Yeungnam Univ J Med.
2020 Oct;37(4):253-261. 10.12701/yujm.2020.00584.
An update on the role of bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2508169
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00584
Abstract
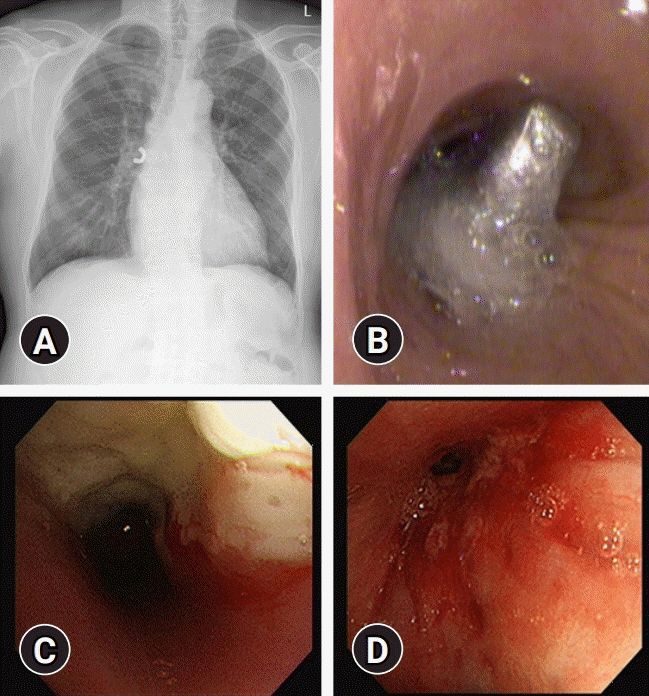
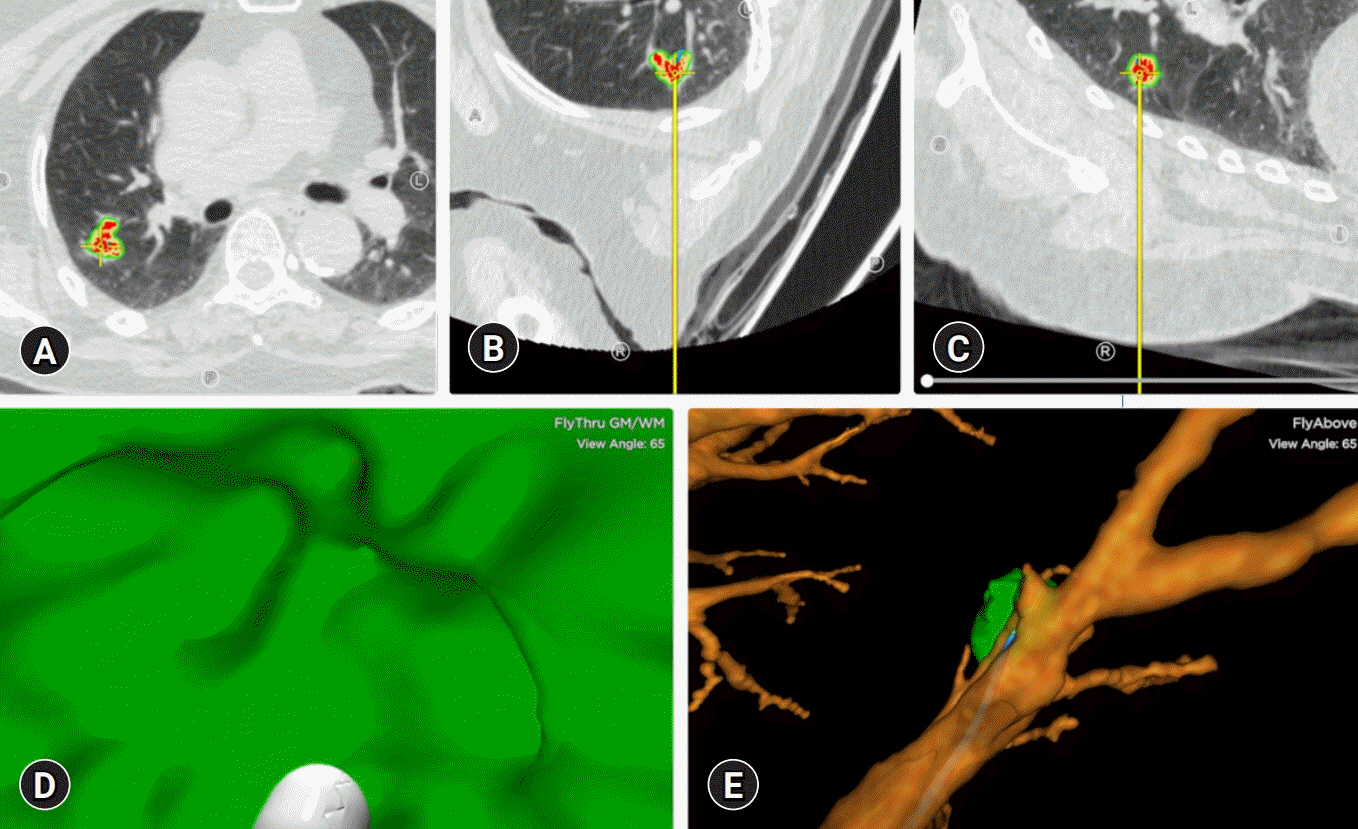
- Bronchoscopy has evolved over the past few decades and has been used by respiratory physicians to diagnose various airway and lung diseases. With the popularization of medical check-ups and growing interest in health, early diagnosis of lung diseases is essential. With the development of endobronchial ultrasound, ultrathin bronchoscopy, and electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy, bronchoscopy has been able to widen its scope in diagnosing pulmonary diseases. In this review, we have described the brief history, role, and complications of bronchoscopy used in diagnosing pulmonary lesions, from simple flexible bronchoscopy to bronchoscopy combined with several up-to-date technologies.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Utility of Radial Probe Endobronchial Ultrasound Guided Transbronchial Lung Biopsy in Bronchus Sign Negative Peripheral Pulmonary Lesions
Kyung Soo Hong, Kwan Ho Lee, Jin Hong Chung, Kyeong-Cheol Shin, Hyun Jung Jin, Jong Geol Jang, June Hong Ahn
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(24):e176. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e176.Advances in the science and treatment of respiratory diseases
Jin Hong Chung
Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):251-252. doi: 10.12701/yujm.2020.00661.
Reference
-
References
1. Panchabhai TS, Mehta AC. Historical perspectives of bronchoscopy: connecting the dots. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015; 12:631–41.
Article2. Silvestri GA, Gonzalez AV, Jantz MA, Margolis ML, Gould MK, Tanoue LT, et al. Methods for staging non-small cell lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013; 143(5 Suppl):e211S–e250S.3. Silvestri GA, Bevill BT, Huang J, Brooks M, Choi Y, Kennedy G, et al. An evaluation of diagnostic yield from bronchoscopy: the impact of clinical/radiographic factors, procedure type, and degree of suspicion for cancer. Chest. 2020; 157:1656–64.
Article4. Kurimoto N, Miyazawa T, Okimasa S, Maeda A, Oiwa H, Miyazu Y, et al. Endobronchial ultrasonography using a guide sheath increases the ability to diagnose peripheral pulmonary lesions endoscopically. Chest. 2004; 126:959–65.
Article5. Zhan P, Zhu QQ, Miu YY, Liu YF, Wang XX, Zhou ZJ, et al. Comparison between endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial biopsy and CT-guided transthoracic lung biopsy for the diagnosis of peripheral lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2017; 6:23–34.
Article6. Gupta AA, Sehgal IS, Dhooria S, Singh N, Aggarwal AN, Gupta D, et al. Indications for performing flexible bronchoscopy: trends over 34 years at a tertiary care hospital. Lung India. 2015; 32:211–5.
Article7. Du Rand IA, Blaikley J, Booton R, Chaudhuri N, Gupta V, Khalid S, et al. British Thoracic Society guideline for diagnostic flexible bronchoscopy in adults: accredited by NICE. Thorax. 2013; 68(Suppl 1):i1–44.
Article8. Bai C, Huang H, Yao X, Zhu S, Li B, Hang J, et al. Application of flexible bronchoscopy in inhalation lung injury. Diagn Pathol. 2013; 8:174.
Article9. Marek K, Piotr W, Stanisław S, Stefan G, Justyna G, Mariusz N, et al. Fibreoptic bronchoscopy in routine clinical practice in confirming the diagnosis and treatment of inhalation burns. Burns. 2007; 33:554–60.
Article10. Cha SI, Kim CH, Lee JH, Park JY, Jung TH, Choi WI, et al. Isolated smoke inhalation injuries: acute respiratory dysfunction, clinical outcomes, and short-term evolution of pulmonary functions with the effects of steroids. Burns. 2007; 33:200–8.
Article11. Cassada DC, Munyikwa MP, Moniz MP, Dieter RA Jr, Schuchmann GF, Enderson BL. Acute injuries of the trachea and major bronchi: importance of early diagnosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2000; 69:1563–7.
Article12. Chen CH, Lai CL, Tsai TT, Lee YC, Perng RP. Foreign body aspiration into the lower airway in Chinese adults. Chest. 1997; 112:129–33.
Article13. Dikensoy O, Usalan C, Filiz A. Foreign body aspiration: clinical utility of flexible bronchoscopy. Postgrad Med J. 2002; 78:399–403.
Article14. Rivera MP, Mehta AC, Wahidi MM. Establishing the diagnosis of lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013; 143(5 Suppl):e142S–e165S.15. Shure D, Fedullo PF. Transbronchial needle aspiration in the diagnosis of submucosal and peribronchial bronchogenic carcinoma. Chest. 1985; 88:49–51.
Article16. Andersen HA, Fontana RS. Transbronchoscopic lung biopsy for diffuse pulmonary diseases: technique and results in 450 cases. Chest. 1972; 62:125–8.
Article17. Thomson CC, Duggal A, Bice T, Lederer DJ, Wilson KC, Raghu G. 2018 Clinical practice guideline summary for clinicians: diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019; 16:285–90.18. Kebbe J, Abdo T. Interstitial lung disease: the diagnostic role of bronchoscopy. J Thorac Dis. 2017; 9(Suppl 10):S996–1010.
Article19. Sakr L, Dutau H. Massive hemoptysis: an update on the role of bronchoscopy in diagnosis and management. Respiration. 2010; 80:38–58.
Article20. Revel MP, Fournier LS, Hennebicque AS, Cuenod CA, Meyer G, Reynaud P, et al. Can CT replace bronchoscopy in the detection of the site and cause of bleeding in patients with large or massive hemoptysis? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002; 179:1217–24.
Article21. Khalil A, Soussan M, Mangiapan G, Fartoukh M, Parrot A, Carette MF. Utility of high-resolution chest CT scan in the emergency management of haemoptysis in the intensive care unit: severity, localization and aetiology. Br J Radiol. 2007; 80:21–5.
Article22. Gagnon S, Quigley N, Dutau H, Delage A, Fortin M. Approach to hemoptysis in the modern era. Can Respir J. 2017; 2017:1565030.
Article23. Pue CA, Pacht ER. Complications of fiberoptic bronchoscopy at a university hospital. Chest. 1995; 107:430–2.
Article24. Facciolongo N, Patelli M, Gasparini S, Lazzari Agli L, Salio M, Simonassi C, et al. Incidence of complications in bronchoscopy. Multicentre prospective study of 20,986 bronchoscopies. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2009; 71:8–14.
Article25. Um SW. The role of EBUS-TBNA in the diagnosis and staging of lung cancer. Hanyang Med Rev. 2014; 34:20–5.
Article26. Yasufuku K, Chiyo M, Sekine Y, Chhajed PN, Shibuya K, Iizasa T, et al. Real-time endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration of mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes. Chest. 2004; 126:122–8.
Article27. Hwangbo B, Lee HS, Lee GK, Lim KY, Lee SH, Kim HY, et al. Transoesophageal needle aspiration using a convex probe ultrasonic bronchoscope. Respirology. 2009; 14:843–9.
Article28. Hwangbo B, Lee GK, Lee HS, Lim KY, Lee SH, Kim HY, et al. Transbronchial and transesophageal fine-needle aspiration using an ultrasound bronchoscope in mediastinal staging of potentially operable lung cancer. Chest. 2010; 138:795–802.
Article29. Lee R, Cousins DJ, Ortiz-Zapater E, Breen R, McLean E, Santis G. Gene expression profiling of endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS)-derived cytological fine needle aspirates from hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes in non-small cell lung cancer. Cytopathology. 2013; 24:351–5.
Article30. Schmid-Bindert G, Wang Y, Jiang H, Sun H, Henzler T, Wang H, et al. EBUS-TBNA provides highest RNA yield for multiple biomarker testing from routinely obtained small biopsies in non-small cell lung cancer patients: a comparative study of three different minimal invasive sampling methods. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e77948.31. Goag EK, Lee JM, Chung KS, Kim SY, Leem AY, Song JH, et al. Usefulness of bronchoscopic rebiopsy of non-small cell lung cancer with acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor. J Cancer. 2018; 9:1113–20.
Article32. Izumo T, Matsumoto Y, Chavez C, Tsuchida T. Re-biopsy by endobronchial ultrasound procedures for mutation analysis of non-small cell lung cancer after EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment. BMC Pulm Med. 2016; 16:106.
Article33. Lee HS, Lee GK, Lee HS, Kim MS, Lee JM, Kim HY, et al. Real-time endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in mediastinal staging of non-small cell lung cancer: how many aspirations per target lymph node station? Chest. 2008; 134:368–74.
Article34. Wahidi MM, Herth F, Yasufuku K, Shepherd RW, Yarmus L, Chawla M, et al. Technical aspects of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest. 2016; 149:816–35.
Article35. Tournoy KG, Rintoul RC, van Meerbeeck JP, Carroll NR, Praet M, Buttery RC, et al. EBUS-TBNA for the diagnosis of central parenchymal lung lesions not visible at routine bronchoscopy. Lung Cancer. 2009; 63:45–9.
Article36. Nakajima T, Yasufuku K, Fujiwara T, Chiyo M, Sekine Y, Shibuya K, et al. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for the diagnosis of intrapulmonary lesions. J Thorac Oncol. 2008; 3:985–8.
Article37. Kuijvenhoven JC, Leoncini F, Crombag LC, Spijker R, Bonta PI, Korevaar DA, et al. Endobronchial ultrasound for the diagnosis of centrally located lung tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Respiration. 2020; 99:441–50.
Article38. Labarca G, Sierra-Ruiz M, Kheir F, Folch E, Majid A, Mehta HJ, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of endobronchial ultrasound transbronchial needle aspiration in lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019; 16:1432–9.
Article39. Agarwal R, Srinivasan A, Aggarwal AN, Gupta D. Efficacy and safety of convex probe EBUS-TBNA in sarcoidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir Med. 2012; 106:883–92.
Article40. Ye W, Zhang R, Xu X, Liu Y, Ying K. Diagnostic efficacy and safety of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in intrathoracic tuberculosis: a meta-analysis. J Ultrasound Med. 2015; 34:1645–50.41. Asano F, Aoe M, Ohsaki Y, Okada Y, Sasada S, Sato S, et al. Complications associated with endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration: a nationwide survey by the Japan Society for Respiratory Endoscopy. Respir Res. 2013; 14:50.
Article42. Dhooria S, Sehgal IS, Gupta N, Aggarwal AN, Behera D, Agarwal R. Diagnostic yield and complications of EBUS-TBNA performed under bronchoscopist-directed conscious sedation: single center experience of 1004 subjects. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol. 2017; 24:7–14.
Article43. Caglayan B, Yilmaz A, Bilaceroglu S, Comert SS, Demirci NY, Salepci B. Complications of convex-probe endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration: a multi-center retrospective study. Respir Care. 2016; 61:243–8.
Article44. Hurter T, Hanrath P. Endobronchial sonography: feasibility and preliminary results. Thorax. 1992; 47:565–7.
Article45. Kurimoto N, Murayama M, Yoshioka S, Nishisaka T. Analysis of the internal structure of peripheral pulmonary lesions using endobronchial ultrasonography. Chest. 2002; 122:1887–94.
Article46. Kikuchi E, Yamazaki K, Sukoh N, Kikuchi J, Asahina H, Imura M, et al. Endobronchial ultrasonography with guide-sheath for peripheral pulmonary lesions. Eur Respir J. 2004; 24:533–7.
Article47. Chavez C, Sasada S, Izumo T, Watanabe J, Katsurada M, Matsumoto Y, et al. Endobronchial ultrasound with a guide sheath for small malignant pulmonary nodules: a retrospective comparison between central and peripheral locations. J Thorac Dis. 2015; 7:596–602.48. Tamiya M, Okamoto N, Sasada S, Shiroyama T, Morishita N, Suzuki H, et al. Diagnostic yield of combined bronchoscopy and endobronchial ultrasonography, under LungPoint guidance for small peripheral pulmonary lesions. Respirology. 2013; 18:834–9.
Article49. Yamada N, Yamazaki K, Kurimoto N, Asahina H, Kikuchi E, Shinagawa N, et al. Factors related to diagnostic yield of transbronchial biopsy using endobronchial ultrasonography with a guide sheath in small peripheral pulmonary lesions. Chest. 2007; 132:603–8.
Article50. Moon SM, Choe J, Jeong BH, Um SW, Kim H, Kwon OJ, et al. Diagnostic performance of radial probe endobronchial ultrasound without a guide-sheath and the feasibility of molecular analysis. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2019; 82:319–27.
Article51. Yu KL, Tsai TH, Ho CC, Liao WY, Lin CK, Hsu CL, et al. The value of radial endobronchial ultrasound-guided bronchial brushing in peripheral non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:5837.
Article52. Good WR, Christensen PM, Herath S, Dawkins P, Yap E. Radial-probe endobronchial ultrasound outcomes in the investigation of peripheral pulmonary lesions: a New Zealand perspective. Intern Med J. 2018; 48:1481–7.
Article53. Izumo T, Sasada S, Chavez C, Tsuchida T. The diagnostic utility of endobronchial ultrasonography with a guide sheath and tomosynthesis images for ground glass opacity pulmonary lesions. J Thorac Dis. 2013; 5:745–50.54. Izumo T, Sasada S, Chavez C, Matsumoto Y, Tsuchida T. Radial endobronchial ultrasound images for ground-glass opacity pulmonary lesions. Eur Respir J. 2015; 45:1661–8.
Article55. Kim EJ, Kim KC. Utility of radial probe endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial lung biopsy in diffuse lung lesions. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2019; 82:201–10.
Article56. Han Y, Kim HJ, Kong KA, Kim SJ, Lee SH, Ryu YJ, et al. Diagnosis of small pulmonary lesions by transbronchial lung biopsy with radial endobronchial ultrasound and virtual bronchoscopic navigation versus CT-guided transthoracic needle biopsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2018; 13:e0191590.
Article57. Ahn JH, Jang JG. Initial experience in CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of lung lesions performed by a pulmonologist. J Clin Med. 2019; 8:821.
Article58. Zhang L, Wu H, Wang G. Endobronchial ultrasonography using a guide sheath technique for diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary lesions. Endosc Ultrasound. 2017; 6:292–9.
Article59. Steinfort DP, Khor YH, Manser RL, Irving LB. Radial probe endobronchial ultrasound for the diagnosis of peripheral lung cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J. 2011; 37:902–10.
Article60. Shinagawa N. A review of existing and new methods of bronchoscopic diagnosis of lung cancer. Respir Investig. 2019; 57:3–8.
Article61. Hasegawa S, Hitomi S, Murakawa M, Mori K. Development of an ultrathin fiberscope with a built-in channel for bronchoscopy in infants. Chest. 1996; 110:1543–6.
Article62. Oki M, Saka H, Kitagawa C, Tanaka S, Shimokata T, Mori K, et al. Novel thin bronchoscope with a 1.7-mm working channel for peripheral pulmonary lesions. Eur Respir J. 2008; 32:465–71.
Article63. Yamamoto S, Ueno K, Imamura F, Matsuoka H, Nagatomo I, Omiya Y, et al. Usefulness of ultrathin bronchoscopy in diagnosis of lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2004; 46:43–8.
Article64. Oki M, Saka H, Ando M, Asano F, Kurimoto N, Morita K, et al. Ultrathin bronchoscopy with multimodal devices for peripheral pulmonary lesions: a randomized trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015; 192:468–76.
Article65. Schwarz Y, Greif J, Becker HD, Ernst A, Mehta A. Real-time electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy to peripheral lung lesions using overlaid CT images: the first human study. Chest. 2006; 129:988–94.
Article66. Dhillon SS, Harris K. Bronchoscopy for the diagnosis of peripheral lung lesions. J Thorac Dis. 2017; 9(Suppl 10):S1047–58.
Article67. Zhang W, Chen S, Dong X, Lei P. Meta-analysis of the diagnostic yield and safety of electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy for lung nodules. J Thorac Dis. 2015; 7:799–809.68. Folch EE, Pritchett MA, Nead MA, Bowling MR, Murgu SD, Krimsky WS, et al. Electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy for peripheral pulmonary lesions: one-year results of the prospective, multicenter NAVIGATE study. J Thorac Oncol. 2019; 14:445–58.69. Eberhardt R, Anantham D, Ernst A, Feller-Kopman D, Herth F. Multimodality bronchoscopic diagnosis of peripheral lung lesions: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007; 176:36–41.
Article70. Mahajan AK, Patel S, Hogarth DK, Wightman R. Electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy: an effective and safe approach to diagnose peripheral lung lesions unreachable by conventional bronchoscopy in high-risk patients. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol. 2011; 18:133–7.71. Ganganah O, Guo SL, Chiniah M, Li YS. Efficacy and safety of cryobiopsy versus forceps biopsy for interstitial lung diseases and lung tumours: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Respirology. 2016; 21:834–41.
Article72. Johannson KA, Marcoux VS, Ronksley PE, Ryerson CJ. Diagnostic yield and complications of transbronchial lung cryobiopsy for interstitial lung disease: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016; 13:1828–38.
Article73. Schuhmann M, Bostanci K, Bugalho A, Warth A, Schnabel PA, Herth FJ, et al. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided cryobiopsies in peripheral pulmonary lesions: a feasibility study. Eur Respir J. 2014; 43:233–9.
Article74. Dhooria S, Sehgal IS, Aggarwal AN, Behera D, Agarwal R. Diagnostic yield and safety of cryoprobe transbronchial lung biopsy in diffuse parenchymal lung diseases: systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir Care. 2016; 61:700–12.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Respiratory Review of 2012: Bronchoscopic Innovations and Advances
- Comparison of Induced Sputum and Bronchoscopy in Diagnosis of Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- The Role of Bronchoscopy for the Staging in Patient with Peripheral Lung Cancer
- The Value of Routinely Culturing for Tuberculosis During Bronchoscopies in an Intermediate Tuberculosis-Burden Country
- Advanced Bronchoscopic Diagnostic Techniques in Lung Cancer