Int J Thyroidol.
2020 Nov;13(2):118-127. 10.11106/ijt.2020.13.2.118.
Changes of Nodular Size and Its Risk Factors in Iodine-Sufficient Area: a Retrospective Cohort Analysis of 7753 Thyroid Nodules
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Preventive Medicine, College of Korean Medicine, Dongguk University, Gyeongju, Korea
- 7National Evidence-Based Healthcare Collaborating Agency, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2509190
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11106/ijt.2020.13.2.118
Abstract
- Background and Objectives
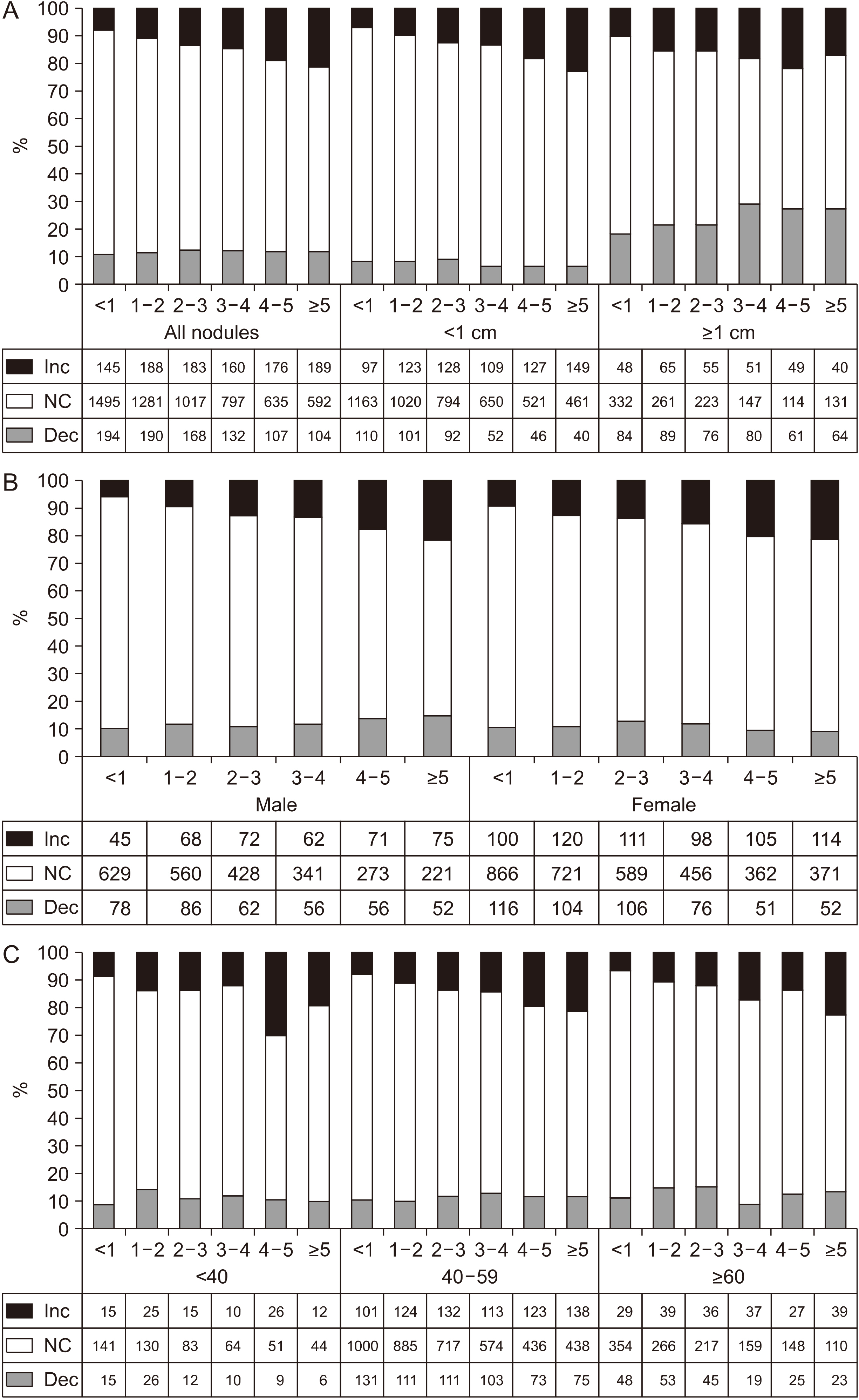
Iodine is known to be an important factor in the occurrence of goiter, and South Korea is a region with sufficient iodine supplementation. In this regard, we checked the size change of thyroid nodules found by health check-up in Koreans and examined which risk factors influence the size change.
Materials and Methods
A total 7753 subjects who underwent thyroid sonography two or more times were included. We defined that there was a change in the size of the nodule when the difference in diameter identified in the last ultrasound was more than 3 mm.
Results
Thyroid nodules were decreased in 895 subjects (11.5%) and increased in 1041 subjects (13.5%). The rate of increased nodule was on an increasing trend according to the duration (annual percent change 2.6%, p<0.001). In contrast, the rate of decreased nodule was unchanged. Predictive factors related to decrease of the nodule size were young age, male sex, larger initial nodule size and thyroiditis. Similarly, young age, larger initial nodule size and diffuse parenchymal abnormality were significant predictive factors for increased nodules. However, diffuse parenchymal abnormality was not a predictive factor when we analyzed only thyroid nodules larger than 1 cm.
Conclusion
In our study, 11.5-13.5% of benign thyroid nodules were increased or decreased during median 27 months of follow-up in iodine sufficient condition. Young age, larger initial size and diffuse parenchymal abnormality were common predictive factor affecting both the increase and decrease of thyroid nodules.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ezzat S, Sarti DA, Cain DR, Braunstein GD. 1994; Thyroid incidentalomas. Prevalence by palpation and ultrasonography. Arch Intern Med. 154(16):1838–40. DOI: 10.1001/archinte.1994.00420160075010. PMID: 8053752.
Article2. Brander A, Viikinkoski P, Nickels J, Kivisaari L. 1991; Thyroid gland: US screening in a random adult population. Radiology. 181(3):683–7. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.181.3.1947082. PMID: 1947082.
Article3. Tan GH, Gharib H. 1997; Thyroid incidentalomas: management approaches to nonpalpable nodules discovered incidentally on thyroid imaging. Ann Intern Med. 126(3):226–31. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-126-3-199702010-00009. PMID: 9027275.
Article4. Werk EE Jr, Vernon BM, Gonzalez JJ, Ungaro PC, McCoy RC. 1984; Cancer in thyroid nodules. A community hospital survey. Arch Intern Med. 144(3):474–6. DOI: 10.1001/archinte.1984.00350150058018. PMID: 6703815.
Article5. Papini E, Guglielmi R, Bianchini A, Crescenzi A, Taccogna S, Nardi F, et al. 2002; Risk of malignancy in nonpalpable thyroid nodules: predictive value of ultrasound and color-Doppler features. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 87(5):1941–6. DOI: 10.1210/jcem.87.5.8504. PMID: 11994321.
Article6. Moumen M, Mehhane M, Kadiri B, Mawfik H, el Fares F. 1989; Compressive goiters. Apropos of 80 cases. J Chir (Paris). 126(10):521–6. PMID: 2592460.7. Arora N, Scognamiglio T, Zhu B, Fahey TJ 3rd. 2008; Do benign thyroid nodules have malignant potential? An evidence-based review. World J Surg. 32(7):1237–46. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-008-9484-1. PMID: 18327528.
Article8. Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, et al. 2016; 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American Thyroid Association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 26(1):1–133. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2015.0020. PMID: 26462967. PMCID: PMC4739132.9. Lee KH, Lee EK, Kang HC, Ko Y, Kim SW, Kim IJ, et al. 2016; 2016 revised Korean Thyroid Association management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer. Int J Thyroidol. 9(2):59–126. DOI: 10.11106/ijt.2016.9.2.59.
Article10. Quadbeck B, Pruellage J, Roggenbuck U, Hirche H, Janssen OE, Mann K, et al. 2002; Long-term follow-up of thyroid nodule growth. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 110(7):348–54. DOI: 10.1055/s-2002-34992. PMID: 12397534.
Article11. Erdogan MF, Gursoy A, Erdogan G. 2006; Natural course of benign thyroid nodules in a moderately iodine-deficient area. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 65(6):767–71. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2006.02664.x. PMID: 17121528.
Article12. Delange F. 1994; The disorders induced by iodine deficiency. Thyroid. 4(1):107–28. DOI: 10.1089/thy.1994.4.107. PMID: 8054857.
Article13. Yu X, Fan C, Shan Z, Teng X, Guan H, Li Y, et al. 2008; A five-year follow-up study of goiter and thyroid nodules in three regions with different iodine intakes in China. J Endocrinol Invest. 31(3):243–50. DOI: 10.1007/BF03345597. PMID: 18401207.
Article14. Lim DJ, Kim JY, Baek KH, Kim MK, Park WC, Lee JM, et al. 2013; Natural course of cytologically benign thyroid nodules: observation of ultrasonographic changes. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 28(2):110–8. DOI: 10.3803/EnM.2013.28.2.110. PMID: 24396664. PMCID: PMC3811716.
Article15. Alexander EK, Hurwitz S, Heering JP, Benson CB, Frates MC, Doubilet PM, et al. 2003; Natural history of benign solid and cystic thyroid nodules. Ann Intern Med. 138(4):315–8. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-138-4-200302180-00010. PMID: 12585829.
Article16. Anil C, Akkurt A, Ayturk S, Kut A, Gursoy A. 2013; Impaired glucose metabolism is a risk factor for increased thyroid volume and nodule prevalence in a mild-to-moderate iodine deficient area. Metabolism. 62(7):970–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.01.009. PMID: 23395200.
Article17. Ayturk S, Gursoy A, Kut A, Anil C, Nar A, Tutuncu NB. 2009; Metabolic syndrome and its components are associated with increased thyroid volume and nodule prevalence in a mild-to-moderate iodine-deficient area. Eur J Endocrinol. 161(4):599–605. DOI: 10.1530/EJE-09-0410. PMID: 19633072.
Article18. Blanc E, Ponce C, Brodschi D, Nepote A, Barreto A, Schnitman M, et al. 2015; Association between worse metabolic control and increased thyroid volume and nodular disease in elderly adults with metabolic syndrome. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 13(5):221–6. DOI: 10.1089/met.2014.0158. PMID: 25789844.
Article19. Kim JY, Moon SJ, Kim KR, Sohn CY, Oh JJ. 1998; Dietary iodine intake and urinary iodine excretion in normal Korean adults. Yonsei Med J. 39(4):355–62. DOI: 10.3349/ymj.1998.39.4.355. PMID: 9752802.
Article20. Kim TH, Kim KW, Ahn HY, Choi HS, Won H, Choi Y, et al. 2013; Effect of seasonal changes on the transition between subclinical hypothyroid and euthyroid status. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 98(8):3420–9. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2013-1607. PMID: 23771919.
Article21. Ito Y, Miyauchi A, Inoue H, Fukushima M, Kihara M, Higashiyama T, et al. 2010; An observational trial for papillary thyroid microcarcinoma in Japanese patients. World J Surg. 34(1):28–35. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-009-0303-0. PMID: 20020290.
Article22. Pedersen OM, Aardal NP, Larssen TB, Varhaug JE, Myking O, Vik-Mo H. 2000; The value of ultrasonography in predicting autoimmune thyroid disease. Thyroid. 10(3):251–9. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2000.10.251. PMID: 10779140.
Article23. Cooper DS, Doherty GM, Haugen BR, Kloos RT, Lee SL, et al. American Thyroid Association (ATA) Guidelines Taskforce on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. 2009; Revised American Thyroid Association management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 19(11):1167–214. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2009.0110. PMID: 19860577.
Article24. Rago T, Chiovato L, Aghini-Lombardi F, Grasso L, Pinchera A, Vitti P. 2001; Non-palpable thyroid nodules in a borderline iodine-sufficient area: detection by ultrasonography and follow-up. J Endocrinol Invest. 24(10):770–6. DOI: 10.1007/BF03343926. PMID: 11765046.
Article25. Durante C, Costante G, Lucisano G, Bruno R, Meringolo D, Paciaroni A, et al. 2015; The natural history of benign thyroid nodules. JAMA. 313(9):926–35. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2015.0956. PMID: 25734734.
Article26. Braverman LE, Cooper DS, Werner SC, Ingbar SH. 2013. Werner & Ingbar's the thyroid : a fundamental and clinical text. 10th ed. Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health;Philadelphia: p. 224–6.27. Medeiros-Neto G. 1983; TSH secretion and regulation in endemic goiter and endemic cretinism. Prog Clin Biol Res. 116:119–30. PMID: 6304776.28. Papini E, Petrucci L, Guglielmi R, Panunzi C, Rinaldi R, Bacci V, et al. 1998; Long-term changes in nodular goiter: a 5-year prospective randomized trial of levothyroxine suppressive therapy for benign cold thyroid nodules. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 83(3):780–3. DOI: 10.1210/jcem.83.3.4615. PMID: 9506726.
Article29. Hwang S, Shin DY, Kim EK, Yang WI, Byun JW, Lee SJ, et al. 2015; Focal lymphocytic thyroiditis nodules share the features of papillary thyroid cancer on ultrasound. Yonsei Med J. 56(5):1338–44. DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.5.1338. PMID: 26256977. PMCID: PMC4541664.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Non-surgical Management of Thyroid Nodules
- Dietary Factors and the Risk of Thyroid Diseases: A Review
- Predicting the Size of Benign Thyroid Nodules and Analysis of Associated Factors That Affect Nodule Size
- The size and radioactive iodine 131-I uptake rate of thyroid glands of Korean woman
- The Relative Risk of Cancer in Sonographically Detected Thyroid Nodules with Calcifications