Cancer Res Treat.
2020 Oct;52(4):1103-1111. 10.4143/crt.2020.337.
Challenge for Diagnostic Assessment of Deep Learning Algorithm for Metastases Classification in Sentinel Lymph Nodes on Frozen Tissue Section Digital Slides in Women with Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Engineering, Asan Institute of Life Science, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Hospital Pathology, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 3Health Innovation Big Data Center, Asan Institute for Life Science, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Convergence Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 6KakaoBrain-BrainCloud Team, Seongnam, Korea
- 7Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Ulsan, Korea
- 8Image Laboratory, School of Computer Science and Engineering, ChungAng University, Seoul, Korea
- 9DoAI Inc., Seoul, Korea
- 10Department of Business Management and Convergence Software, Sogang University, Seoul, Korea
- 11Data Science & Business Analytics Lab, School of Industrial Management Engineering, College of Engineering, Korea University, Seoul, Korea
- 12Software Graduate Program, School of Computing, College of Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul, Korea
- 13Department of Biomedical Engineering, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
- 14Department of Social Studies Education, College of Education, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 15Department of Math, University of Kwangwoon, Seoul, Korea
- 16Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
- 17Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine and SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 18Department of Biostatistics, Seoul National University College of Medicine and SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 19Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2507936
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2020.337
Abstract
- Purpose
Assessing the status of metastasis in sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs) by pathologists is an essential task for the accurate staging of breast cancer. However, histopathological evaluation of sentinel lymph nodes by a pathologist is not easy and is a tedious and time-consuming task. The purpose of this study is to review a challenge competition (HeLP 2018) to develop automated solutions for the classification of metastases in hematoxylin and eosin–stained frozen tissue sections of SLNs in breast cancer patients.
Materials and Methods
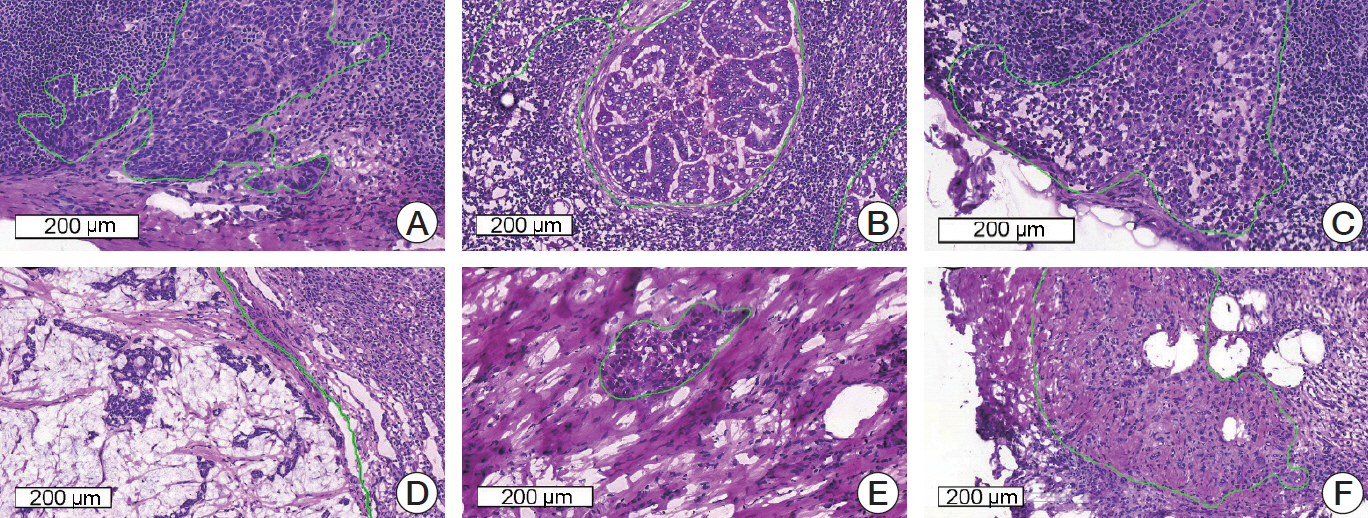
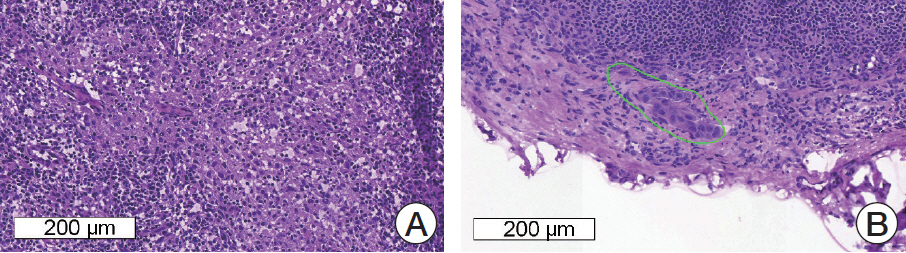
A total of 297 digital slides were obtained from frozen SLN sections, which include post–neoadjuvant cases (n = 144, 48.5%) in Asan Medical Center, South Korea. The slides were divided into training, development, and validation sets. All of the imaging datasets have been manually segmented by expert pathologists. A total of 10 participants were allowed to use the Kakao challenge platform for six weeks with two P40 GPUs. The algorithms were assessed in terms of the AUC (area under receiver operating characteristic curve).
Results
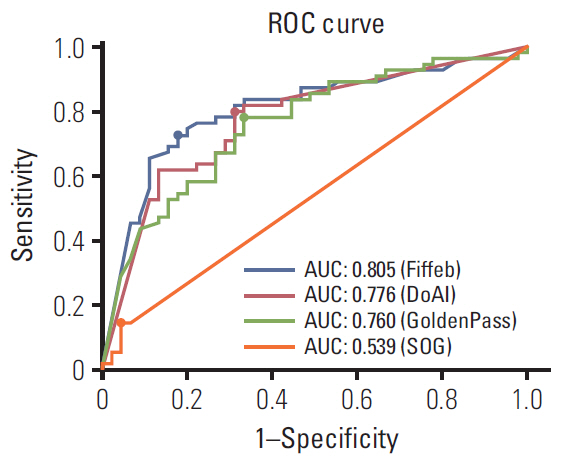
The top three teams showed 0.986, 0.985, and 0.945 AUCs for the development set and 0.805, 0.776, and 0.765 AUCs for the validation set. Micrometastatic tumors, neoadjuvant systemic therapy, invasive lobular carcinoma, and histologic grade 3 were associated with lower diagnostic accuracy.
Conclusion
In a challenge competition, accurate deep learning algorithms have been developed, which can be helpful in making frozen diagnosis of intraoperative sentinel lymph node biopsy. Whether this approach has clinical utility will require evaluation in a clinical setting
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Diagnostic Assessment of Deep Learning Algorithms for Frozen Tissue Section Analysis in Women with Breast Cancer
Young-Gon Kim, In Hye Song, Seung Yeon Cho, Sungchul Kim, Milim Kim, Soomin Ahn, Hyunna Lee, Dong Hyun Yang, Namkug Kim, Sungwan Kim, Taewoo Kim, Daeyoung Kim, Jonghyeon Choi, Ki-Sun Lee, Minuk Ma, Minki Jo, So Yeon Park, Gyungyub Gong
Cancer Res Treat. 2023;55(2):513-522. doi: 10.4143/crt.2022.055.
Reference
-
References
1. Williams BJ, Bottoms D, Treanor D. Future-proofing pathology: the case for clinical adoption of digital pathology. J Clin Pathol. 2017; 70:1010–8.
Article2. Wang S, Chen A, Yang L, Cai L, Xie Y, Fujimoto J, et al. Comprehensive analysis of lung cancer pathology images to discover tumor shape and boundary features that predict survival outcome. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:10393.
Article3. Litjens G, Sanchez CI, Timofeeva N, Hermsen M, Nagtegaal I, Kovacs I, et al. Deep learning as a tool for increased accuracy and efficiency of histopathological diagnosis. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:26286.
Article4. Ehteshami Bejnordi B, Veta M, Johannes van Diest P, van Ginneken B, Karssemeijer N, Litjens G, et al. Diagnostic assessment of deep learning algorithms for detection of lymph node metastases in women with breast cancer. JAMA. 2017; 318:2199–210.
Article5. Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J. Harrison’s principles of internal medicine. 19th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;2015.6. Hayes SC, Janda M, Cornish B, Battistutta D, Newman B. Lymphedema after breast cancer: incidence, risk factors, and effect on upper body function. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:3536–42.
Article7. Fleissig A, Fallowfield LJ, Langridge CI, Johnson L, Newcombe RG, Dixon JM, et al. Post-operative arm morbidity and quality of life: results of the ALMANAC randomised trial comparing sentinel node biopsy with standard axillary treatment in the management of patients with early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006; 95:279–93.
Article8. Lyman GH, Temin S, Edge SB, Newman LA, Turner RR, Weaver DL, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy for patients with early-stage breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2014; 32:1365–83.
Article9. Manca G, Rubello D, Tardelli E, Giammarile F, Mazzarri S, Boni G, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer: indications, contraindications, and controversies. Clin Nucl Med. 2016; 41:126–33.10. Galimberti V, Cole BF, Viale G, Veronesi P, Vicini E, Intra M, et al. Axillary dissection versus no axillary dissection in patients with breast cancer and sentinel-node micrometastases (IBCSG 23-01): 10-year follow-up of a randomised, controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018; 19:1385–93.11. Giuliano AE, Ballman KV, McCall L, Beitsch PD, Brennan MB, Kelemen PR, et al. Effect of axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection on 10-year overall survival among women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: the ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017; 318:918–26.12. Wang J, Tang H, Li X, Song C, Xiong Z, Wang X, et al. Is surgical axillary staging necessary in women with T1 breast cancer who are treated with breast-conserving therapy? Cancer Commun (Lond). 2019; 39:25.
Article13. Donker M, van Tienhoven G, Straver ME, Meijnen P, van de Velde CJ, Mansel RE, et al. Radiotherapy or surgery of the axilla after a positive sentinel node in breast cancer (EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014; 15:1303–10.
Article14. Celebioglu F, Sylvan M, Perbeck L, Bergkvist L, Frisell J. Intraoperative sentinel lymph node examination by frozen section, immunohistochemistry and imprint cytology during breast surgery: a prospective study. Eur J Cancer. 2006; 42:617–20.15. Chen Y, Anderson KR, Xu J, Goldsmith JD, Heher YK. Frozen-section checklist implementation improves quality and patient safety. Am J Clin Pathol. 2019; 151:607–12.
Article16. Bandi P, Geessink O, Manson Q, Van Dijk M, Balkenhol M, Hermsen M, et al. From detection of individual metastases to classification of lymph node status at the patient level: the CAMELYON17 challenge. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2019; 38:550–60.
Article17. Honkoop AH, Pinedo HM, De Jong JS, Verheul HM, Linn SC, Hoekman K, et al. Effects of chemotherapy on pathologic and biologic characteristics of locally advanced breast cancer. Am J Clin Pathol. 1997; 107:211–8.
Article18. Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, Shlens J, Wojna Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In : 2016 Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2016 Jun 27-30; Las Vegas, NV, USA.
Article19. Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In : International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI); 2015 Oct 5-9; Munich, Germany. Cham: Springer;2015. p. 234–41.
Article20. Liaw A, Wiener M. Classification and regression by random forest. R News. 2002; 2:18–22.21. Youden WJ. Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer. 1950; 3:32–5.
Article22. Laurent-Bellue A, Poullier E, Pomerol JF, Adnet E, Redon MJ, Posseme K, et al. Four-year experience of digital slide telepathology for intraoperative frozen section consultations in a two-site French academic department of pathology. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020; 154:414–23.
Article23. Menter T, Nicolet S, Baumhoer D, Tolnay M, Tzankov A. Intraoperative frozen section consultation by remote whole-slide imaging analysis: validation and comparison to robotic remote microscopy. J Clin Pathol. 2020; 73:350–2.
Article24. Akay CL, Albarracin C, Torstenson T, Bassett R, Mittendorf EA, Yi M, et al. Factors impacting the accuracy of intra-operative evaluation of sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer. Breast J. 2018; 24:28–34.
Article25. Houpu Y, Fei X, Yang Y, Fuzhong T, Peng L, Bo Z, et al. Use of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center nomogram to guide intraoperative sentinel lymph node frozen sections in patients with early breast cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2019; 120:587–92.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnostic Assessment of Deep Learning Algorithms for Frozen Tissue Section Analysis in Women with Breast Cancer
- Short Term Follow-up Data in Breast Cancer Patients with Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Alone
- The Number of Removed Lymph Nodes for an Acceptable False Negative Rate in Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Breast Cancer
- Optimized Criteria for Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Patients with Clinically Node Negative Breast Cancer
- Sentinel Lymph Node in Breast Cancer: Review Article from a Pathologist's Point of View