Anesth Pain Med.
2020 Oct;15(4):486-491. 10.17085/apm.20052.
Incidence of inadvertent intercostal or epidural spread during thoracic sympathetic ganglion block
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2508412
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.20052
Abstract
- Background
Sympathetic blocks (SBs) have been used widely to relieve the symptoms of sympathetically maintained pain (SMP). The thoracic sympathetic ganglion is not separated from somatic nerves by muscles and connective tissue. The upper thoracic ganglion runs along the posterior surface of the vertebral column in close proximity to the adjacent epidural region. This anatomical difference leads to frequent epidural and intercostal spread in cases of thoracic SBs. The purpose of this study was to investigate the incidence of inadvertent intercostal and epidural injections during thoracic SBs.
Methods
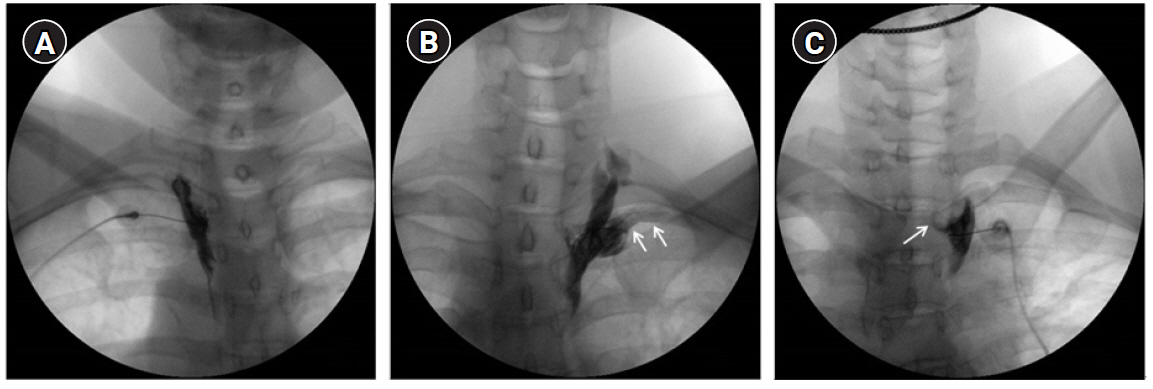
Twenty-two patients who were suffering from complex regional pain syndrome or lymphedema after breast cancer surgery were managed with two or three times of thoracic SBs. Therefore, injections of 63 thoracic SBs from 22 patients were enrolled in this study. An investigator who did not attend the procedure evaluated the occurrence of intercostal or epidural spread using anteroposterior fluoroscopic images.
Results
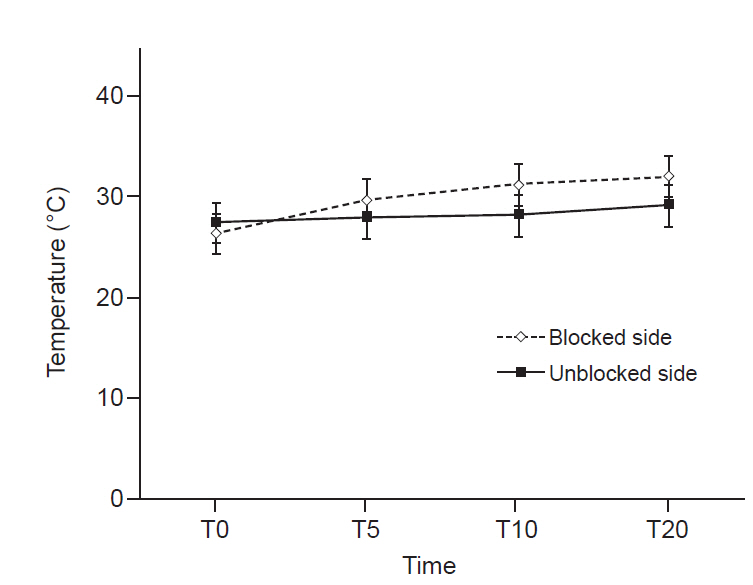
The overall incidence of inadvertent intercostal or epidural spread of contrast was 47.5%. Among the inadvertent injections, intercostal spread (34.9%) was more frequent than epidural spread (12.6%). Only 52.5% of the thoracic SBs demonstrated successful contrast spread without any inadvertent spread. The mean difference in skin temperature between the blocked and unblocked sides was 2.5 ± 1.8ºC. Fifty-nine (93.6%) injections demonstrated more than 1.5ºC difference.
Conclusions
Thoracic SBs showed a high incidence (47.5%) of inadvertent epidural or intercostal injection. Thus, special attention is required for the diagnosis of SMP or the injection of any neurolytic agent around sympathetic ganglion.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chaudhry A, Kamali A, Herzka DA, Wang KC, Carrino JA, Blitz AM. Detection of the stellate and thoracic sympathetic chain ganglia with high-resolution 3D-CISS MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018; 39:1550–4.2. Elias M. Cervical sympathetic and stellate ganglion blocks. Pain Physician. 2000; 3:294–304.3. Wehrwein EA, Orer HS, Barman SM. Overview of the anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology of the autonomic nervous system. Compr Physiol. 2016; 6:1239–78.4. Krumova EK, Gussone C, Regeniter S, Westermann A, Zenz M, Maier C. Are sympathetic blocks useful for diagnostic purposes? Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2011; 36:560–7.5. Gibbs GF, Drummond PD, Finch PM, Phillips JK. Unravelling the pathophysiology of complex regional pain syndrome: focus on sympathetically maintained pain. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2008; 35:717–24.6. Sommer C, Leinders M, Üçeyler N. Inflammation in the pathophysiology of neuropathic pain. Pain. 2018; 159:595–602.7. Park J, Lee YJ, Kim ED. Clinical effects of pulsed radiofrequency to the thoracic sympathetic ganglion versus the cervical sympathetic chain in patients with upper-extremity complex regional pain syndrome: a retrospective analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98:e14282.8. Zhu X, Kohan LR, Morris JD, Hamill-Ruth RJ. Sympathetic blocks for complex regional pain syndrome: a survey of pain physicians. Reg Anesth Pain Med;2019; doi: 10.1136/rapm-2019-100418 [Epub ahead of print].9. Rocha Rde O, Teixeira MJ, Yeng LT, Cantara MG, Faria VG, Liggieri V, et al. Thoracic sympathetic block for the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome type I: a double-blind randomized controlled study. Pain. 2014; 155:2274–81.10. Murata Y, Takahashi K, Yamagata M, Takahashi Y, Shimada Y, Moriya H. Variations in the number and position of human lumbar sympathetic ganglia and rami communicantes. Clin Anat. 2003; 16:108–13.11. Hong JH, Kim AR, Lee MY, Kim YC, Oh MJ. A prospective evaluation of psoas muscle and intravascular injection in lumbar sympathetic ganglion block. Anesth Analg. 2010; 111:802–7.12. Schiller Y. The anatomy and physiology of the sympathetic innervation to the upper limbs. Clin Auton Res. 2003; 13 Suppl 1:I2–5.13. Kim WH, Lee CJ, Kim TH, Shin BS, Sim WS. The optimal oblique angle of fluoroscope for thoracic sympathetic ganglion block. Clin Auton Res. 2011; 21:89–96.14. Schürmann M, Gradl G, Wizgal I, Tutic M, Moser C, Azad S, et al. Clinical and physiologic evaluation of stellate ganglion blockade for complex regional pain syndrome type I. Clin J Pain. 2001; 17:94–100.15. Cho HM, Lee DY, Sung SW. Anatomical variations of rami communicantes in the upper thoracic sympathetic trunk. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2005; 27:320–4.16. Akil A, Semik M, Fischer S. Efficacy of miniuniportal video-assisted thoracoscopic selective sympathectomy (ramicotomy) for the treatment of severe palmar and axillar hyperhidrosis. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019; 67:415–9.17. Brock M, Frangakis C, Georgiades CS. CT-guided, percutaneous ethanol sympatholysis for primary hyperhidrosis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018; 41:477–82.18. Ramsaroop L, Partab P, Singh B, Satyapal KS. Thoracic origin of a sympathetic supply to the upper limb: the 'nerve of Kuntz' revisited. J Anat. 2001; 199(Pt 6):675–82.19. Choi E, Nahm FS, Lee PB. Sympathetic block as a new treatment for lymphedema. Pain Physician. 2015; 18:365–72.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Thoracic Sympathetic Ganglion Block for Two Patients with Thoracic Cancer Pain: A case report
- Thoracic Sympathetic Ganglion Block for a Patient with Hyperhidrosis
- The Clinical Experiences and Complications of Percutaneous Neurolysis of Upper Thoracic Sympathetic Ganglion by Using Ethylalcohol: A report of three cases
- Clinical study on the Management of Postherpetic Neuralgia
- Anatomical Variations in the Communicating Rami of the Upper Thoracic Sympathetic Ganglia Related to the Essential Palmar Hyperhidrosis