Yeungnam Univ J Med.
2020 Oct;37(4):349-355. 10.12701/yujm.2020.00640.
Yeungnam University type drive-through (YU-Thru) coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) screening system: a rapid and safe screening system
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 5Department of Neurology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 6Department of General Affairs, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea
- 7Department of Psychiatry, Yeungnam University Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2508184
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00640
Abstract
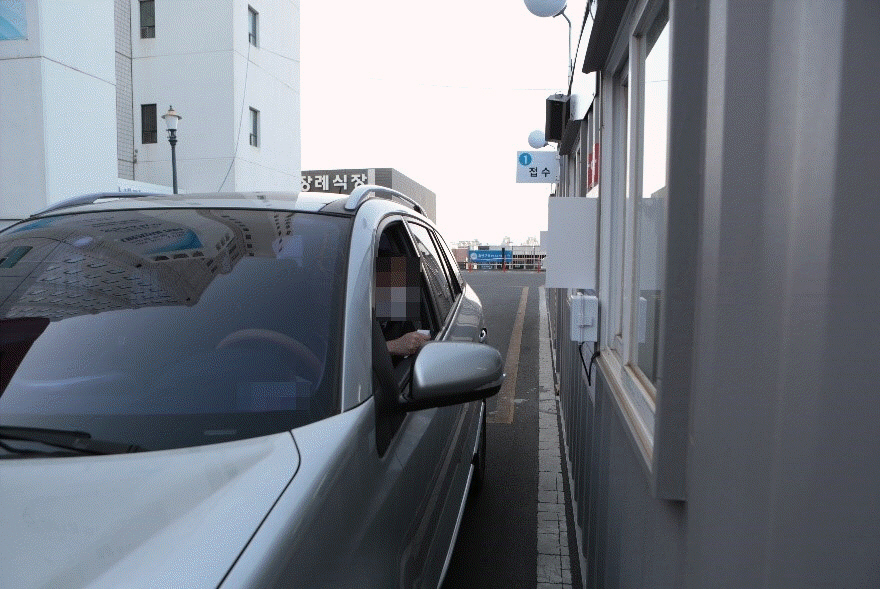
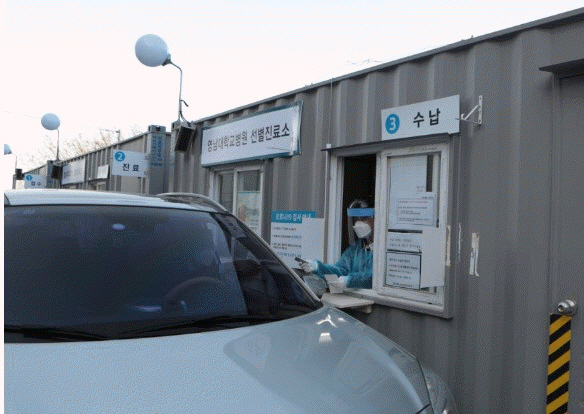
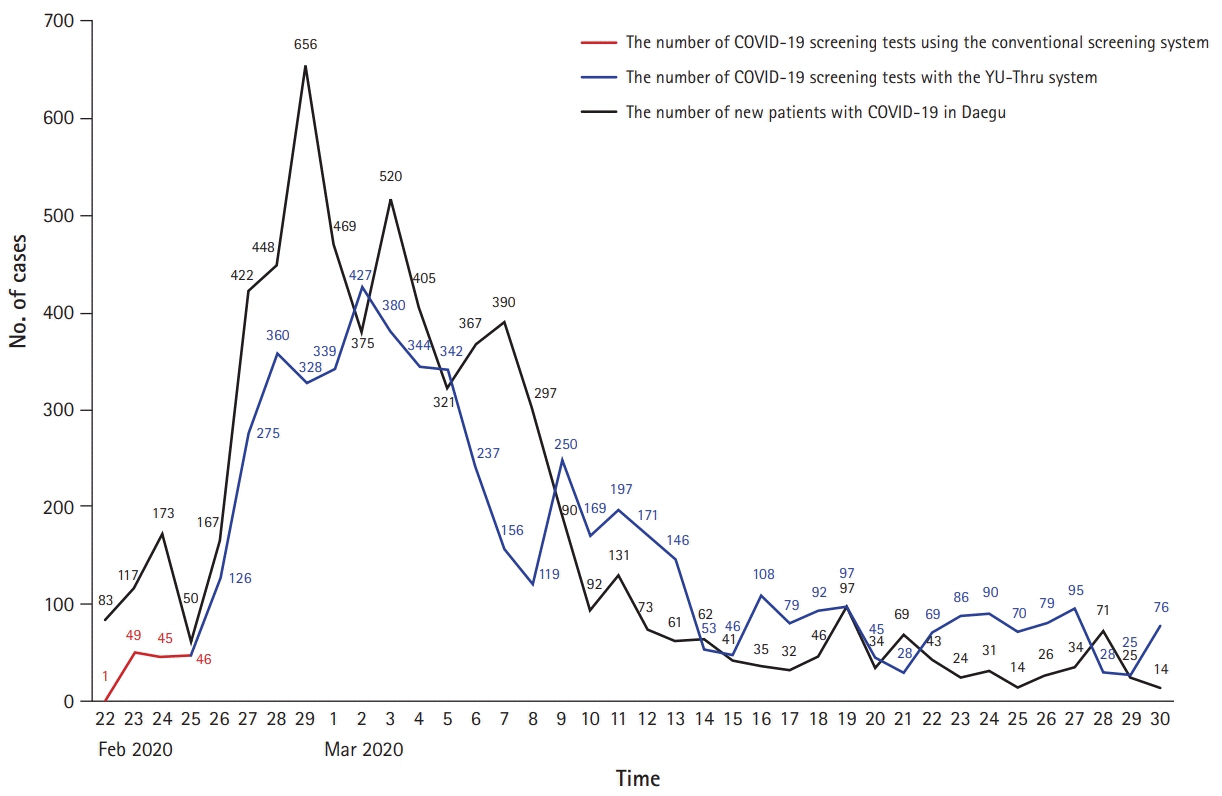
- Active and prompt scale-up screening tests are essential to efficiently control the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak. The goal of this work was to identify shortcomings in the conventional screening system (CSS) implemented in the beginning of the outbreak. To overcome these shortcomings, we then introduced a novel, independently developed system called the Yeungnam University type drive-through (YU-Thru), and distributed it nationwide in Korea. This system is similar to the drive-throughs utilized by fast food restaurants. YU-Thru system has shortened the time taken to test a single person to 2–4 minutes, by completely eliminating the time required to clean and ventilate the specimen collection room. This time requirement was a major drawback of the CSS. YU-Thru system also reduced the risk of subjects and medical staff infecting one another by using a separate and closed examination system. On average, 50 to 60 tests were conducted per day when using the CSS, while now up to 350 tests per day are conducted with the YU-Thru system. We believe that the YU-Thru system has made an important contribution to the rapid detection of COVID-19 in Daegu, South Korea. Here, we will describe the YU-Thru system in detail so that other countries experiencing COVID-19 outbreaks can take advantage of this system.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A study on the mental health of students at a medical school during COVID-19 outbreak: a retrospective study
Yu Ra Kim, Hye Jin Park, Bon-Hoon Koo, Ji Young Hwang, Young Hwan Lee
J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2022;39(4):314-321. doi: 10.12701/jyms.2022.00437.
Reference
-
References
1. Wang C, Horby PW, Hayden FG, Gao GF. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet. 2020; 395:470–3.
Article2. CoronaBoard. COVID-19 dashboard [Internet]. CoronaBoard;2020. [cited 2020 Jul 7]. https://coronaboard.kr/.3. Corona Virus Resource Center, Johns Hopkins University & Medicine. COVID-19 dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU) [Interent]. Baltimore (MD): Johns Hopkins University & Medicine;2020. [cited 2020 Jul 7]. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.4. World Health Organization Regional Office For Europe. WHO announces COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic [Internet]. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe;2020. [cited 2020 Jul 7]. http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/health-emergencies/coronavirus-covid-19/news/news/2020/3/who-announces-covid-19-outbreak-a-pandemic.5. Korean Society of Infectious Diseases; Korean Society of Pediatric Infectious Diseases; Korean Society of Epidemiology; Korean Society for Antimicrobial Therapy; Korean Society for Healthcare-associated Infection Control and Prevention; Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Report on the epidemiological features of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in the Republic of Korea from January 19 to March 2, 2020. J Korean Med Sci. 2020; 35:e112.6. Central Disaster Management Headquarters, Central Diease Control Headquarters. Guidance for operation of COVID-19 screening centers. Released on February 21, 2020. Sejong (KR): Ministry of Health and Welfare;2020.7. AccuWeather. Monthly weather forecast. February 2020 in Daegu, South Korea [Internet]. State College (PA): AccuWeather;2020. [cited 2020 Jul 7]. https://www.accuweather.com/en/kr/daegu/223347/february-weather/223347.8. Jung SM, Akhmetzhanov AR, Hayashi K, Linton NM, Yang Y, Yuan B, et al. Real-time estimation of the risk of death from novel coronavirus (COVID-19) infection: inference using exported cases. J Clin Med. 2020; 9:523.
Article9. Kohn WG, Collins AS, Cleveland JL, Harte JA, Eklund KJ, Malvitz DM, et al. Guidelines for infection control in dental health-care settings: 2003. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2003; 52(RP-17):1–61.10. Sophie Lewis. CBS News: South Korea is using fast food-style drive-thrus to test for coronavirus [Internet]. New York: CBS Interactive Inc;Mar. 6. 2020. [cited 2020 Jul 7]. https://www.cbsnews.com/news/coronavirus-south-korea-drive-thru-test-covid-19/.11. Reuters. South Korea runs ‘drive-thru’ virus testing in Daegu [Internet]. London: Reuters;March. 4. 2020. [cited 2020 Jul 7]. https://uk.reuters.com/video/watch/south-korea-runs-drive-thru-virus-testin-id689445178.12. Nikkei staff writers. Coronavirus: Week of Mar. 1 to Mar. 7, confirmed cases top 100,000 worldwide [Internet]. Tokyo: Nikkei Asian Review;March. 2. 2020. [cited 2020 Jul 7]. https://asia.nikkei.com/Spotlight/Coronavirus/Coronavirus-Free-to-read/Coronavirus-Week-of-Mar.-1-to-Mar.-7-confirmed-cases-top-100-000-worldwide.13. AFP. COVID-19: China reports fall in cases, South Korea death toll hits 32 [Internet]. Beijing: The Hindu;March. 4. 2020. [cited 2020 Jul 7]. https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/covid-19-china-reports-fall-in-cases-south-korea-death-toll-hits-32/article30978782.ece#.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Drive-Through Screening Center for COVID-19: a Safe and Efficient Screening System against Massive Community Outbreak
- Walk-Through Screening Center for COVID-19: an Accessible and Efficient Screening System in a Pandemic Situation
- Experience of Nurses Working at the Drive-Thru COVID-19 Screening Clinic
- The coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic and chronic diseases
- Advice on Standardized Diagnosis and Treatment for Spinal Diseases during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic