J Korean Med Sci.
2020 Oct;35(40):e340. 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e340.
Mortality Rate and Major Causes of Death by Gestational Age in Korean Children under 5 Years of Age
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Konyang University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea
- KMID: 2507617
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e340
Abstract
- Background
Preterm birth is associated with increased infant mortality. However, it is not clear whether prematurity is associated with mortality after 1 year of age. There is a lack of research on mortality rate and causes of death after infancy in preterm babies in Korea. We aimed to analyze the mortality rates and causes of deaths up to 5 years of age in Korea.
Methods
Using the Microdata Integrated Service of Statistics Korea database, this retrospective cohort study screened infants born between 2010 and 2012. After applying the exclusion criteria, 1,422,913 live births were classified into the following groups by gestational age: those born at < 32 weeks' gestation (n = 10,411), those born between 32 and 36 weeks' gestation (n = 75,657), and those born at ≥ 37 weeks' gestation (n = 1,336,845). The association of gestational age with mortality in infancy (< 1 year of age) and childhood (1–5 years of age) was analyzed, with and without covariates. The major causes of death in infancy and childhood were analyzed by gestational age.
Results
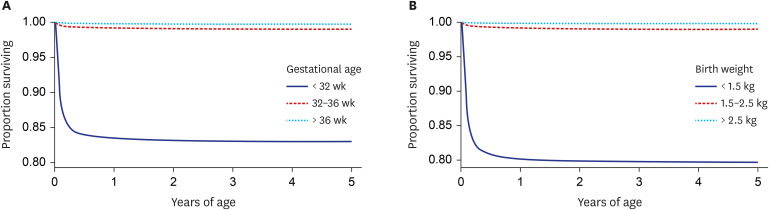
Overall, 4,930 (0.3%) children died between birth and 5 years of age, with 19.1% of these deaths occurring after infancy. Adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) for infant death were 78.79 (95% confidence interval [CI], 71.33–87.04) and 4.62 (95% CI, 4.07–5.24) for the < 32 and 32–36 weeks groups, respectively, compared to the full-term group; the adjusted HRs for deaths occurring at ages 1–5 years were 9.25 (95% CI, 6.85–12.50) and 2.42 (95% CI, 1.95–3.01), respectively. In infancy, conditions originating in the perinatal period were the most common cause of deaths in the < 32 and 32–36 weeks groups (88.7% and 41.9%, respectively). Contrarily, in the ≥ 37 weeks group, conditions originating in the perinatal period explained 22.7% of infant deaths, with congenital malformations primarily accounting for 29.6% of these deaths. The most common cause of death in children (after infancy) in the < 32 weeks group was perinatal causes (25.0%); in the 32–36 weeks group, congenital malformation and nervous system disease were the common causes (21.7% and 19.1%, respectively). In the ≥ 37 weeks group, injury, poisoning, and other consequences of external causes explained 26.6% of childhood deaths, followed by neoplasms and nervous system disease (15.7% and 14.7%, respectively).
Conclusion
Low gestational age is associated with not only infant mortality but also child mortality. The major causes of death differed by gestational age in infancy and childhood. For the care of preterm infants, especially those born at < 32 weeks' gestation, particular attention and continuous monitoring are needed in consideration of the major causes of deaths until 5 years of age.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fanaroff AA, Stoll BJ, Wright LL, Carlo WA, Ehrenkranz RA, Stark AR, et al. Trends in neonatal morbidity and mortality for very low birthweight infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007; 196(2):147.e1–147.e8. PMID: 17306659.
Article2. Callaghan WM, MacDorman MF, Rasmussen SA, Qin C, Lackritz EM. The contribution of preterm birth to infant mortality rates in the United States. Pediatrics. 2006; 118(4):1566–1573. PMID: 17015548.
Article3. Kramer MS, Demissie K, Yang H, Platt RW, Sauvé R, Liston R, et al. The contribution of mild and moderate preterm birth to infant mortality. JAMA. 2000; 284(7):843–849. PMID: 10938173.
Article4. Doyle LW, Roberts G, Anderson PJ. Victorian Infant Collaborative Study Group. Changing long-term outcomes for infants 500–999 g birth weight in Victoria, 1979–2005. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2011; 96(6):F443–7. PMID: 21393312.
Article5. Power C, Li L. Cohort study of birthweight, mortality, and disability. BMJ. 2000; 320(7238):840–841. PMID: 10731178.
Article6. Kajantie E, Osmond C, Barker DJ, Forsén T, Phillips DIW, Eriksson JG. Size at birth as a predictor of mortality in adulthood: a follow-up of 350 000 person-years. Int J Epidemiol. 2005; 34(3):655–663. PMID: 15764690.
Article7. Swamy GK, Ostbye T, Skjaerven R. Association of preterm birth with long-term survival, reproduction, and next-generation preterm birth. JAMA. 2008; 299(12):1429–1436. PMID: 18364485.
Article8. Watkins WJ, Kotecha SJ, Kotecha S. All-cause mortality of low birthweight infants in infancy, childhood, and adolescence: population study of England and Wales. PLoS Med. 2016; 13(5):e1002018. PMID: 27163787.
Article9. Liu L, Oza S, Hogan D, Chu Y, Perin J, Zhu J, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of under-5 mortality in 2000–15: an updated systematic analysis with implications for the sustainable development goals. Lancet. 2016; 388(10063):3027–3035. PMID: 27839855.
Article10. Korean Statistical Information Service. Birth statistics. Updated 2018. Accessed May 21, 2018. http://www.kosis.kr.11. Statistics Korea. Korean Standard Classification of Diseases. Updated 2016. Accessed January 5, 2019. http://kssc.kostat.go.kr/ksscNew_web/index.jsp#.12. Statistics Korea. Microdata Integrated Service. Updated 2019. Accessed January 5, 2019. https://mdis.kostat.go.kr.13. García-Basteiro AL, Quintó L, Macete E, Bardají A, González R, Nhacolo A, et al. Infant mortality and morbidity associated with preterm and small-for-gestational-age births in Southern Mozambique: a retrospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2017; 12(2):e0172533. PMID: 28212393.
Article14. Horta BL, Gigante DP, Candiota JS, Barros FC, Victora CG. Monitoring mortality in Pelotas birth cohort from 1982 to 2006, Southern Brazil. Rev Saude Publica. 2008; 42(Suppl 2):108–114.15. Mourani PM, Sontag MK, Younoszai A, Miller JI, Kinsella JP, Baker CD, et al. Early pulmonary vascular disease in preterm infants at risk for bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015; 191(1):87–95. PMID: 25389562.
Article16. Mirza H, Ziegler J, Ford S, Padbury J, Tucker R, Laptook A. Pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants: prevalence and association with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 2014; 165(5):909–914.e1. PMID: 25189821.
Article17. Berenz A, Vergales JE, Swanson JR, Sinkin RA. Evidence of early pulmonary hypertension is associated with increased mortality in very low birth weight infants. Am J Perinatol. 2017; 34(8):801–807. PMID: 28201824.
Article18. Gibson AM, Reddington C, McBride L, Callanan C, Robertson C, Doyle LW. Lung function in adult survivors of very low birth weight, with and without bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2015; 50(10):987–994. PMID: 25195792.
Article19. Gough A, Spence D, Linden M, Halliday HL, McGarvey LPA. General and respiratory health outcomes in adult survivors of bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a systematic review. Chest. 2012; 141(6):1554–1567. PMID: 22116801.20. Greenough A. Does low birth weight confer a lifelong respiratory disadvantage? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009; 180(2):107–108. PMID: 19578139.
Article21. Pilgaard K, Færch K, Carstensen B, Poulsen P, Pisinger C, Pedersen O, et al. Low birthweight and premature birth are both associated with type 2 diabetes in a random sample of middle-aged Danes. Diabetologia. 2010; 53(12):2526–2530. PMID: 20859612.
Article22. Hack M, Schluchter M, Cartar L, Rahman M. Blood pressure among very low birth weight (<1.5 kg) young adults. Pediatr Res. 2005; 58(4):677–684. PMID: 16192252.23. Saigal S, Doyle LW. An overview of mortality and sequelae of preterm birth from infancy to adulthood. Lancet. 2008; 371(9608):261–269. PMID: 18207020.
Article24. Gross SJ, Iannuzzi DM, Kveselis DA, Anbar RD. Effect of preterm birth on pulmonary function at school age: a prospective controlled study. J Pediatr. 1998; 133(2):188–192. PMID: 9709704.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Trends and Characteristics of Mortality Associated with Congenital Anomalies in Korean Children under 5 Years of Age
- Early Neonatal Mortality Rate; Neonatal Factors
- Clinical observation of small for gestational age
- Perinatal Mortality rates: IV. A Practical Classification of Infants by Birth weight and Gestational Age
- Analysis of the Causes and Trends of Maternal Mortality in Korea: 2009-2014