatric donor liver grafts to pediatric recipients on a priority basis.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Indications and outcomes of liver transplantation for post-Kasai biliary atresia in young adults
Jung-Man Namgoong, Shin Hwang, Chul-Soo Ahn, Deok-Bog Moon, Tae-Yong Ha, Gi-Won Song, Dong-Hwan Jung, Gil-Chun Park, Young-In Yoon, Kyung Mo Kim, Sung-Gyu Lee
Korean J Transplant. 2021;35(3):177-182. doi: 10.4285/kjt.21.0018.
Reference
-
1. Ye H, Zhao Q, Wang Y, Wang D, Zheng Z, Schroder PM, et al. 2015; Outcomes of technical variant liver transplantation versus whole liver transplantation for pediatric patients: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 10:e0138202. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138202. PMID: 26368552. PMCID: PMC4569420.
Article2. Lee S, Lee SK. 2019; Pediatric liver transplantation in Korea: long-term outcomes and allocations. J Korean Soc Transplant. 33:1–5. DOI: 10.4285/jkstn.2019.33.1.1.
Article3. Feng AC, Liao CY, Fan HL, Chen TW, Hsieh CB. 2015; A successful child-to-adult deceased donor liver transplantation: a case report and literature review. Ann Transplant. 20:21–4. DOI: 10.12659/AOT.893101. PMID: 25582243.
Article4. Zhang R, Zhu ZJ, Sun LY, Wei L, Qu W. 2018; Outcomes of liver transplantation using pediatric deceased donor livers: a single-center analysis of 102 donors. Chin Med J (Engl). 131:677–83. DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.226901. PMID: 29521290. PMCID: PMC5865313.5. Emre S, Soejima Y, Altaca G, Facciuto M, Fishbein TM, Sheiner PA, et al. 2001; Safety and risk of using pediatric donor livers in adult liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 7:41–7. DOI: 10.1053/jlts.2001.20940. PMID: 11150421.
Article6. Namgung JM, Hwang S, Ahn CS, Kim KH, Moon DB, Ha TY, et al. 2020; Korea-nationwide incidence of pediatric deceased donors and single-institutional status of liver transplantation using pediatric donor liver grafts. Korean J Transplant. 34:178–84. DOI: 10.4285/kjt.2020.34.3.178.
Article7. Kang SH, Hwang S, Ha TY, Song GW, Jung DH, Ahn CS, et al. 2019; Cross-sectional analysis of immunosuppressive regimens focused on everolimus after liver transplantation in a Korean high-volume transplantation center. Korean J Transplant. 33:98–105. DOI: 10.4285/jkstn.2019.33.4.98.
Article8. Hwang S, Namgoong JM, Oh SH, Kim KM, Ahn CS, Kwon H, et al. 2020; Effect of everolimus rescue therapy for acute cellular rejection following pediatric living donor liver transplantation: report of one case. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 24:216–20. DOI: 10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.2.216. PMID: 32457270. PMCID: PMC7271111.
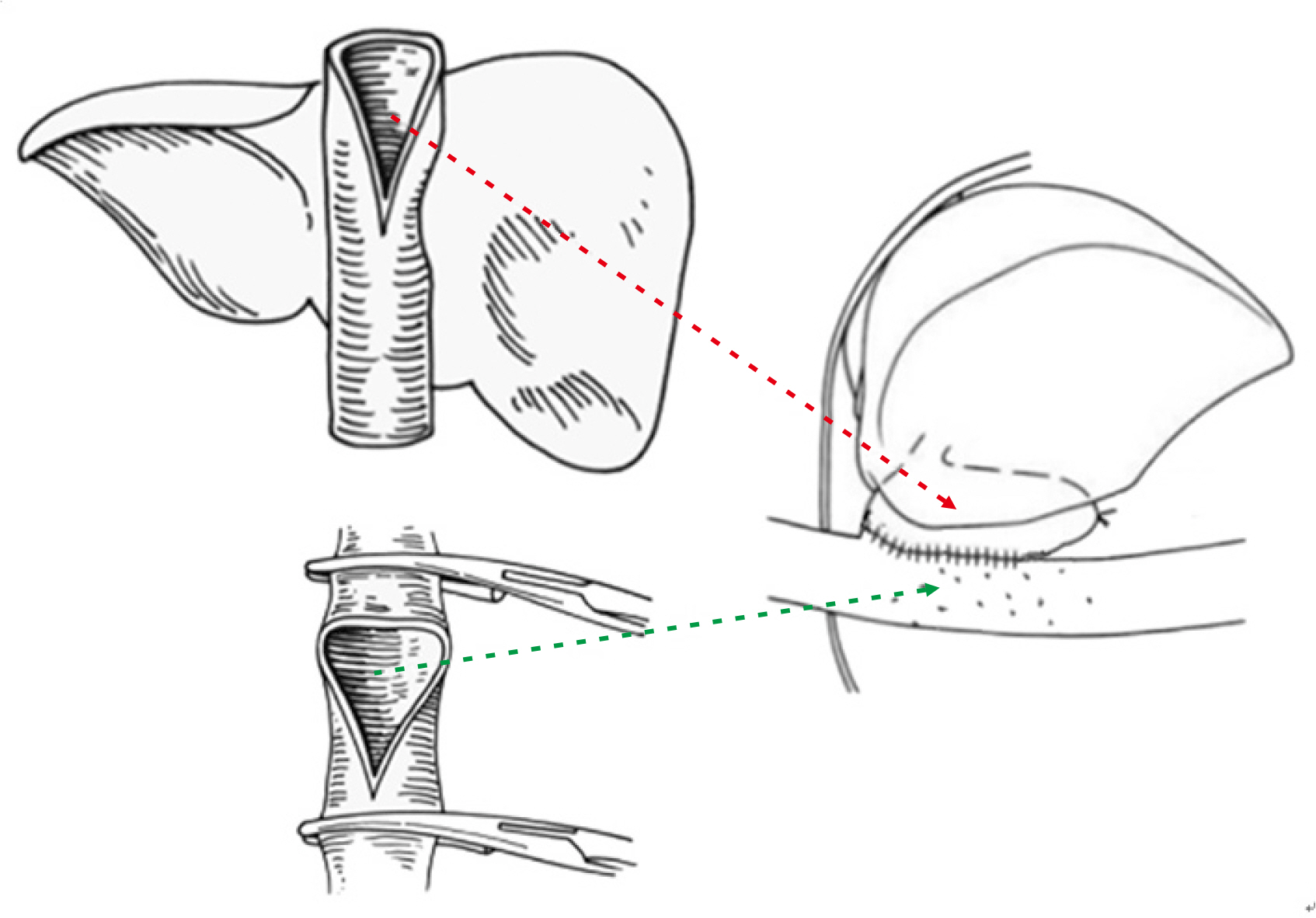
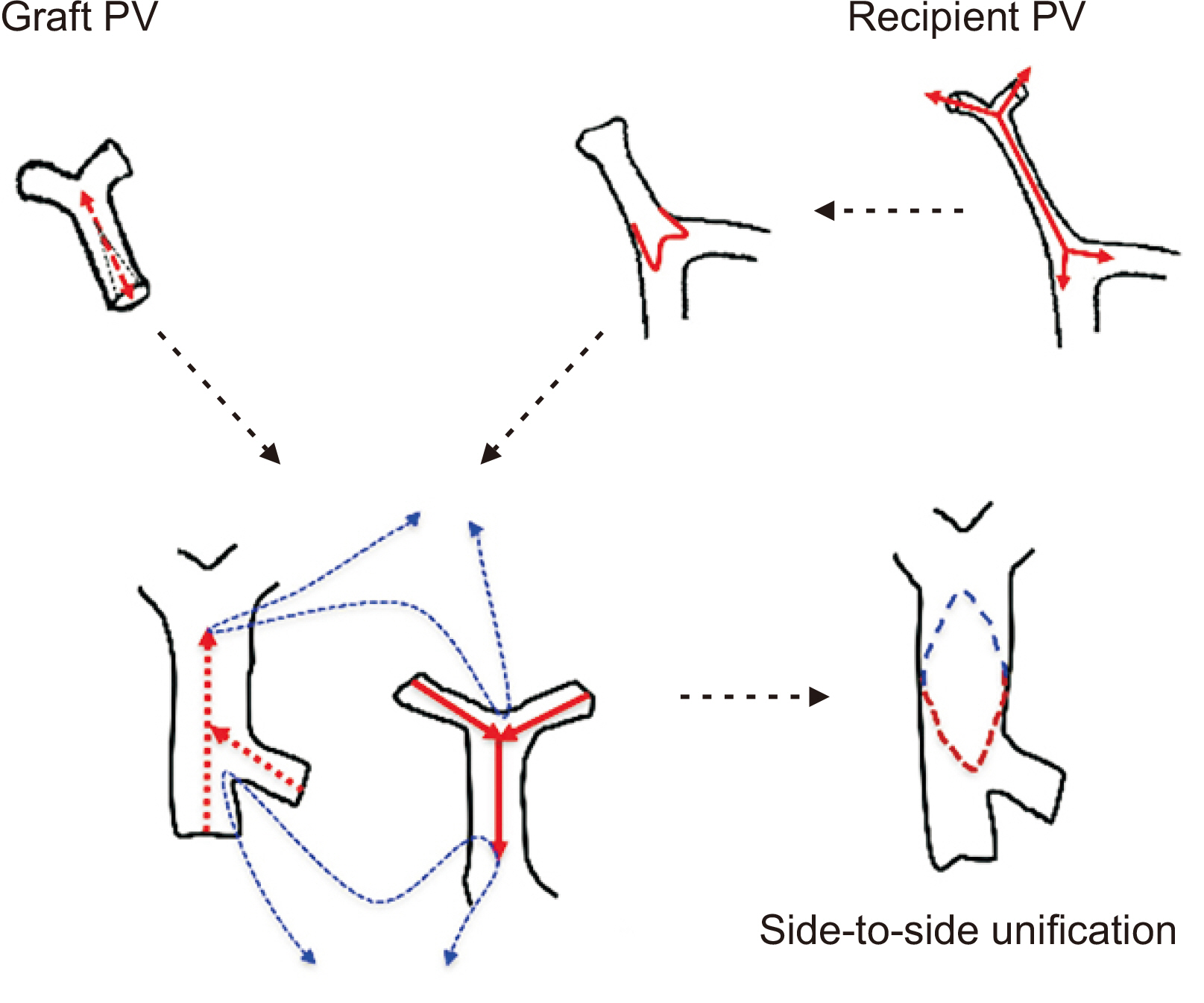
Article9. Namgoong JM, Hwang S, Ahn CS, Jung DH, Park GC. 2020; Side-to-side portal vein reconstruction for infant-to-infant deceased donor whole liver transplantation: report of 2 cases with video. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 24:301–4. DOI: 10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.3.301. PMID: 32843595. PMCID: PMC7452795.
Article10. Kiuchi T, Kasahara M, Uryuhara K, Inomata Y, Uemoto S, Asonuma K, et al. 1999; Impact of graft size mismatching on graft prognosis in liver transplantation from living donors. Transplantation. 67:321–7. DOI: 10.1097/00007890-199901270-00024. PMID: 10075602.11. Vanatta JM, Esquivel CO. 2007; Status of liver transplantation in infants <5 kg. Pediatr Transplant. 11:5–9. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-3046.2006.00627.x. PMID: 17328158.12. Heffron TG, Welch D, Pillen T, Fasola C, Redd D, Smallwood GA, et al. 2005; Low incidence of hepatic artery thrombosis after pediatric liver transplantation without the use of intraoperative microscope or parenteral anticoagulation. Pediatr Transplant. 9:486–90. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-3046.2005.00327.x. PMID: 16048601.
Article13. Shackleton CR, Goss JA, Swenson K, Colquhoun SD, Seu P, Kinkhabwala MM, et al. 1997; The impact of microsurgical hepatic arterial reconstruction on the outcome of liver transplantation for congenital biliary atresia. Am J Surg. 173:431–5. DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9610(97)00066-4. PMID: 9168083.
Article14. Ooi CY, Brandão LR, Zolpys L, De Angelis M, Drew W, Jones N, et al. 2010; Thrombotic events after pediatric liver transplantation. Pediatr Transplant. 14:476–82. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-3046.2009.01252.x. PMID: 19849808.
Article15. United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS). 2011. Organ distribution: allocation of livers [Internet]. UNOS;Richmond, VA: Available from: https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov. cited 2020 Oct 30.16. United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS). 2011. Ethical principles of pediatric organ allocation [Internet]. UNOS;Richmond, VA: Available from: https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov. cited 2020 Oct 30.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Whole liver deceased donor liver transplantation for pediatric recipients: single-center experience for 20 years
- Split liver transplantation for one adult and one pediatric recipient: A collective review of Korean experience
- Experience of split liver transplantation from deceased marginal donor: eight adult recipients from four deceased donors
- Korea-nationwide incidence of pediatric deceased donors and single-institutional status of liver transplantation using pediatric donor liver grafts
- Split liver transplantation for two adult recipients: A collective review of Korean experience