Korean Circ J.
2020 Dec;50(12):1062-1073. 10.4070/kcj.2019.0420.
Association Between Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Preimplantation Screening and the Response to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Cardiac Arrhythmia Center, Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Cardiology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, China
- KMID: 2509025
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2019.0420
Abstract
- Background and Objectives
Preimplantation QRS-T morphology screening (TMS) is a composite tool for selecting subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator (S-ICD) candidates. However, its role in predicting the patient's response to cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is uncertain.
Methods
A total of 55 consecutive de novo CRT candidates were enrolled between January 2016 and March 2017. Electrocardiogram (ECG) and TMS were performed before and soon after implantation. The ECG parameters were recorded, including QRS duration and morphology (such as ΔQRS_Index, QTc during biventricular pacing mode [BiV pacing QTc], and QRS/T ratio during biventricular pacing mode [BiV pacing QRS/T ratio]). TMS monitored three sensory vectors of the S-ICD. Six months after implantation, the responses to CRT were evaluated.
Results
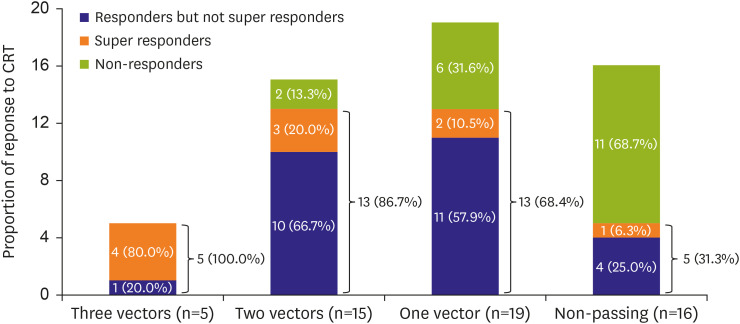
Thirty-nine patients (70.9%) passed the TMS during biventricular pacing mode. At the six-month follow-up, the number of responders and super-responders was significantly higher in the passing group than in the non-passing group (responders: 31/39 [79.5%] vs. 5/16 [31.3%], p<0.001; super-responders: 9/39 [23.1%] vs. 1/16 [6.3%], p=0.020). The superresponse rate was higher among patients who passed all three vectors than among those who passed 1 or 2 vectors (3 vs. 2 vectors, p=0.018; 3 vs. 1 vector, p=0.003). A smaller left atrial diameter, vectors that passed TMS during biventricular pacing mode, and larger ΔQRS_Index values were independently associated with good CRT response.
Conclusions
Our study demonstrated that patients on CRT who pass the TMS during biventricular pacing mode are more likely to respond and super-respond to CRT.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Finding Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Responders: Postprocedural QRS-T Morphologies Matter
Min Kim, Tae-Hoon Kim
Korean Circ J. 2020;50(12):1074-1076. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2020.0434.
Reference
-
1. Brouwer TF, Yilmaz D, Lindeboom R, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes of subcutaneous versus transvenous implantable defibrillator therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016; 68:2047–2055. PMID: 27810043.
Article2. Burke MC, Gold MR, Knight BP, et al. Safety and efficacy of the totally subcutaneous implantable defibrillator: 2-year results from a pooled analysis of the IDE study and EFFORTLESS registry. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015; 65:1605–1615. PMID: 25908064.3. Groh CA, Sharma S, Pelchovitz DJ, et al. Use of an electrocardiographic screening tool to determine candidacy for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm. 2014; 11:1361–1366. PMID: 24755323.
Article4. Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, et al. 2016 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2016; 69:1167. PMID: 27894487.5. Olde Nordkamp LR, Warnaars JL, Kooiman KM, et al. Which patients are not suitable for a subcutaneous ICD: incidence and predictors of failed QRS-T-wave morphology screening. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2014; 25:494–499. PMID: 24320684.
Article6. Burri H. Iterative method for atrioventricular optimization of cardiac resynchronization therapy: is beauty only in the eye of the beholder? Europace. 2014; 16:1865–1866. PMID: 25034719.
Article7. Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015; 16:233–270. PMID: 25712077.
Article8. Chalil S, Stegemann B, Muhyaldeen SA, et al. Effect of posterolateral left ventricular scar on mortality and morbidity following cardiac resynchronization therapy. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2007; 30:1201–1209. PMID: 17897122.
Article9. Corbalan R, Bassand JP, Illingworth L, et al. Analysis of outcomes in ischemic vs nonischemic cardiomyopathy in patients with atrial fibrillation: a report from the GARFIELD-AF registry. JAMA Cardiol. 2019; 4:526–548. PMID: 31066873.10. Yanagisawa S, Inden Y, Shimano M, et al. Clinical characteristics and predictors of super-response to cardiac resynchronization therapy: a combination of predictive factors. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2014; 37:1553–1564. PMID: 25223930.
Article11. Rickard J, Cheng A, Spragg D, et al. QRS narrowing is associated with reverse remodeling in patients with chronic right ventricular pacing upgraded to cardiac resynchronization therapy. Heart Rhythm. 2013; 10:55–60. PMID: 23000040.
Article12. Cai C, Hua W, Ding LG, et al. High sensitivity C-reactive protein and cardfiac resynchronization therapy in patients with advanced heart failure. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2014; 11:296–302. PMID: 25593578.13. Hsu JC, Solomon SD, Bourgoun M, et al. Predictors of super-response to cardiac resynchronization therapy and associated improvement in clinical outcome: the MADIT-CRT (multicenter automatic defibrillator implantation trial with cardiac resynchronization therapy) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012; 59:2366–2373. PMID: 22698490.14. António N, Teixeira R, Coelho L, et al. Identification of ‘super-responders’ to cardiac resynchronization therapy: the importance of symptom duration and left ventricular geometry. Europace. 2009; 11:343–349. PMID: 19240109.
Article15. Fujinami M, Kondo H, Yufu K, et al. Association between the baseline peripheral blood monocyte counts, the size of spleen, and the response to cardiac resynchronization therapy. J Cardiol. 2018; 71:299–304. PMID: 29054593.
Article16. Killu AM, Grupper A, Friedman PA, et al. Predictors and outcomes of “super-response” to cardiac resynchronization therapy. J Card Fail. 2014; 20:379–386. PMID: 24632340.
Article17. Guo JP, Wang YT, Shan ZL, et al. Role of electrocardiogram in predicting cardiac resynchronization therapy response. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2016; 44:483–488. PMID: 27346260.18. Hiraiwa H, Okumura T, Sawamura A, et al. The Selvester QRS score as a predictor of cardiac events in nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Cardiol. 2018; 71:284–290. PMID: 29066100.
Article19. Xue C, Hua W, Cai C, et al. Effect of cardiac resynchronization therapy in patients with dispersion of re-polarization and ventricular arrhythmia. Chin Circul J. 2016; 31:250–253.20. Ziacchi M, Corzani A, Diemberger I, et al. Electrocardiographic eligibility for subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator: evaluation during bicycle exercise. Heart Lung Circ. 2016; 25:476–483. PMID: 27044657.
Article21. Kawabata M, Goya M, Takahashi Y, et al. Candidacy for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator in patients with cardiac resynchronization therapy. Int Heart J. 2018; 59:951–958. PMID: 30101850.
Article22. Bacharova L, Schocken D, Estes EH, Strauss D. The role of ECG in the diagnosis of left ventricular hypertrophy. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2014; 10:257–261. PMID: 24827796.
Article23. Zeb M, Curzen N, Allavatam V, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator pre-implant screening tool. Int J Cardiol. 2015; 195:205–209. PMID: 26048376.
Article24. Hadjis A, AlTurki A, Proietti R, et al. Predicting response to cardiac resynchronization therapy: use of strict left bundle branch block criteria. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2019; 42:431–438. PMID: 30779177.
Article25. van Stipdonk AM, Ter Horst I, Kloosterman M, et al. QRS area is a strong determinant of outcome in cardiac resynchronization therapy. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2018; 11:e006497. PMID: 30541356.
Article26. Randles DA, Hawkins NM, Shaw M, Patwala AY, Pettit SJ, Wright DJ. How many patients fulfil the surface electrocardiogram criteria for subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator implantation? Europace. 2014; 16:1015–1021. PMID: 24351884.
Article27. Fontaine JM, Gupta A, Franklin SM, Kang CU, Whigham LA. Biventricular paced QRS predictors of left ventricular lead locations in relation to mortality in cardiac resynchronization therapy. J Electrocardiol. 2015; 48:226–235. PMID: 25552478.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
- Transvenous Implantation of an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator in a Patient Who Had Undergone Tricuspid Valve Replacement
- Recent Advancement in the Management of the Cardiac Arrhythmia
- Implantable Cardioverter-defibrillator for Primary Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death in Non-ischemic Cardiomyopathy
- Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD) Therapy: Initial Clinical Experience in 6 Patients