Anesth Pain Med.
2020 Oct;15(4):472-477. 10.17085/apm.20059.
Domino living donor liver transplantation of familial amyloid polyneuropathy patient - A case report -
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Nursing, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2508410
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.20059
Abstract
- Background
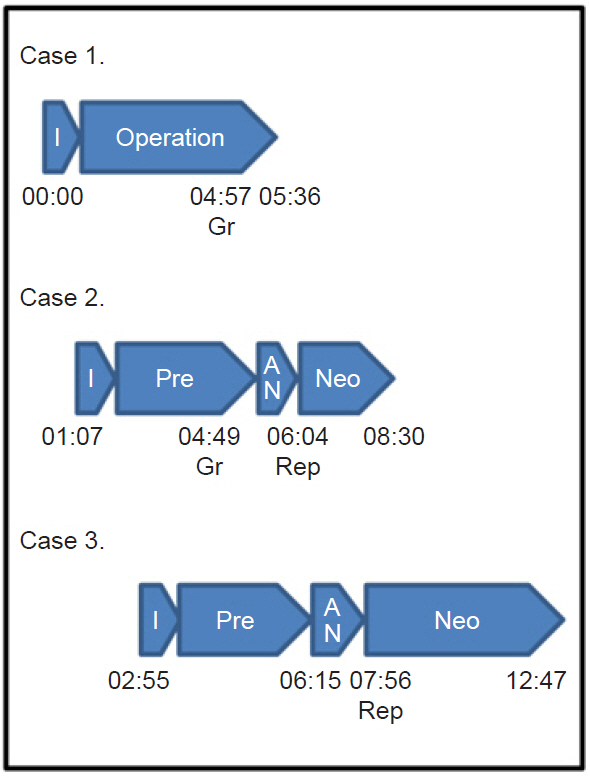
Familial amyloid polyneuropathy (FAP) is caused by mutation in a gene transcribing transport protein produced mainly by the liver. Liver transplantation is required to stop FAP progression, but the pathology causes anesthetic management challenges. Case: We report a case of domino living donor liver transplantation in an FAP patient. No intraoperative events occurred; however, during postoperative day 1 in the intensive care unit (ICU), the FAP patient underwent multiple cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) sessions due to pulseless electrical activity following a sudden drop in blood pressure and ventricular tachycardia. Despite ICU management, the patient died after the third CPR session.
Conclusions
Various anesthetic management techniques should be considered for FAP patients. Anesthetic management was carefully assessed with the use of isoflurane, isoproterenol, and an external patch. The cause of deterioration in the ICU is unclear, but further investigation is needed to prevent and better manage postoperative morbidity and mortality.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Andrade C. A peculiar form of peripheral neuropathy; familiar atypical generalized amyloidosis with special involvement of the peripheral nerves. Brain. 1952; 75:408–27.2. Benson MD. Liver transplantation and transthyretin amyloidosis. Muscle Nerve. 2013; 47:157–62.3. Sekijima Y. Transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis: clinical spectrum, molecular pathogenesis and disease-modifying treatments. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015; 86:1036–43.4. Adams D, Samuel D, Goulon-Goeau C, Nakazato M, Costa PM, Feray C, et al. The course and prognostic factors of familial amyloid polyneuropathy after liver transplantation. Brain. 2000; 123(Pt 7):1495–504.5. Furtado A, Tomé L, Oliveira FJ, Furtado E, Viana J, Perdigoto R. Sequential liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1997; 29:467–8.6. Stangou AJ, Heaton ND, Hawkins PN. Transmission of systemic transthyretin amyloidosis by means of domino liver transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:2356.7. Bang SR, Ahn HJ, Kim GS, Yang M, Gwak MS, Ko JS, et al. Predictors of high intraoperative blood loss derived by simple and objective method in adult living donor liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2010; 42:4148–50.8. Delahaye N, Dinanian S, Slama MS, Mzabi H, Samuel D, Adams D, et al. Cardiac sympathetic denervation in familial amyloid polyneuropathy assessed by iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy and heart rate variability. Eur J Nucl Med. 1999; 26:416–24.9. Delahaye N, Le Guludec D, Dinanian S, Delforge J, Slama MS, Sarda L, et al. Myocardial muscarinic receptor upregulation and normal response to isoproterenol in denervated hearts by familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Circulation. 2001; 104:2911–6.10. Neelakanta G, Mahajan A, Antin C. Systemic vasodilation is a predominant cause of hypotension in a patient with familial amyloid polyneuropathy during liver transplantation. J Clin Anesth. 2005; 17:202–4.11. Eger EI 2nd. Isoflurane: a review. Anesthesiology. 1981; 55:559–76.12. Castro Tavares J, Maciel L. Anaesthetic management of a patient with familial amyloid polyneuropathy of the Portuguese type. Can J Anaesth. 1989; 36:209–11.13. Bosnjak ZJ, Kampine JP. Effects of halothane, enflurane, and isoflurane on the SA node. Anesthesiology. 1983; 58:314–21.14. Milner J, Teixeira RN, Marinho AV, Silva N, Calretas S, Ferrão J, et al. Pacemaker implantation in familial amyloid polyneuropathy: when and for whom? J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2019; 55:207–11.15. Eriksson P, Karp K, Bjerle P, Olofsson BO. Disturbances of cardiac rhythm and conduction in familial amyloidosis with polyneuropathy. Br Heart J. 1984; 51:658–62.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Liver retransplantation for adult recipients
- Secondary Open-angle Glaucoma and Vitreous Opacity as Presenting Manifestations of Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy
- Portal vein fenestration: a case report of an unusual portal vein developmental anomaly
- Left at right heterotopic implantation of left liver graft in adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation: the technical concern for decision-making
- Unilateral Versus Bilateral Biliary Drainage for Post-Transplant Anastomotic Stricture