Anat Cell Biol.
2020 Sep;53(3):252-260. 10.5115/acb.20.079.
An anatomical study on locations of the mandibular foramen and the accessory mandibular foramen in the mandible and their clinical implication in a Thai population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Medical Student, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
- 2Department of Oral Biology and Diagnostic Sciences, Faculty of Dentistry, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
- 3Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
- 4Excellence in Osteology Research and Training Center (ORTC), Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
- KMID: 2507637
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.20.079
Abstract
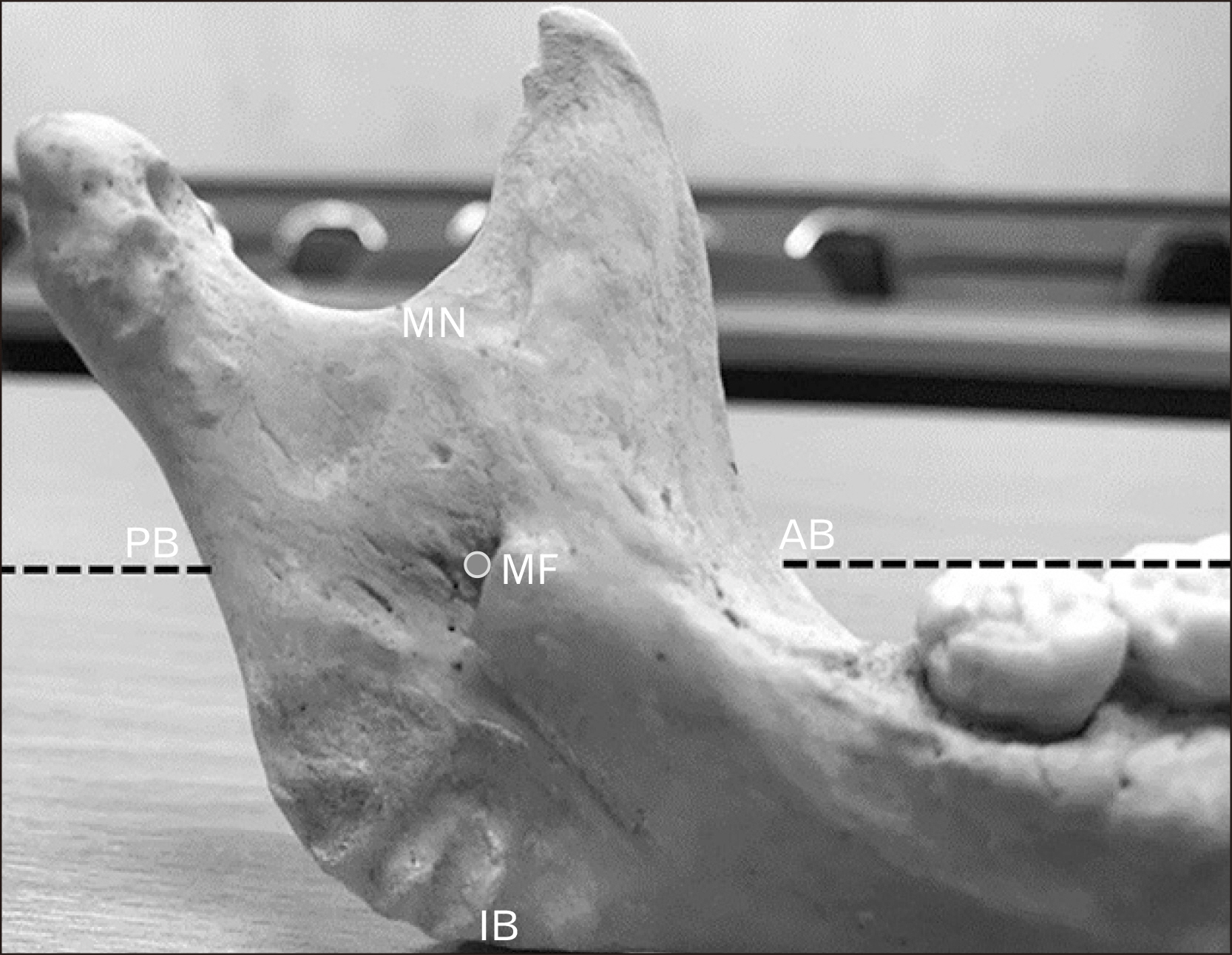
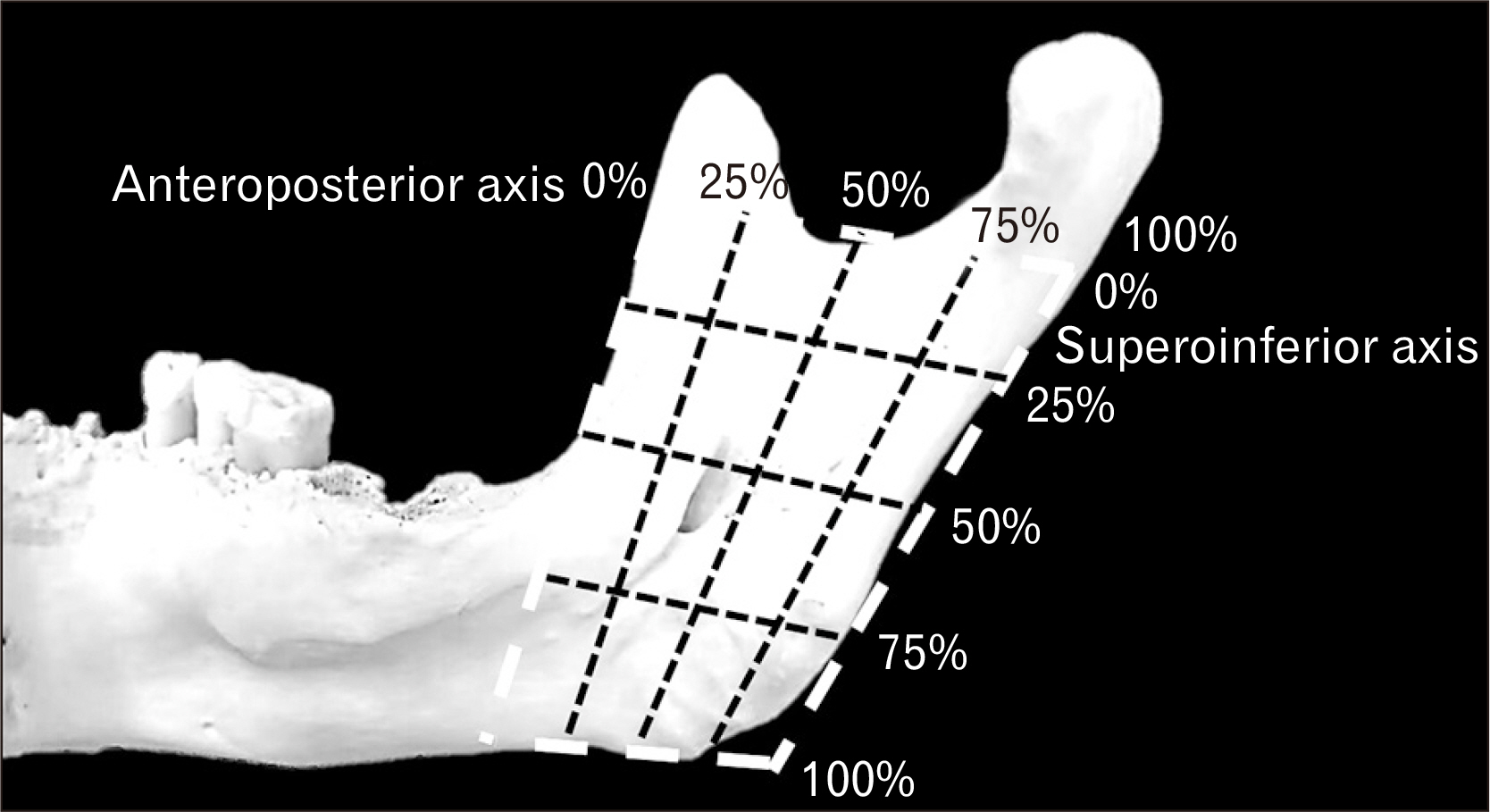
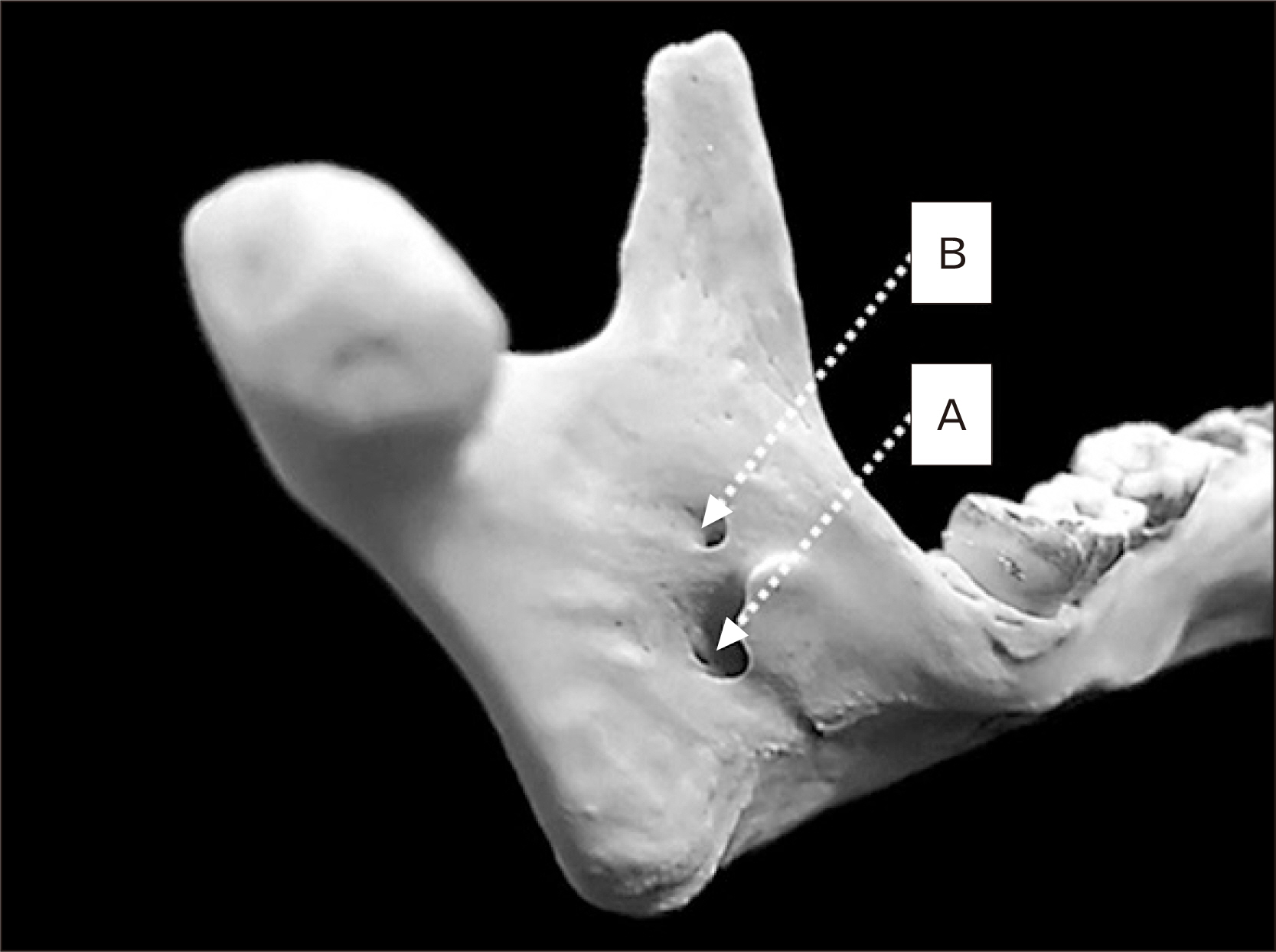
- Mandibular foramen (MF) is a structure that inferior alveolar nerve and artery pass through itself which is found on the mandible. The objective of this research aims to locate MF among the Thai population including other MF characteristics. The sampling is conducted in the Thai population of the total number of 220 samples from the Forensic Osteology Research Center, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University. The MF anteroposterior and superoinferior localizations are similar in both sex which at Q3 of right anteroposterior, Q2 of left anteroposterior and Q2 of left and right superoinferior axis. Otherwise, the prevalence of accessory MF has in 68 samples which are 30.89%. The prevalence of unilateral single accessory MF is 20.45%, bilateral single accessory MF is 6.36%, unilateral double accessory MF is 2.27% and bilateral double accessory MF is 0.45%. This present research results that the Thai population has a difference in MF location while comparing to other populations. Moreover, Thai MF and accessory MF location and localization will be helpful to clinical implications.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Drake RL, Vogl AW, Mitchell AWM. 2010. Gray's anatomy for students. 2nd ed. Elsevier;Philadelphia:2. Khoury J, Townsend G. 2011; Neural blockade anaesthesia of the mandibular nerve and its terminal branches: rationale for different anaesthetic techniques including their advantages and disadvantages. Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2011:307423. DOI: 10.1155/2011/307423. PMID: 21716730. PMCID: PMC3119427.
Article3. Rao TR, Chitturi RT, Sudhiksha S, Rao SR. 2017; Presence of accessory mandibular foramina and their clinical implications. Case Stud J. 6:14–7. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-019-02197-9. PMID: 30701271.4. Gupta S, Soni A, Singh P. 2013; Morphological study of accessory foramina in mandible and its clinical implication. Indian J Oral Sci. 4:12. DOI: 10.4103/0976-6944.118512. PMID: 20499031. PMCID: PMC6251292.
Article5. Shalini R, RaviVarman C, Manoranjitham R, Veeramuthu M. 2016; Morphometric study on mandibular foramen and incidence of accessory mandibular foramen in mandibles of south Indian population and its clinical implications in inferior alveolar nerve block. Anat Cell Biol. 49:241. DOI: 10.5115/acb.2016.49.4.241. PMID: 28127498.
Article6. Khalil H. 2014; A basic review on the inferior alveolar nerve block techniques. Anesth Essays Res. 8:3. DOI: 10.4103/0259-1162.128891. PMID: 25886095. PMCID: PMC4173572.
Article7. Sella-Tunis T, Pokhojaev A, Sarig R, O'Higgins P, May H. 2018; Human mandibular shape is associated with masticatory muscle force. Sci Rep. 8:6042. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-24293-3. PMID: 29662127. PMCID: PMC5902585.
Article8. Rispoli DZ, Camargo PM, Fonseca VR, Mandelli KK, Pereira MAC. 2008; Benign masseter muscle hypertrophy. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 74:790–3. DOI: 10.1016/S1808-8694(15)31393-8. PMID: 30890839. PMCID: PMC7424172.
Article9. Simione M, Loret C, Le Révérend B, Richburg B, Del Valle M, Adler M, Moser M, Green JR. 2018; Differing structural properties of foods affect the development of mandibular control and muscle coordination in infants and young children. Physiol Behav. 186:62–72. DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2018.01.009. PMID: 29343459. PMCID: PMC6052439.
Article10. Ennes JP, de Medeiros RM. 2009; Localization of mandibular foramen and clinical implications. Int J Morphol. 27:1305–11. DOI: 10.4067/S0717-95022009000400053. PMID: 32727955.
Article11. Oguz O, Bozkir MG. 2002; Evaluation of location of mandibular and mental foramina in dry, young, adult human male, dentulous mandibles. West Indian Med J. 51:14. PMID: 12089867.12. Padmavathi G, Tiwari S, Varalakshmi KL, Roopashree R. 2014; An anatomical study of mandibular and accessory mandibular foramen in dry adult human mandibles of South Indian origin. IOSR J Dent Med Sci. 13:83–8. DOI: 10.9790/0853-13428388. PMID: 23059593.13. Galdames ICS, Matamala DAZ, Smith RL. 2009; Is the conduct of Serres an anatomical variation in adults? Int J Morphol. 27:43–7. DOI: 10.4067/S0717-95022009000100008.
Article14. Lima FJC, Oliveira Neto OB, Barbosa FT, Dantas LCS, Olave E, Sousa-Rodrigues CF. 2016; Occurrence of the accessory foramina of the mandibular ramus in Brazilian adults and its relation to important mandibular landmarks. Int J Morphol. 34:330–4. DOI: 10.4067/S0717-95022016000100047.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Morphometric study on mandibular foramen and incidence of accessory mandibular foramen in mandibles of south Indian population and its clinical implications in inferior alveolar nerve block
- Unusual Course of the Accessory Meningeal Artery
- Anatomical Study on the Location of the Mental Foramen in Adult Korean Mandibles
- Radiologic study of mandibular foramen of mandibular prognathism by three-dimensional computed tomography
- A Comparative Study On The Location Of The Mandibular Foramen In Panoramic Radiographs Of Normal Occlusion and Mandibular Prognathism