Blood Res.
2020 Dec;55(4):193-199. 10.5045/br.2020.2020009.
Prognostic value of TNF-α-308 and IFN-γ-874 single nucleotide polymorphisms and their plasma levels in patients with aplastic anemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Hematology, King George’s Medical University, Lucknow, India
- KMID: 2509957
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2020.2020009
Abstract
- Background
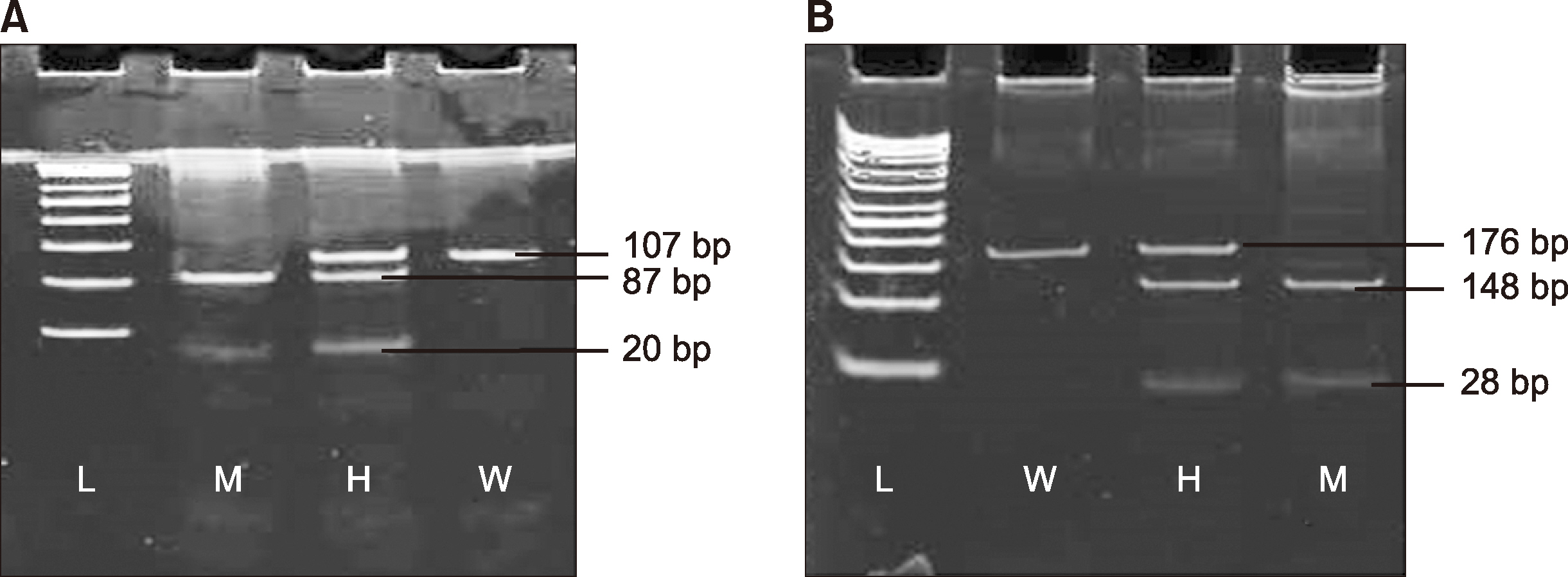
Aplastic anemia (AA), an unusual hematological disease, is characterized by hypoplasia of the bone marrow and failure to form blood cells of all three lineages resulting in pancytopenia. This study aimed to investigate TNF-α-308 and IFN-γ-874 gene polymorphisms and their respective plasma protein levels in patients with AA and healthy controls.
Methods
Two hundred and forty individuals were included in this study; the case group comprised 120 AA patients, while 120 healthy individuals served as controls. Genotyping was performed using the PCR-restriction length fragment polymorphism method and TNF-α-308 and IFN-γ-874 plasma levels were evaluated using an ELISA kit.
Results
There was a significantly higher prevalence of the IFN-γ-874 genotype in patients with AA than in healthy controls, while the TNF-α-308 genotype was associated with lower risk of developing AA. Furthermore, the levels of both TNF-α-308 and IFN-γ-874 were higher in the plasma of AA patients.
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that the IFN-γ-874 genotype may be a greater risk factor in the causation of AA, whereas the TNF-α-308 genotype has a protective role in the North Indian population.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dezern AE, Brodsky RA. 2011; Clinical management of aplastic anemia. Expert Rev Hematol. 4:221–30. DOI: 10.1586/ehm.11.11. PMID: 21495931. PMCID: PMC3138728.
Article2. Issaragrisil S, Kaufman DW, Anderson T, et al. 2006; The epidemiology of aplastic anemia in Thailand. Blood. 107:1299–307. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-01-0161. PMID: 16254144. PMCID: PMC1895423.
Article3. Cuglievan B, DePombo A, De Angulo G. 2016; Aplastic anemia: the correct nomenclature matters. Haematologica. 101:e391. DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2016.146522. PMID: 27582572. PMCID: PMC5060039.
Article4. Malhotra P, Gella V, Guru Murthy GS, Varma N, Varma S. 2016; High incidence of aplastic anemia is linked with lower socioeconomic status of Indian population. J Public Health (Oxf). 38:223–8. DOI: 10.1093/pubmed/fdv027. PMID: 25755247.
Article5. Shallis RM, Ahmad R, Zeidan AM. 2018; Aplastic anemia: etiology, molecular pathogenesis, and emerging concepts. Eur J Haematol. 101:711–20. DOI: 10.1111/ejh.13153. PMID: 30055055.
Article6. Romagnani S. 2004; The increased prevalence of allergy and the hygiene hypothesis: missing immune deviation, reduced immune suppression, or both? Immunology. 112:352–63. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01925.x. PMID: 15196202. PMCID: PMC1782506.
Article7. Medinger M, Drexler B, Lengerke C, Passweg J. 2018; Pathogenesis of acquired aplastic anemia and the role of the bone marrow microenvironment. Front Oncol. 8:587. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00587. PMID: 30568919. PMCID: PMC6290278.
Article8. Luzzatto L, Risitano AM. 2018; Advances in understanding the pathogenesis of acquired aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 182:758–76. DOI: 10.1111/bjh.15443. PMID: 29974931.
Article9. Kastrinaki MC, Pavlaki K, Batsali AK, et al. 2013; Mesenchymal stem cells in immune-mediated bone marrow failure syndromes. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013:265608. DOI: 10.1155/2013/265608. PMID: 24386000. PMCID: PMC3872391.
Article10. Zhang CC, Lodish HF. 2008; Cytokines regulating hematopoietic stem cell function. Curr Opin Hematol. 15:307–11. DOI: 10.1097/MOH.0b013e3283007db5. PMID: 18536567. PMCID: PMC2677548.
Article11. Sun W, Wu Z, Lin Z, et al. 2018; Macrophage TNF-α licenses donor T cells in murine bone marrow failure and can be implicated in human aplastic anemia. Blood. 132:2730–43. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2018-05-844928. PMID: 30361263. PMCID: PMC6307988.
Article12. Araujo Z, Palacios A, Biomon R, et al. 2017; Concordance between IFNγ gene +874 A/T polymorphism and interferon-γ expression in a TB-endemic indigenous setting. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 50:199–207. DOI: 10.1590/0037-8682-0398-2016. PMID: 28562756.
Article13. Marsh JC, Ball SE, Cavenagh J, et al. 2009; Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 147:43–70. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2009.07842.x. PMID: 19673883.
Article14. Yadav DK, Tripathi AK, Gupta D, et al. 2017; Interleukin-1B (IL-1B-31 and IL-1B-511) and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) gene polymorphisms in primary immune thrombocytopenia. Blood Res. 52:264–9. DOI: 10.5045/br.2017.52.4.264. PMID: 29333402. PMCID: PMC5762736.15. Xiao Y, Zhao S, Li B. 2017; Aplastic anemia is related to alterations in T cell receptor signaling. Stem Cell Investig. 4:85. DOI: 10.21037/sci.2017.09.07. PMID: 29167806. PMCID: PMC5676186.
Article16. Zheng M, Liu C, Fu R, et al. 2015; Abnormal immunomodulatory ability on memory T cells in humans with severe aplastic anemia. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:3659–69. PMID: 26097547. PMCID: PMC4466934.17. Yu Z, Huang Z, Dai X, Wu X, Huang J. 2014; Th1/Th2 imbalance in the pathogenesis of chronic aplastic anemia. J Hard Tissue Biol. 23:455–60. DOI: 10.2485/jhtb.23.455.
Article18. Găman A, Găman G, Bold A. 2009; Acquired aplastic anemia: correlation between etiology, pathophysiology, bone marrow histology and prognosis factors. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 50:669–74. PMID: 19942964.19. Mavroudi I, Papadaki HA. 2012; Genetic associations in acquired immune-mediated bone marrow failure syndromes: insights in aplastic anemia and chronic idiopathic neutropenia. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012:123789. DOI: 10.1155/2012/123789. PMID: 22956967. PMCID: PMC3432560.
Article20. Zhang JY, Chang H, Meng WT. 2008; The polymorphism of interferon gamma gene CA short tandem repeat is associated with aplastic anemia. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 39:23–5. PMID: 18390192.21. Deng S, Lin S, Shen J, Zeng Y. 2020; The relationship between interferon gamma (IFN-γ) single nucleotide polymorphism +874(T/A) and occurrence risk of aplastic anemia: a meta-analysis. Hematology. 25:85–90. DOI: 10.1080/16078454.2019.1631508. PMID: 32063160.22. Zayed RA, Abdel-Hamid SM, El-Lithy H. 2016; The association of cytokine genes polymorphisms and susceptibility to aplastic anemia in Egyptian patients. Hematology. 21:106–12. DOI: 10.1179/1607845415Y.0000000038. PMID: 26214243.
Article23. Bestach Y, Sieza Y, Attie M, et al. 2015; Polymorphisms in TNF and IFNG are associated with clinical characteristics of aplastic anemia in Argentinean population. Leuk Lymphoma. 56:1793–8. DOI: 10.3109/10428194.2014.966707. PMID: 25248876.24. Chang H, Zeng F, Zhang JY, et al. 2010; Association of the interferon-gamma single nucleotide polymorphism +874(T/A) with response to immunosuppressive therapy in patients with severe aplastic anemia. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 45:313–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2010.09.003. PMID: 20934357.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of Cytokine Genes are Associated with Fibrosis of the Intrahepatic Bile Duct Wall in Human Clonorchiasis
- Polymorphisms of TNF-alpha Gene and TNF Receptor Gene in Behcet's Disease
- Increased Expression of Fas Antigen and Apoptosis in Aplastic Anemia Bone Marrow Cells
- A Case of Pregnancy-Associated Aplastic Anemia
- The -308 and -238 Polymorphisms of the TNF-alpha Promoter Gene in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus