Anesth Pain Med.
2020 Oct;15(4):459-465. 10.17085/apm.20042.
Comparing hemostatic resuscitation management of intraoperative massive bleeding with traumatic massive bleeding: a computer simulation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Hanyang University Graduate School, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Hanyang University Seoul Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2508408
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.20042
Abstract
- Background
Appropriate blood component transfusion might differ between intraoperative massive bleeding and traumatic massive bleeding in the emergency department because trauma patients initially bleed undiluted blood and replacement typically lags behind blood loss. We compared these two blood loss scenarios, intraoperative and traumatic, using a computer simulation.
Methods
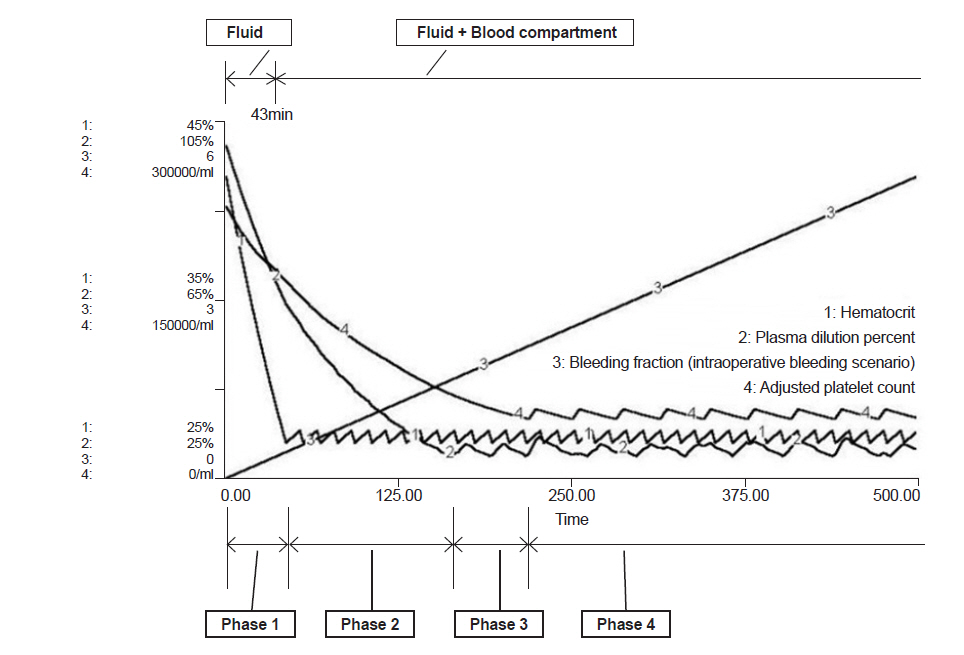
We modified the multi-compartment dynamic model developed by Hirshberg and implemented it using STELLA 9.0. In this model, blood pressure changes as blood volume fluctuates as bleeding rate and transcapillary refill rate are controlled by blood pressure. Using this simulation, we compared the intraoperative bleeding scenario with the traumatic bleeding scenario. In both scenarios, patients started to bleed at a rate of 50 ml/min. In the intraoperative bleeding scenario, fluid was administered to maintain isovolemic status; however, in the traumatic bleeding scenario, no fluid was supplied for up to 30 min and no blood was supplied for up to 50 min. Each unit of packed red blood cells (PRBC) was given when the hematocrit decreased to 27%, fresh frozen plasma (FFP) was transfused when plasma was diluted to 30%, and platelet concentrate (PC) was transfused when platelet count became 50,000/ml.
Results
In both scenarios, the appropriate ratio of PRBC:FFP was 1:0.47 before PC transfusion, and the ratio of PRBC:FFP:platelets was 1:0.35:0.39 after initiation of PC transfusion.
Conclusion
The ratio of transfused blood component did not differ between the intraoperative bleeding and traumatic bleeding scenarios.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Guerado E, Medina A, Mata MI, Galvan JM, Bertrand ML. Protocols for massive blood transfusion: when and why, and potential complications. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2016; 42:283–95.2. Gentilello LM, Pierson DJ. Trauma critical care. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 163(3 Pt 1):604–7.3. Cinat ME, Wallace WC, Nastanski F, West J, Sloan S, Ocariz J, et al. Improved survival following massive transfusion in patients who have undergone trauma. Arch Surg. 1999; 134:964–8; discussion 968-70.4. Eddy VA, Morris JA Jr, Cullinane DC. Hypothermia, coagulopathy, and acidosis. Surg Clin North Am. 2000; 80:845–54.5. Hardaway RM. The significance of coagulative and thrombotic changes after haemorrhage and injury. J Clin Pathol Suppl (R Coll Pathol). 1970; 4:110–20.6. Miller RD, Robbins TO, Tong MJ, Barton SL. Coagulation defects associated with massive blood transfusions. Ann Surg. 1971; 174:794–801.7. Reiss RF. Hemostatic defects in massive transfusion: rapid diagnosis and management. Am J Crit Care. 2000; 9:158–65. ; quiz 166-7.8. Hirshberg A, Dugas M, Banez EI, Scott BG, Wall MJ Jr, Mattox KL. Minimizing dilutional coagulopathy in exsanguinating hemorrhage: a computer simulation. J Trauma. 2003; 54:454–63.9. Hiippala S. Replacement of massive blood loss. Vox Sang. 1998; 74 Suppl 2:399–407.10. Flint AWJ, McQuilten ZK, Wood EM. Massive transfusions for critical bleeding: is everything old new again? Transfus Med. 2018; 28:140–9.11. Cervera AL, Moss G. Crystalloid distribution following hemorrhage and hemodilution: mathematical model and prediction of optimum volumes for equilibration at normovolemia. J Trauma. 1974; 14:506–20.12. Lewis FR Jr. Prehospital intravenous fluid therapy: physiologic computer modelling. J Trauma. 1986; 26:804–11.13. Mardel SN, Simpson SH, Kelly S, Wytch R, Beattie TF, Menezes G. Validation of a computer model of haemorrhage and transcapillary refill. Med Eng Phys. 1995; 17:215–8.14. Simpson SH, Menezes G, Mardel SN, Kelly S, White R, Beattie T. A computer model of major haemorrhage and resuscitation. Med Eng Phys. 1996; 18:339–43.15. Wears RL, Winton CN. Load and go versus stay and play: analysis of prehospital i.v. fluid therapy by computer simulation. Ann Emerg Med. 1990; 19:163–8.16. Lundsgaard-Hansen P. Treatment of acute blood loss. Vox Sang. 1992; 63:241–6.17. American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Perioperative Blood Transfusion and Adjuvant Therapies. Practice guidelines for perioperative blood transfusion and adjuvant therapies: an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Perioperative Blood Transfusion and Adjuvant Therapies. Anesthesiology. 2006; 105:198–208.18. Hirshberg A, Hoyt DB, Mattox KL. Timing of fluid resuscitation shapes the hemodynamic response to uncontrolled hemorrhage: analysis using dynamic modeling. J Trauma. 2006; 60:1221–7.19. Spahn DR, Bouillon B, Cerny V, Coats TJ, Duranteau J, Fernández-Mondéjar E, et al. Management of bleeding and coagulopathy following major trauma: an updated European guideline. Crit Care. 2013; 17:R76.20. Hardy JF, De Moerloose P, Samama M. Massive transfusion and coagulopathy: pathophysiology and implications for clinical management. Can J Anaesth. 2004; 51:293–310.21. Holcomb JB, Tilley BC, Baraniuk S, Fox EE, Wade CE, Podbielski JM, et al. PROPPR Study Group. Transfusion of plasma, platelets, and red blood cells in a 1:1:1 vs a 1:1:2 ratio and mortality in patients with severe trauma: the PROPPR randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015; 313:471–82.22. Johnson JL, Moore EE, Kashuk JL, Banerjee A, Cothren CC, Biffl WL, et al. Effect of blood products transfusion on the development of postinjury multiple organ failure. Arch Surg. 2010; 145:973–7.23. Scalea TM, Bochicchio KM, Lumpkins K, Hess JR, Dutton R, Pyle A, et al. Early aggressive use of fresh frozen plasma does not improve outcome in critically injured trauma patients. Ann Surg. 2008; 248:578–84.24. Scott E, Puca K, Heraly J, Gottschall J, Friedman K. Evaluation and comparison of coagulation factor activity in fresh-frozen plasma and 24-hour plasma at thaw and after 120 hours of 1 to 6°C storage. Transfusion. 2009; 49:1584–91.25. Spahn DR, Rossaint R. Coagulopathy and blood component transfusion in trauma. Br J Anaesth. 2005; 95:130–9.26. Johnson JW, Gracias VH, Schwab CW, Reilly PM, Kauder DR, Shapiro MB, et al. Evolution in damage control for exsanguinating penetrating abdominal injury. J Trauma. 2001; 51:261–9; discussion 269-71.27. Robb WJ. Massive transfusion in trauma. AACN Clin Issues. 1999; 10:69–84; quiz 138-40.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Simple Comment of Trauma-Induced Coagulopathy and Massive Transfusion
- Laparoscopic uterine artery occlusion before cervical curettage in cervical ectopic pregnancy: Safe and effective for preventing massive bleeding
- Traumatic Pseudoaneurysm of the Superior Rectal Artery with Recurrent Lower Gastrointestinal and Pelvic Extraperitoneal Bleeding: Importance of Pretreatment Recognition
- Massive Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding from the Appendix
- A novel method to cease traumatic urethral bleeding