Int J Stem Cells.
2020 Nov;13(3):342-352. 10.15283/ijsc20037.
Cdo Is Required for Efficient Motor Neuron Generation of Embryonic Stem Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Molecular Cell Biology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- 2Department of Physiology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- 3Single Cell Network Research Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- KMID: 2508908
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15283/ijsc20037
Abstract
- Background and Objectives
The directed differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into motor neurons is critical for the development of disease modelling and therapeutics to intervene degenerative motor neuron diseases. Cell surface receptor Cdo functions as a coreceptor for Sonic hedgehog (Shh) with Boc and Gas1 in the patterning of ventral spinal cord neurons including motor neurons. However, the discrete function of Cdo is not fully understood.
Methods and Results
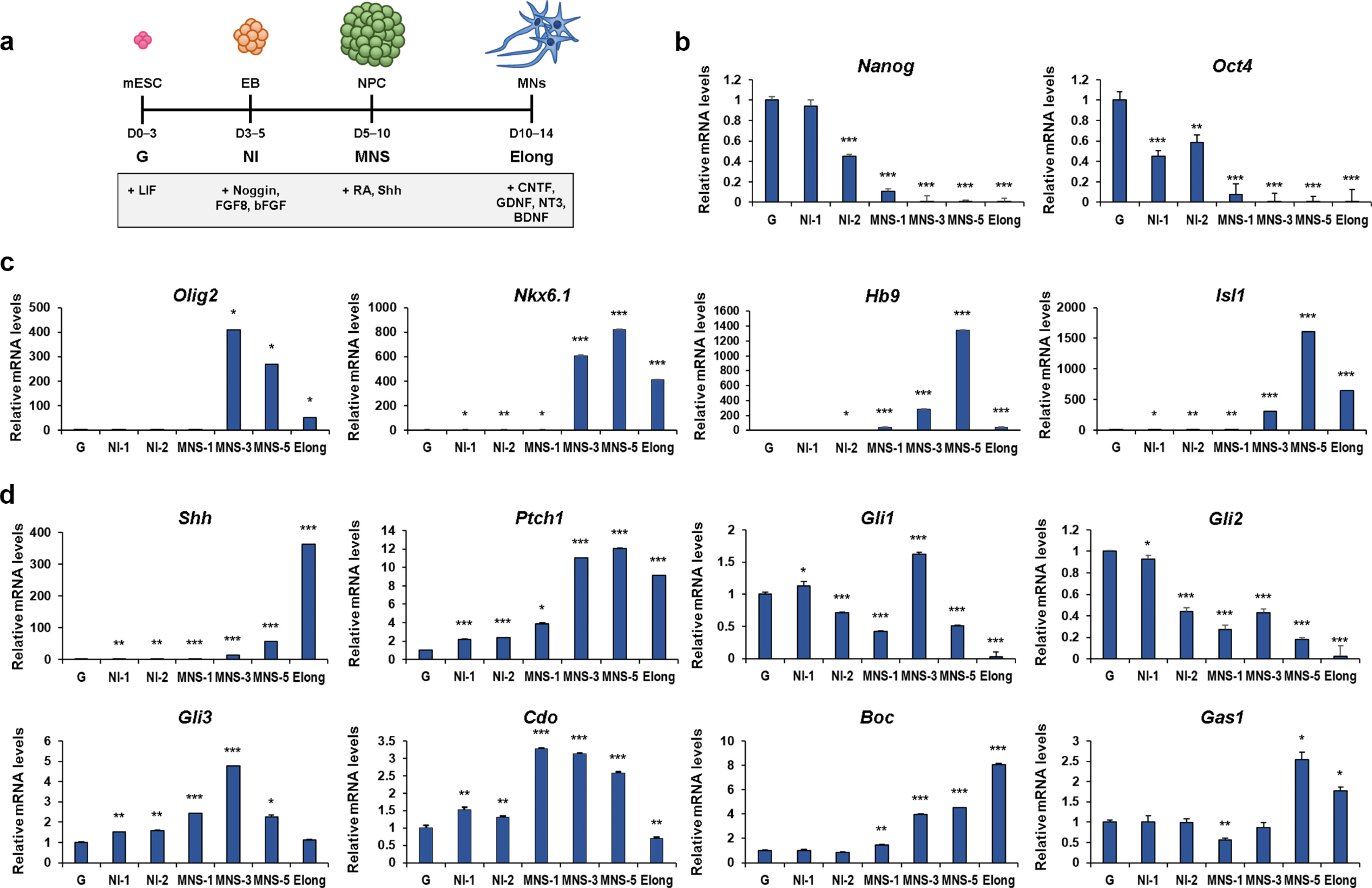
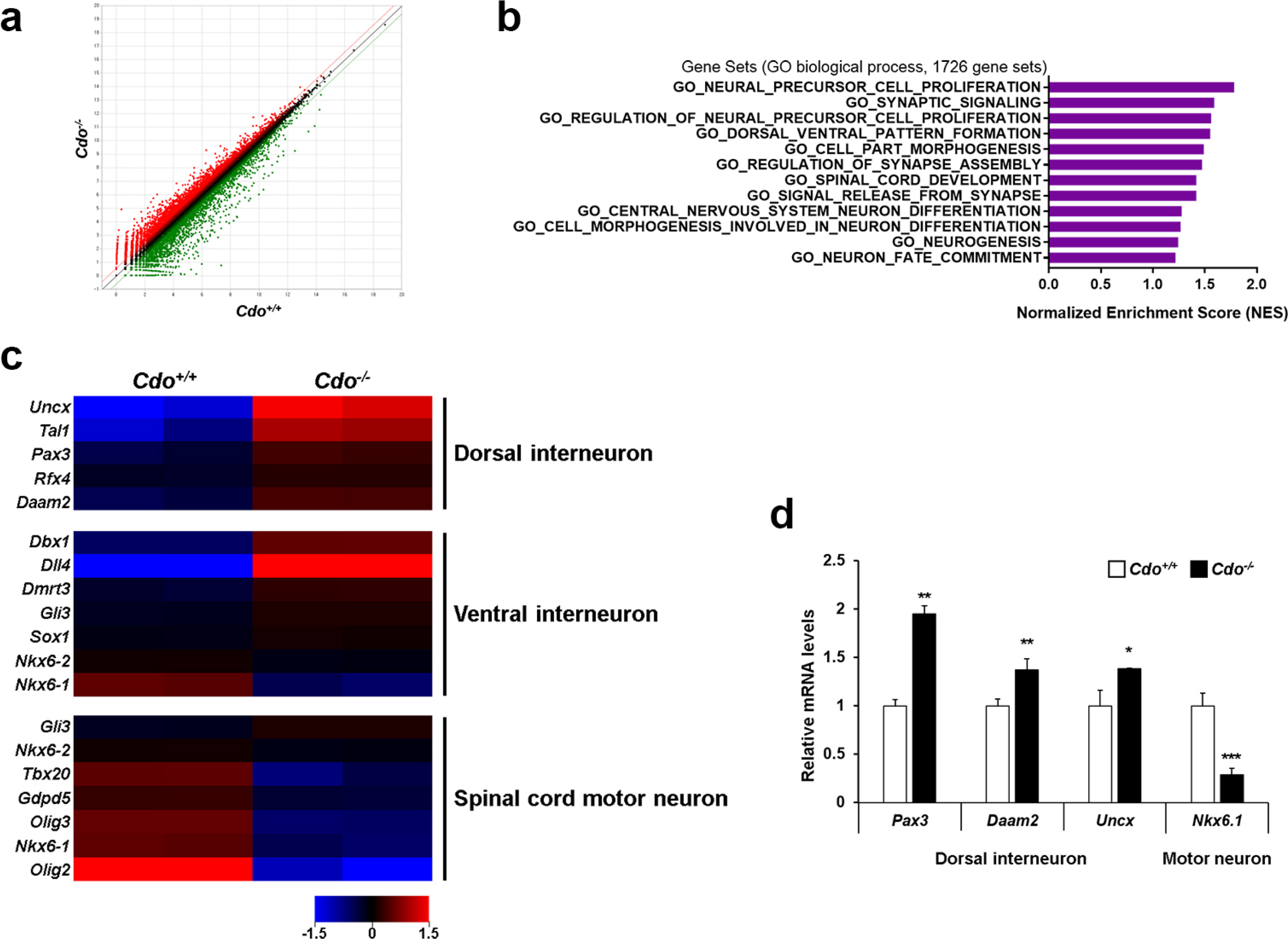
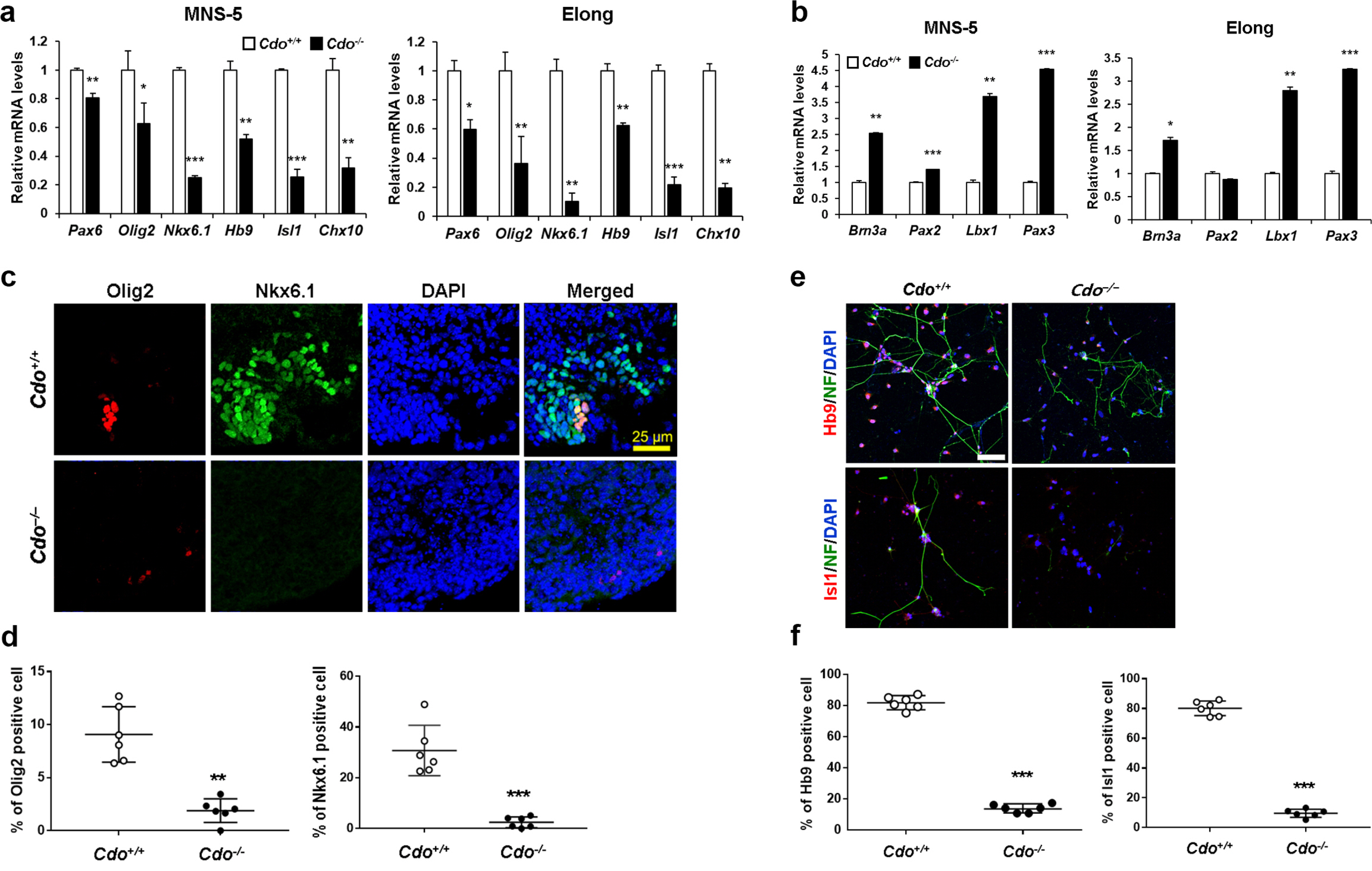
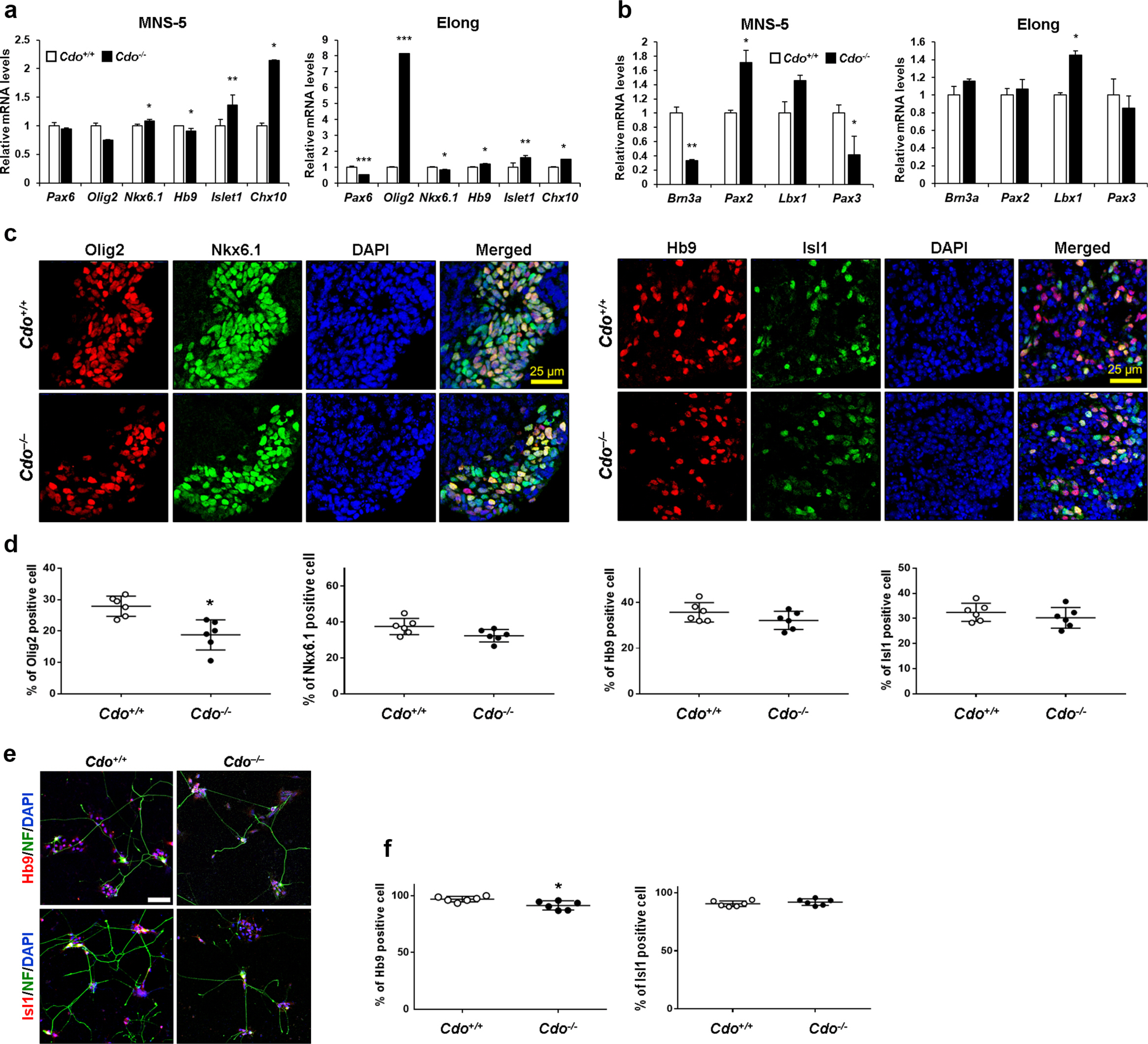
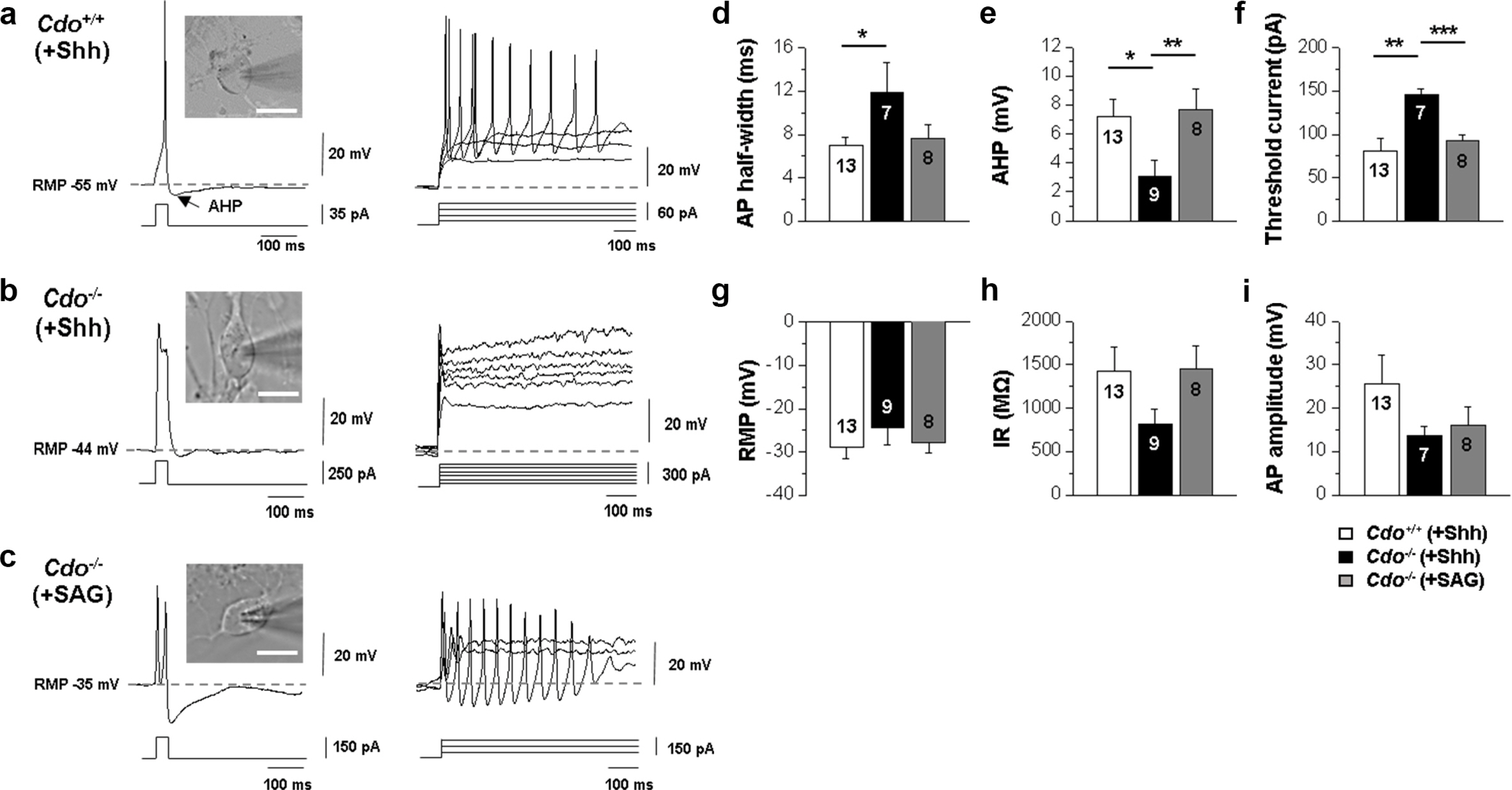
In this study, we examined the role of Cdo in motor neuron generation by utilizing in vitro differentiation of Cdo+/+ and Cdo−/− embryonic stem cells (ESCs). In response to Shh, Cdo−/− ESCs exhibited impaired expression of motor neuron specification markers while dorsal interneuron specification markers were significantly increased, compared to Cdo+/+ ESCs. Reactivation of Shh signalling pathway with Smoothened (Smo) agonist (SAG) restored motor neuron specification in Cdo−/− ESCs. In addition, electrophysiological analysis revealed the immature electrical features of Cdo−/− ESCs-derived neurons which was restored by SAG.
Conclusions
Taken together, these data suggest that Cdo as a Shh coreceptor is required for the induction of motor neuron generation by fully activating Shh signalling pathway and provide additional insights into the biology of motor neuron development.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Jessell TM. 2000; Neuronal specification in the spinal cord: inductive signals and transcriptional codes. Nat Rev Genet. 1:20–29. DOI: 10.1038/35049541. PMID: 11262869.
Article2. Briscoe J, Ericson J. 2001; Specification of neuronal fates in the ventral neural tube. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 11:43–49. DOI: 10.1016/S0959-4388(00)00172-0. PMID: 11179871.
Article3. Briscoe J, Pierani A, Jessell TM, Ericson J. 2000; A homeodomain protein code specifies progenitor cell identity and neuronal fate in the ventral neural tube. Cell. 101:435–445. DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80853-3. PMID: 10830170.
Article4. Helms AW, Johnson JE. 2003; Specification of dorsal spinal cord interneurons. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 13:42–49. DOI: 10.1016/S0959-4388(03)00010-2. PMID: 12593981.
Article5. Ericson J, Briscoe J, Rashbass P, van Heyningen V, Jessell TM. 1997; Graded sonic hedgehog signaling and the specification of cell fate in the ventral neural tube. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 62:451–466. DOI: 10.1101/SQB.1997.062.01.053. PMID: 9598380.6. Briscoe J, Chen Y, Jessell TM, Struhl G. 2001; A hedgehog-insensitive form of patched provides evidence for direct long-range morphogen activity of sonic hedgehog in the neural tube. Mol Cell. 7:1279–1291. DOI: 10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00271-4. PMID: 11430830.
Article7. Roelink H, Porter JA, Chiang C, Tanabe Y, Chang DT, Beachy PA, Jessell TM. 1995; Floor plate and motor neuron induction by different concentrations of the amino-terminal cleavage product of sonic hedgehog autoproteolysis. Cell. 81:445–455. DOI: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90397-6. PMID: 7736596.
Article8. Chiang C, Litingtung Y, Lee E, Young KE, Corden JL, Westphal H, Beachy PA. 1996; Cyclopia and defective axial patterning in mice lacking Sonic hedgehog gene function. Nature. 383:407–413. DOI: 10.1038/383407a0. PMID: 8837770.
Article9. Bai CB, Auerbach W, Lee JS, Stephen D, Joyner AL. 2002; Gli2, but not Gli1, is required for initial Shh signaling and ectopic activation of the Shh pathway. Development. 129:4753–4761.
Article10. Ericson J, Rashbass P, Schedl A, Brenner-Morton S, Kawakami A, van Heyningen V, Jessell TM, Briscoe J. 1997; Pax6 controls progenitor cell identity and neuronal fate in response to graded Shh signaling. Cell. 90:169–180. DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80323-2. PMID: 9230312.
Article11. Dessaud E, Ribes V, Balaskas N, Yang LL, Pierani A, Kicheva A, Novitch BG, Briscoe J, Sasai N. 2010; Dynamic assignment and maintenance of positional identity in the ventral neural tube by the morphogen sonic hedgehog. PLoS Biol. 8:e1000382. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000382. PMID: 20532235. PMCID: PMC2879390.
Article12. Ericson J, Morton S, Kawakami A, Roelink H, Jessell TM. 1996; Two critical periods of Sonic Hedgehog signaling required for the specification of motor neuron identity. Cell. 87:661–673. DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81386-0. PMID: 8929535.
Article13. Allen BL, Tenzen T, McMahon AP. 2007; The Hedgehog-binding proteins Gas1 and Cdo cooperate to positively regulate Shh signaling during mouse development. Genes Dev. 21:1244–1257. DOI: 10.1101/gad.1543607. PMID: 17504941. PMCID: PMC1865495.
Article14. Allen BL, Song JY, Izzi L, Althaus IW, Kang JS, Charron F, Krauss RS, McMahon AP. 2011; Overlapping roles and collective requirement for the coreceptors GAS1, CDO, and BOC in SHH pathway function. Dev Cell. 20:775–787. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.04.018. PMID: 21664576. PMCID: PMC3121104.
Article15. Zhang W, Yi MJ, Chen X, Cole F, Krauss RS, Kang JS. 2006; Cortical thinning and hydrocephalus in mice lacking the immunoglobulin superfamily member CDO. Mol Cell Biol. 26:3764–3772. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.26.10.3764-3772.2006. PMID: 16648472. PMCID: PMC1489002.
Article16. Izzi L, Lévesque M, Morin S, Laniel D, Wilkes BC, Mille F, Krauss RS, McMahon AP, Allen BL, Charron F. 2011; Boc and Gas1 each form distinct Shh receptor complexes with Ptch1 and are required for Shh-mediated cell proliferation. Dev Cell. 20:788–801. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.04.017. PMID: 21664577. PMCID: PMC3432913.
Article17. Tenzen T, Allen BL, Cole F, Kang JS, Krauss RS, McMahon AP. 2006; The cell surface membrane proteins Cdo and Boc are components and targets of the Hedgehog signaling pathway and feedback network in mice. Dev Cell. 10:647–656. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.04.004. PMID: 16647304.
Article18. Kwon YR, Jeong MH, Leem YE, Lee SJ, Kim HJ, Bae GU, Kang JS. 2014; The Shh coreceptor Cdo is required for differen-tiation of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Stem Cell Res. 13:262–274. DOI: 10.1016/j.scr.2014.07.004. PMID: 25117422.
Article19. Zhang W, Kang JS, Cole F, Yi MJ, Krauss RS. 2006; Cdo functions at multiple points in the Sonic Hedgehog pathway, and Cdo-deficient mice accurately model human holopro-sencephaly. Dev Cell. 10:657–665. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.04.005. PMID: 16647303.
Article20. Zhang W, Hong M, Bae GU, Kang JS, Krauss RS. 2011; Boc modifies the holoprosencephaly spectrum of Cdo mutant mice. Dis Model Mech. 4:368–380. DOI: 10.1242/dmm.005744. PMID: 21183473. PMCID: PMC3097458.21. Bae GU, Domené S, Roessler E, Schachter K, Kang JS, Muenke M, Krauss RS. 2011; Mutations in CDON, encoding a hedgehog receptor, result in holoprosencephaly and defective interactions with other hedgehog receptors. Am J Hum Genet. 89:231–240. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.07.001. PMID: 21802063. PMCID: PMC3155179.
Article22. Jeong MH, Leem YE, Kim HJ, Kang K, Cho H, Kang JS. 2016; A Shh coreceptor Cdo is required for efficient cardiomyogenesis of pluripotent stem cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 93:57–66. DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.01.013. PMID: 26906632.
Article23. Jeong HJ, Lee HJ, Vuong TA, Choi KS, Choi D, Koo SH, Cho SC, Cho H, Kang JS. 2016; Prmt7 deficiency causes reduced skeletal muscle oxidative metabolism and age-related obesity. Diabetes. 65:1868–1882. DOI: 10.2337/db15-1500. PMID: 27207521.
Article24. Langmead B, Salzberg SL. 2012; Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods. 9:357–359. DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.1923. PMID: 22388286. PMCID: PMC3322381.
Article25. Quinlan AR, Hall IM. 2010; BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics. 26:841–842. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq033. PMID: 20110278. PMCID: PMC2832824.
Article26. Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, Bolstad B, Dettling M, Dudoit S, Ellis B, Gautier L, Ge Y, Gentry J, Hornik K, Hothorn T, Huber W, Iacus S, Irizarry R, Leisch F, Li C, Maechler M, Rossini AJ, Sawitzki G, Smith C, Smyth G, Tierney L, Yang JY, Zhang J. 2004; Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinfor-matics. Genome Biol. 5:R80. DOI: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-10-r80. PMID: 15461798. PMCID: PMC545600.27. Okada A, Charron F, Morin S, Shin DS, Wong K, Fabre PJ, Tessier-Lavigne M, McConnell SK. 2006; Boc is a receptor for sonic hedgehog in the guidance of commissural axons. Nature. 444:369–373. DOI: 10.1038/nature05246. PMID: 17086203.
Article28. Wichterle H, Lieberam I, Porter JA, Jessell TM. 2002; Directed differentiation of embryonic stem cells into motor neurons. Cell. 110:385–397. DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00835-8. PMID: 12176325.
Article29. Pierani A, Brenner-Morton S, Chiang C, Jessell TM. 1999; A sonic hedgehog-independent, retinoid-activated pathway of neurogenesis in the ventral spinal cord. Cell. 97:903–915. DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80802-8. PMID: 10399918.
Article30. Ribes V, Briscoe J. 2009; Establishing and interpreting graded Sonic Hedgehog signaling during vertebrate neural tube patterning: the role of negative feedback. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 1:a002014. DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002014. PMID: 20066087. PMCID: PMC2742090.
Article31. Lee J, Platt KA, Censullo P. Ruiz i Altaba A. 1997; Gli1 is a target of Sonic hedgehog that induces ventral neural tube development. Development. 124:2537–2552. PMID: 9216996.
Article32. Litingtung Y, Chiang C. 2000; Specification of ventral neuron types is mediated by an antagonistic interaction between Shh and Gli3. Nat Neurosci. 3:979–985. DOI: 10.1038/79916. PMID: 11017169.
Article33. Ericson J, Muhr J, Placzek M, Lints T, Jessell TM, Edlund T. 1995; Sonic hedgehog induces the differentiation of ventral forebrain neurons: a common signal for ventral patterning within the neural tube. Cell. 81:747–756. DOI: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90536-7. PMID: 7774016.
Article34. Takebayashi H, Nabeshima Y, Yoshida S, Chisaka O, Ikenaka K, Nabeshima Y. 2002; The basic helix-loop-helix factor olig2 is essential for the development of motoneuron and oligodendrocyte lineages. Curr Biol. 12:1157–1163. DOI: 10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00926-0. PMID: 12121626.
Article35. Sander M, Paydar S, Ericson J, Briscoe J, Berber E, German M, Jessell TM, Rubenstein JL. 2000; Ventral neural patterning by Nkx homeobox genes: Nkx6.1 controls somatic motor neuron and ventral interneuron fates. Genes Dev. 14:2134–2139. DOI: 10.1101/gad.820400. PMID: 10970877. PMCID: PMC316892.
Article36. Novitch BG, Wichterle H, Jessell TM, Sockanathan S. 2003; A requirement for retinoic acid-mediated transcriptional activation in ventral neural patterning and motor neuron speci-fication. Neuron. 40:81–95. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2003.08.006. PMID: 14527435.
Article37. Yang X, Tomita T, Wines-Samuelson M, Beglopoulos V, Tansey MG, Kopan R, Shen J. 2006; Notch1 signaling influences v2 interneuron and motor neuron development in the spinal cord. Dev Neurosci. 28:102–117. DOI: 10.1159/000090757. PMID: 16508308.
Article38. Ciani L, Salinas PC. 2005; WNTs in the vertebrate nervous system: from patterning to neuronal connectivity. Nat Rev Neurosci. 6:351–362. DOI: 10.1038/nrn1665. PMID: 15832199.
Article39. Jeong MH, Ho SM, Vuong TA, Jo SB, Liu G, Aaronson SA, Leem YE, Kang JS. 2014; Cdo suppresses canonical Wnt signalling via interaction with Lrp6 thereby promoting neuronal differentiation. Nat Commun. 5:5455. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms6455. PMID: 25406935. PMCID: PMC4412020.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of Embryonic Stem Cell-derived Dopaminergic Neurons and E12 Mesencephalic Neuronal-precursor Derived Dopaminergic Neurons as a Source for Transplantation in Parkinsonian Rats
- Efficient Induction of Dopaminergic Neurons from Embryonic Stem Cells for Application to Parkinson's Disease
- In Vitro Neural Cell Differentiation Derived from Human Embryonic Stem Cells: Effects of PDGF-bb and BDNF on the Generation of Functional Neurons
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells: Next Generation Stem Cells to Clinical Applications
- Current Concepts of Stem Cell Therapy