J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2020 Dec;46(6):373-378. 10.5125/jkaoms.2020.46.6.373.
Surgical outcomes of endoscopic versus open resection for the management of sinonasal malignancies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon and Oral Implantologist, RYA Cosmo Foundation, Chennai, India
- KMID: 2510006
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2020.46.6.373
Abstract
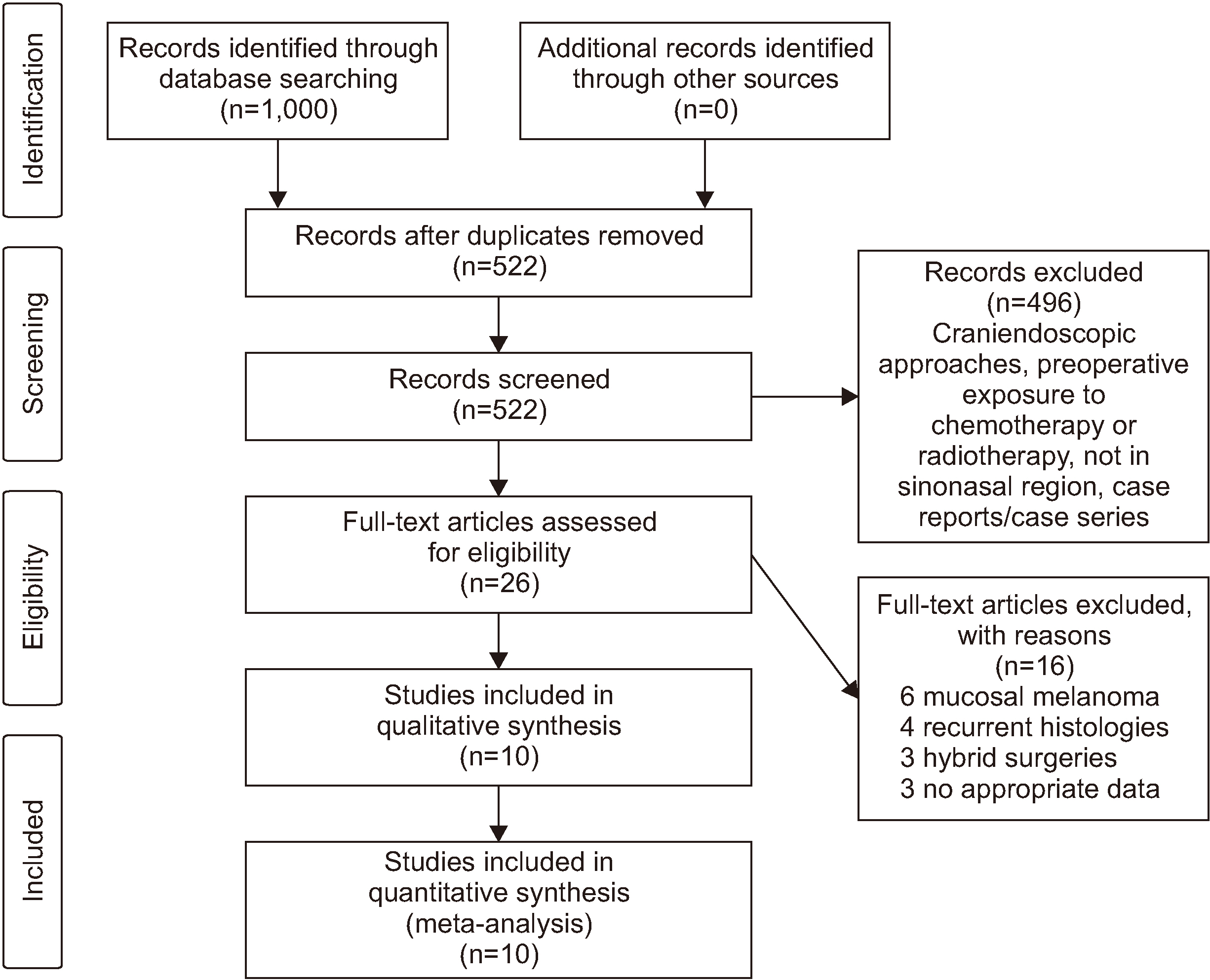
- The purpose of this review is to assess the surgical outcomes of two different treatment modalities, endoscopic and open resection, for the management of sinonasal malignancies by comparing the effectiveness of these two methods. A wide search was carried out considering various electronic databases for English language articles from 2013 to 2018 using keywords such as sinonasal malignancies, endoscopic surgery, open resection for sinonasal malignancies, and endoscopic versus open surgery. One thousand articles were identified from the literature for screening. After a thorough systematic assessment and based on the selection criteria, 10 articles with 4,642 patients were included in this quantitative analysis. With a total of 4,642 patients, 1,730 patients were operated on using endoscopic resection and 2,912 patients were operated on using open resection. The endoscopic approach was found to have a shorter hospital stay compared to open surgical resection (P<0.05). The rate of positive margins and the recurrence rate for open surgical resection were both smaller compared to those for endoscopic resection (P>0.05), and the endoscopic approach had smaller complication rates and a higher survival rate compared to open resection (P>0.05). Though endoscopic resection and open surgical resection have comparable postoperative benefits, preoperative evaluation of cases presenting with sinonasal malignancies is necessary for determining the right treatment method to obtain the best possible results postoperatively.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Yavuz HB, Aslıer M, Demir UL, Kasapoğlu F. 2019; Endoscopic surgery for sinonasal cancer: Uludağ experience. Eur J Rhinol Allergy. 2:75–8.
Article2. Osguthorpe JD, Richardson M. 2001; Frontal sinus malignancies. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 34:269–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0030-6665(05)70311-x . DOI: 10.1016/s0030-6665(05)70311-x. PMID: 11344078.
Article3. Kilic S, Shukla PA, Marchiano EJ, Patel RH, Baredes S, Liu JK, et al. 2016; Malignant primary neoplasms of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinus. Curr Otorhinolaryngol Rep. 4:249–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40136-016-0134-0 .
Article4. Kilic S, Kilic SS, Baredes S, Chan Woo Park R, Mahmoud O, Suh JD, et al. 2018; Comparison of endoscopic and open resection of sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma: a propensity score-matched analysis of 652 patients. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 8:421–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.22040 . DOI: 10.1002/alr.22040. PMID: 29210531.
Article5. Kilic S, Kilic SS, Baredes S, Liu JK, Eloy JA. 2017; Survival, morbidity, and quality-of-life outcomes for sinonasal and ventral skull base malignancies. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 50:467–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2016.12.018 . DOI: 10.1016/j.otc.2016.12.018. PMID: 28160996.
Article6. Lee CH, Hur DG, Roh HJ, Rha KS, Jin HR, Rhee CS, et al. 2007; Survival rates of sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma with the new AJCC staging system. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 133:131–4. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.133.2.131 . DOI: 10.1001/archotol.133.2.131. PMID: 17309980.
Article7. Ansa B, Goodman M, Ward K, Kono SA, Owonikoko TK, Higgins K, et al. 2013; Paranasal sinus squamous cell carcinoma incidence and survival based on surveillance, epidemiology, and end results data, 1973 to 2009. Cancer. 119:2602–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.28108 . DOI: 10.1002/cncr.28108. PMID: 23674262.
Article8. Ketcham AS, Wilkins RH, Vanburen JM, Smith RR. 1963; A combined intracranial facial approach to the paranasal sinuses. Am J Surg. 106:698–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9610(63)90387-8 . DOI: 10.1016/0002-9610(63)90387-8. PMID: 14078719.
Article9. Abu-Ghanem S, Fliss DM. 2013; Surgical approaches to resection of anterior skull base and paranasal sinuses tumors. Balkan Med J. 30:136–41. https://doi.org/10.5152/balkanmedj.2013.9112 . DOI: 10.5152/balkanmedj.2013.9112. PMID: 25207089. PMCID: PMC4115977.
Article10. Patel SG, Singh B, Polluri A, Bridger PG, Cantu G, Cheesman AD, et al. 2003; Craniofacial surgery for malignant skull base tumors: report of an international collaborative study. Cancer. 98:1179–87. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.11630 . DOI: 10.1002/cncr.11630. PMID: 12973841.
Article11. Ganly I, Patel SG, Singh B, Kraus DH, Bridger PG, Cantu G, et al. 2005; Complications of craniofacial resection for malignant tumors of the skull base: report of an international collaborative study. Head Neck. 27:445–51. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.20166 . DOI: 10.1002/hed.20166. PMID: 15825205.
Article12. Naunheim MR, Goyal N, Dedmon MM, Chambers KJ, Sedaghat AR, Bleier BS, et al. 2016; An algorithm for surgical approach to the anterior skull base. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 77:364–70. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1580598 . DOI: 10.1055/s-0036-1580598. PMID: 27441163. PMCID: PMC4949060.
Article13. Wood JW, Eloy JA, Vivero RJ, Sargi Z, Civantos FJ, Weed DT, et al. 2012; Efficacy of transnasal endoscopic resection for malignant anterior skull-base tumors. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2:487–95. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.21062 . DOI: 10.1002/alr.21062. PMID: 22777956.
Article14. Arnold A, Ziglinas P, Ochs K, Alter N, Geretschläger A, Lädrach K, et al. 2012; Therapy options and long-term results of sinonasal malignancies. Oral Oncol. 48:1031–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.04.005 . DOI: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.04.005. PMID: 22595044.
Article15. Farquhar D, Kim L, Worrall D, Chiu A, Lee JY, Khalili S, et al. 2016; Propensity score analysis of endoscopic and open approaches to malignant paranasal and anterior skull base tumor outcomes. Laryngoscope. 126:1724–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.25885 . DOI: 10.1002/lary.25885. PMID: 26972568.
Article16. Hagemann J, Roesner J, Helling S, Jacobi C, Doescher J, Engelbarts M, et al. 2019; Long-term outcome for open and endoscopically resected sinonasal tumors. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 160:862–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599818815881 . DOI: 10.1177/0194599818815881. PMID: 30511889.
Article17. Mortuaire G, Leroy X, Vandenhende-Szymanski C, Chevalier D, Thisse AS. 2016; Comparison of endoscopic and external resections for sinonasal instestinal-type adenocarcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 273:4343–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-016-4181-4 . DOI: 10.1007/s00405-016-4181-4. PMID: 27363404.
Article18. Fu TS, Monteiro E, Witterick I, Vescan A, Zadeh G, Gentili F, et al. 2017; Costs and perioperative outcomes associated with open versus endoscopic resection of sinonasal malignancies with skull base involvement. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 78:430–40. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1603907 . DOI: 10.1055/s-0037-1603907. PMID: 28875123. PMCID: PMC5582964.
Article19. Saedi B, Aghili M, Motiee M, Valadkhani S, Niazi AB, Safavi A. 2014; Surgical outcomes of malignant sinonasal tumours: open versus endoscopic surgical approaches. J Laryngol Otol. 128:784–90. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215114001583 . DOI: 10.1017/S0022215114001583. PMID: 25077511.
Article20. Huang Y, Qiu QH, Zhang SX. 2018; Endoscopic surgery for primary sinonasal malignancies: treatment outcomes and prognostic factors. Ear Nose Throat J. 97:E24–30. PMID: 30036420.21. Banhiran W, Casiano RR. 2005; Endoscopic sinus surgery for benign and malignant nasal and sinus neoplasm. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 13:50–4. https://doi.org/10.1097/00020840-200502000-00012 . DOI: 10.1097/00020840-200502000-00012. PMID: 15654216.
Article22. Buchmann L, Larsen C, Pollack A, Tawfik O, Sykes K, Hoover LA. 2006; Endoscopic techniques in resection of anterior skull base/paranasal sinus malignancies. Laryngoscope. 116:1749–54. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mlg.0000233528.99562.c2 . DOI: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000233528.99562.c2. PMID: 17003718.
Article23. Eviatar E, Vaiman M, Shlamkovitch N, Segal S, Kessler A, Katzenell U. 2004; Removal of sinonasal tumors by the endonasal endoscopic approach. Isr Med Assoc J. 6:346–9. PMID: 15214462.24. Su SY, Kupferman ME, DeMonte F, Levine NB, Raza SM, Hanna EY. 2014; Endoscopic resection of sinonasal cancers. Curr Oncol Rep. 16:369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-013-0369-6 . DOI: 10.1007/s11912-013-0369-6. PMID: 24445501.
Article25. Wellman BJ, Traynelis VC, McCulloch TM, Funk GF, Menezes AH, Hoffman HT. 1999; Midline anterior craniofacial approach for malignancy: results of en bloc versus piecemeal resections. Skull Base Surg. 9:41–6. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1058171 . DOI: 10.1055/s-2008-1058171. PMID: 17171080. PMCID: PMC1656724.
Article26. Povolotskiy R, Farber NI, Bavier RD, Cerasiello SY, Eloy JA, Hsueh WD. 2020; Endoscopic versus open resection of non-squamous cell carcinoma sinonasal malignancies. Laryngoscope. 130:1872–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.28270 . DOI: 10.1002/lary.28270. PMID: 31513298.
Article27. Hanna E, DeMonte F, Ibrahim S, Roberts D, Levine N, Kupferman M. 2009; Endoscopic resection of sinonasal cancers with and without craniotomy: oncologic results. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 135:1219–24. https://doi.org/10.1001/archoto.2009.173 . DOI: 10.1001/archoto.2009.173. PMID: 20026819.
Article28. Nicolai P, Battaglia P, Bignami M, Bolzoni Villaret A, Delù G, Khrais T, et al. 2008; Endoscopic surgery for malignant tumors of the sinonasal tract and adjacent skull base: a 10-year experience. Am J Rhinol. 22:308–16. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajr.2008.22.3170 . DOI: 10.2500/ajr.2008.22.3170. PMID: 18588765.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long-Term Treatment Outcomes in Endoscopic Management of Sinonasal Benign Tumors
- The Usefulness of Endoscopic Management in Benign Sinonasal Tumors
- Inverted Papilloma of the Sinonasal Cavity: The Surgical Strategy of Endoscopic Management Based on the Site of Attachment
- Endoscopic Endonasal Transsphenoidal Skull Base Surgery
- Surgical Management of Sinonasal Cancer