J Korean Med Sci.
2020 Dec;35(46):e376. 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e376.
Therapeutic Drug Level Monitoring of Teicoplanin in Korean Pediatric Patients with Normal versus Impaired Renal Function
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, School of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University of Medicine, Yongin Severance Hospital, Yongin, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 5Department of Infectious Diseases, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea
- 6Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, School of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea
- 7Department of Infectious Diseases, Samsung Medical Center, School of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2509035
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e376
Abstract
- Background
Teicoplanin is used to treat serious gram-positive infections. Optimal teicoplanin trough levels are considered to be ≥ 10 μg/mL. Despite its wide use in various clinical settings, data on teicoplanin trough level in pediatric patients are limited. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the therapeutic drug level monitoring of teicoplanin in Korean pediatric patients, including those with impaired renal function.
Methods
A retrospective study was performed in pediatric patients (age ≤ 18 years old) who received teicoplanin from September 2014 to April 2018. The regimen included a loading dose of 10 mg/kg/dose at 12 hours' interval three times in a row, and a maintenance dose of 10 mg/kg/dose commenced at 24 hours of interval after the loading dose, with a maximum of 400 mg/dose, respectively. The first therapeutic drug levels were measured. Distribution and characteristics of trough levels in patients with decreased renal function and those with bacteremia were also assessed.
Results
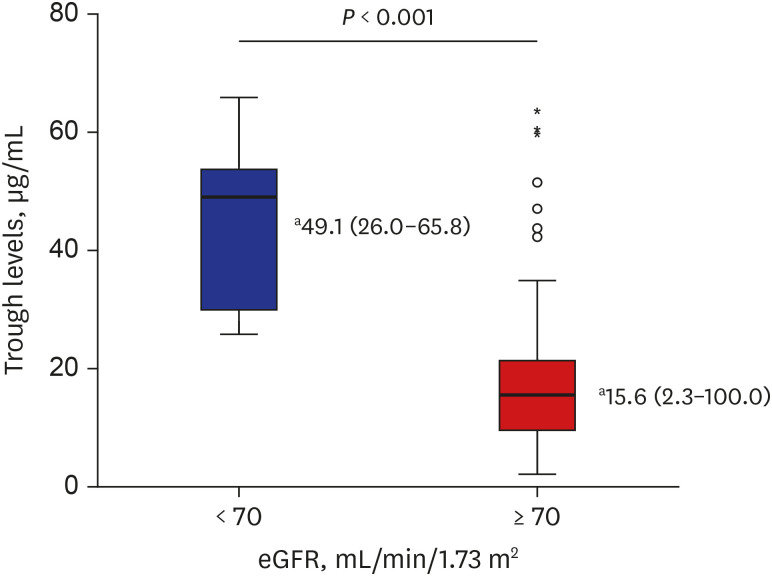
A total of 187 trough levels were collected from 143 patients. Hematologic and oncologic diseases were the most common underlying diseases (83.2%, n = 119). One hundred eighty trough levels were first measured, and their median value was 16.2 μg/mL (range, 2.3–100 μg/mL) and the median interval between initial teicoplanin injection and 1st trough level was 96.5 hours (range 47.6–179.3 hours). Lower steady-state levels were observed in younger age group (median, 13.5 vs. 18.0 μg/mL, P = 0.038). Median trough levels were higher in patients with decreased renal functions (P < 0.001). In addition, among eight with gram-positive bacteremia, seven of them had a favorable outcome.
Conclusion
This study provides additive information on trough level monitoring of teicoplanin in children with impaired renal function and treatment effect in patients with gram-positive bacteremia. Careful monitoring for steady state trough levels of teicoplanin is warranted.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Optimal Use and Need for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Teicoplanin in Children: A Systematic Review
Joon-sik Choi, Seo Hee Yoon, Hyo Jung Park, Soo-Youn Lee, Yae-Jean Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2023;38(7):e62. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e62.
Reference
-
1. Parenti F, Beretta G, Berti M, Arioli V. Teichomycins, new antibiotics from Actinoplanes teichomyceticus Nov. Sp. I. Description of the producer strain, fermentation studies and biological properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1978; 31(4):276–283. PMID: 659325.
Article2. Somma S, Gastaldo L, Corti A. Teicoplanin, a new antibiotic from Actinoplanes teichomyceticus nov. sp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984; 26(6):917–923. PMID: 6240963.3. Pea F, Brollo L, Viale P, Pavan F, Furlanut M. Teicoplanin therapeutic drug monitoring in critically ill patients: a retrospective study emphasizing the importance of a loading dose. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003; 51(4):971–975. PMID: 12654757.
Article4. Cavalcanti AB, Goncalves AR, Almeida CS, Bugano DD, Silva E. Teicoplanin versus vancomycin for proven or suspected infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010; (6):CD007022. PMID: 20556772.
Article5. Tobin CM, Lovering AM, Sweeney E, MacGowan AP. Analyses of teicoplanin concentrations from 1994 to 2006 from a UK assay service. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010; 65(10):2155–2157. PMID: 20682566.
Article6. Wilson AP. Clinical pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2000; 39(3):167–183. PMID: 11020133.
Article7. Schaison G, Graninger W, Bouza E. Teicoplanin in the treatment of serious infection. J Chemother. 2000; 12 Suppl 5:26–33. PMID: 11131961.
Article8. Pottel H, Hoste L, Delanaye P. Abnormal glomerular filtration rate in children, adolescents and young adults starts below 75 mL/min/1.73 m2 . Pediatr Nephrol. 2015; 30(5):821–828. PMID: 25403744.9. Jung J, Lee K, Oh J, Choi R, Woo HI, Park HD, et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring of teicoplanin using an LC-MS/MS method: analysis of 421 measurements in a naturalistic clinical setting. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019; 167:161–165. PMID: 30776754.
Article10. Dong YL, Dong HY, Hu SS, Wang X, Wei YX, Wang MY, et al. An assessment of teicoplanin use and monitoring serum levels in a Chinese teaching hospital. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 49(1):14–22. PMID: 21176720.
Article11. Kim SH, Kang CI, Huh K, Cho SY, Chung DR, Lee SY, et al. Evaluating the optimal dose of teicoplanin with therapeutic drug monitoring: not too high for adverse event, not too low for treatment efficacy. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019; 38(11):2113–2120. PMID: 31372903.
Article12. Nah SY, Im JH, Yeo JY, Baek JH, Kim CW, Nam MS, et al. Therapeutic drug concentrations of teicoplanin in clinical settings. Infect Chemother. 2014; 46(1):35–41. PMID: 24693468.
Article13. Zhou L, Gao Y, Cao W, Liu J, Guan H, Zhang H, et al. Retrospective analysis of relationships among the dose regimen, trough concentration, efficacy, and safety of teicoplanin in Chinese patients with moderate-severe Gram-positive infections. Infect Drug Resist. 2018; 11:29–36. PMID: 29379306.14. Dufort G, Ventura C, Olivé T, Ortega JJ. Teicoplanin pharmacokinetics in pediatric patients. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1996; 15(6):494–498. PMID: 8783345.
Article15. Ramos-Martín V, Neely MN, Padmore K, Peak M, Beresford MW, Turner MA, et al. Tools for the individualized therapy of teicoplanin for neonates and children. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017; 61(10):e00707-17. PMID: 28760897.
Article16. Ramos-Martín V, Paulus S, Siner S, Scott E, Padmore K, Newland P, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin in children. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014; 58(11):6920–6927. PMID: 25224001.
Article17. Reed MD, Yamashita TS, Myers CM, Blumer JL. The pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin in infants and children. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1997; 39(6):789–796. PMID: 9222049.
Article18. Sánchez A, López-Herce J, Cueto E, Carrillo A, Moral R. Teicoplanin pharmacokinetics in critically ill paediatric patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1999; 44(3):407–409. PMID: 10511412.
Article19. Strenger V, Hofer N, Rödl S, Hönigl M, Raggam R, Seidel MG, et al. Age- and gender-related differences in teicoplanin levels in paediatric patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013; 68(10):2318–2323. PMID: 23702837.
Article20. Yamada T, Kubota T, Nakamura M, Ochiai M, Yonezawa M, Yano T, et al. Evaluation of teicoplanin concentrations and safety analysis in neonates. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2014; 44(5):458–462. PMID: 25218156.
Article21. Byrne CJ, Parton T, McWhinney B, Fennell JP, O'Byrne P, Deasy E, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of total and unbound teicoplanin concentrations and dosing simulations in patients with haematological malignancy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018; 73(4):995–1003. PMID: 29272419.
Article22. Byrne CJ, Roberts JA, McWhinney B, Fennell JP, O'Byrne P, Deasy E, et al. Variability in trough total and unbound teicoplanin concentrations and achievement of therapeutic drug monitoring targets in adult patients with hematological malignancy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017; 61(6):e02466-16. PMID: 28320714.
Article23. Byrne CJ, Roberts JA, McWhinney B, Ryder SA, Fennell JP, O'Byrne P, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin and attainment of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic targets in adult patients with haematological malignancy. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2017; 23(9):674.e7–674.13.24. Roberts JA, Stove V, De Waele JJ, Sipinkoski B, McWhinney B, Ungerer JP, et al. Variability in protein binding of teicoplanin and achievement of therapeutic drug monitoring targets in critically ill patients: lessons from the DALI Study. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2014; 43(5):423–430. PMID: 24630304.
Article25. Sato Y, Hiramatsu K, Suzuki Y, Tanaka R, Kaneko T, Nonoshita K, et al. Optimal trough concentration of teicoplanin in febrile neutropenic patients with hematological malignancy. Chemotherapy. 2018; 63(1):29–34. PMID: 29169153.
Article26. Yamada T, Kubota T, Yonezawa M, Nishio H, Kanno S, Yano T, et al. Evaluation of teicoplanin trough values after the recommended loading dose in children with associated safety analysis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2017; 36(4):398–400. PMID: 27977550.
Article27. Chae H, Lee JJ, Cha K, Her SH, Kim HY, Han E, et al. Measurement of teicoplanin concentration with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method demonstrates the usefulness of therapeutic drug monitoring in hematologic patient populations. Ther Drug Monit. 2018; 40(3):330–336. PMID: 29746433.
Article28. Svetitsky S, Leibovici L, Paul M. Comparative efficacy and safety of vancomycin versus teicoplanin: systematic review and meta-analysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009; 53(10):4069–4079. PMID: 19596875.
Article29. Wilson AP, Grüneberg RN, Neu H. A critical review of the dosage of teicoplanin in Europe and the USA. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 1994; 4 Suppl 1:1–30.
Article30. Derbyshire N, Webb DB, Roberts D, Glew D, Williams JD. Pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin in subjects with varying degrees of renal function. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989; 23(6):869–876. PMID: 2527223.
Article31. Guay DR, Awni WM, Halstenson CE, Kenny MT, Keane WF, Matzke GR. Teicoplanin pharmacokinetics in patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis after intravenous and intraperitoneal dosing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989; 33(11):2012–2015. PMID: 2532874.
Article32. Höffler D, Koeppe P, Naumann E, Lang E, Sörgel F. Pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin in hemodialysis patients. Infection. 1991; 19(5):324–327. PMID: 1839299.
Article33. Wolter K, Claus M, Fritschka E. Pharmacokinetics and dosage recommendations of teicoplanin in patients treated by continuous veno-venous haemodialysis (CVVHD). Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1994; 46(2):179–180. PMID: 8039541.
Article34. Wolter K, Claus M, Wagner K, Fritschka E. Teicoplanin pharmacokinetics and dosage recommendations in chronic hemodialysis patients and in patients undergoing continuous veno-venous hemodialysis. Clin Nephrol. 1994; 42(6):389–397. PMID: 7882603.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Is Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Teicoplanin Useful?
- Therapeutic Drug Concentrations of Teicoplanin in Clinical Settings
- Optimal Use and Need for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Teicoplanin in Children: A Systematic Review
- Therapeutic drug monitoring of vancomycin in a patient with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD): A case report
- Appropriate Use of Glycopeptide Antibiotics and Therapeutic Drug Monitoring for Invasive Infections