Clin Endosc.
2020 Sep;53(5):583-593. 10.5946/ce.2019.211.
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided, Percutaneous, and Transjugular Liver Biopsy: A Comparative Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Endoscopy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, MA, USA
- 2Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- 3Section of Digestive Diseases, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA
- KMID: 2507593
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2019.211
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Percutaneous liver biopsy (PCLB) or transjugular liver biopsy (TJLB) have traditionally been performed to obtain a sample of hepatic tissue; however, endoscopic ultrasound-guided liver biopsy (EUSLB) has become an attractive alternative. The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy and safety of EUSLB, PCLB, and TJLB.
Methods
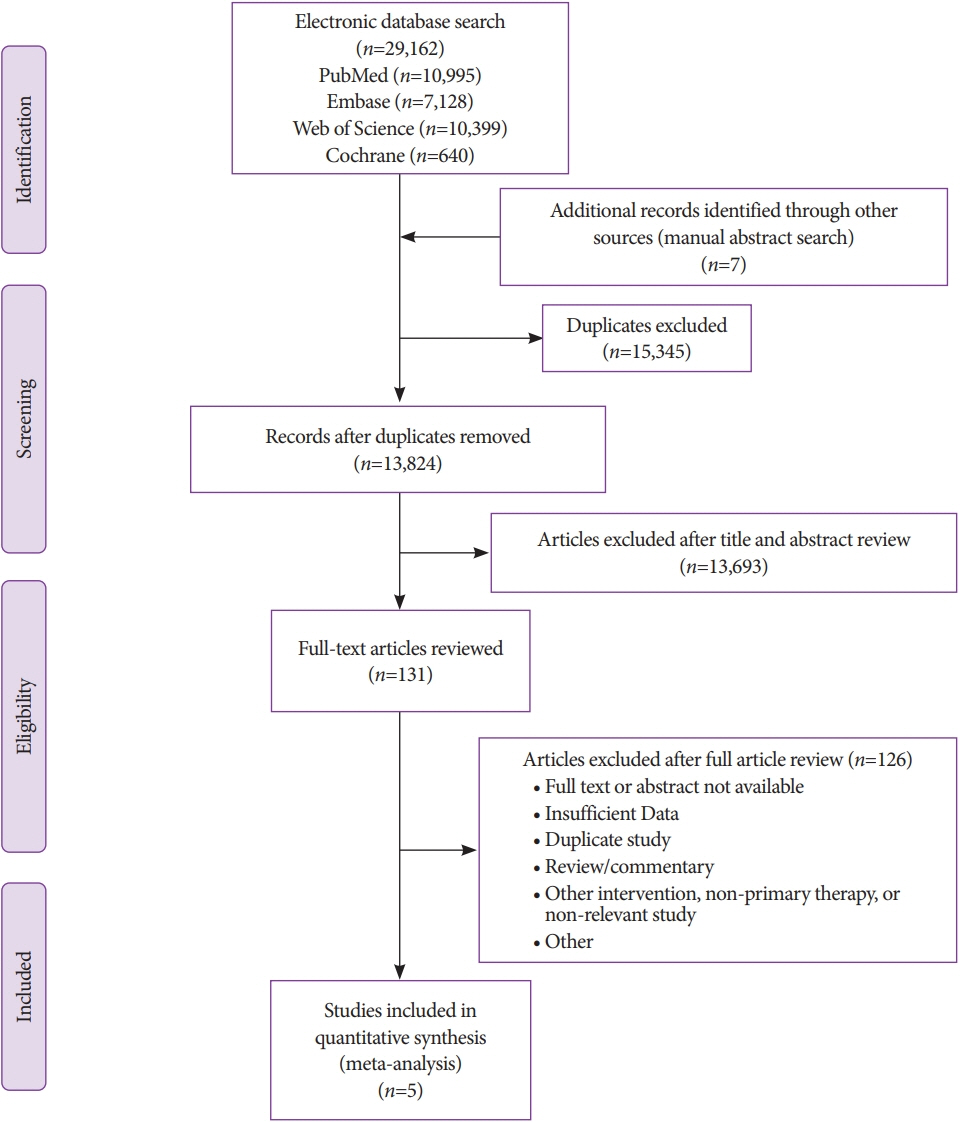
Search strategies were developed in accordance with PRISMA and MOOSE guidelines. Major outcomes included the following: adequacy of biopsy specimens (i.e., complete portal triads [CPT], total specimen length [TSL] in mm, and length of longest piece [LLP]) in mm), and rate of adverse events. Only studies comparing all biopsy approaches (i.e., EUSLB, PCLB, and TJLB) were included.
Results
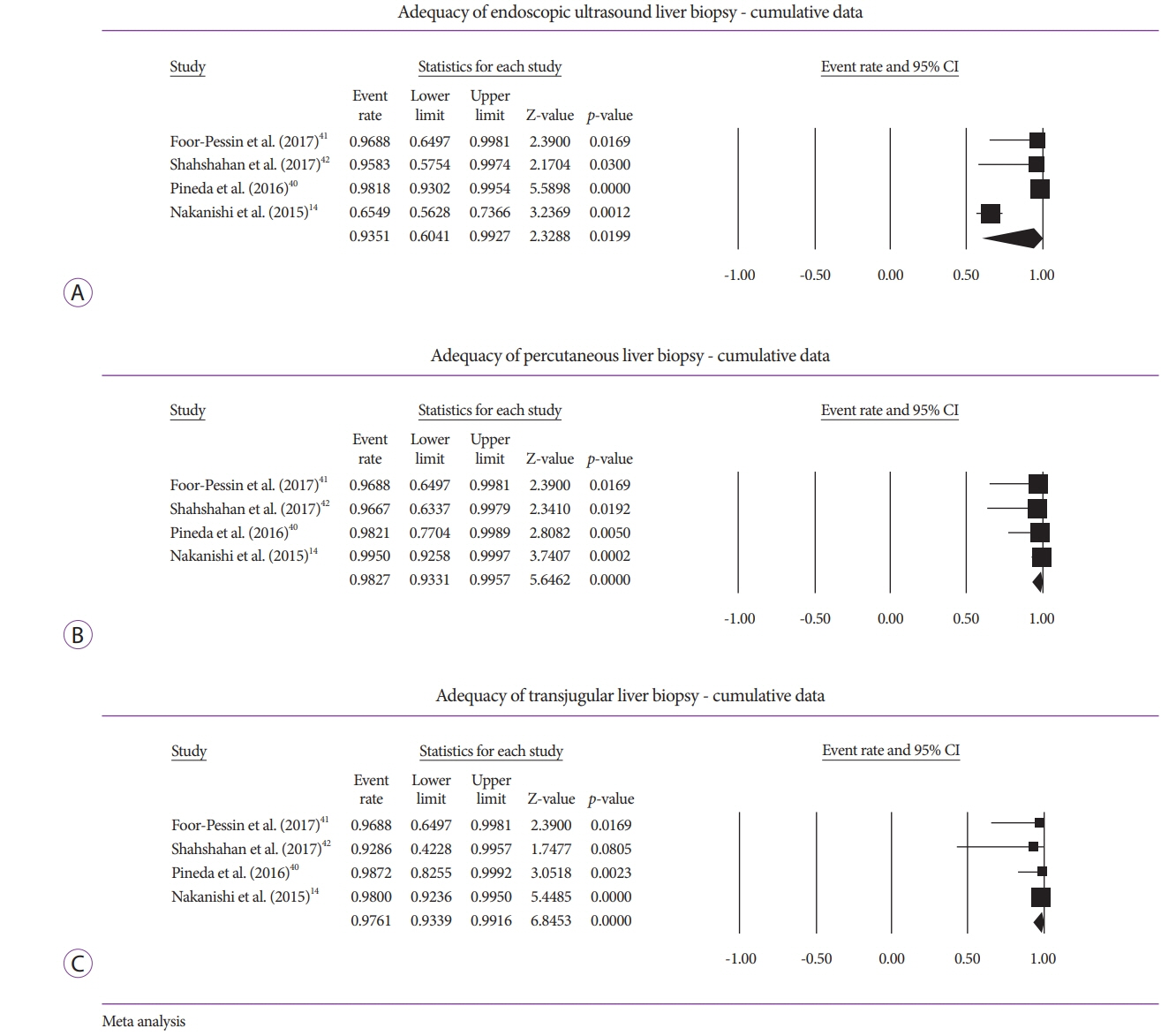
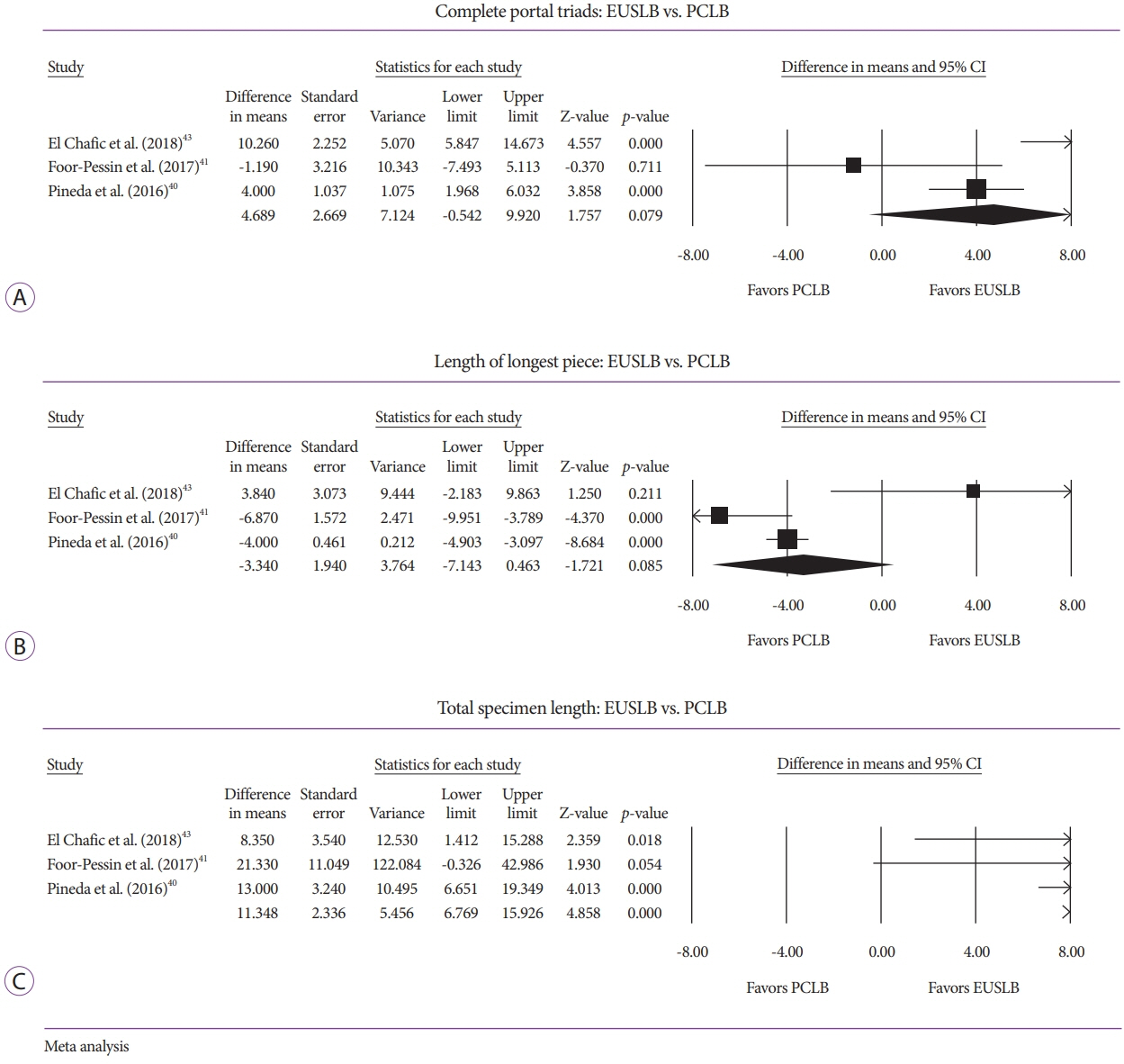
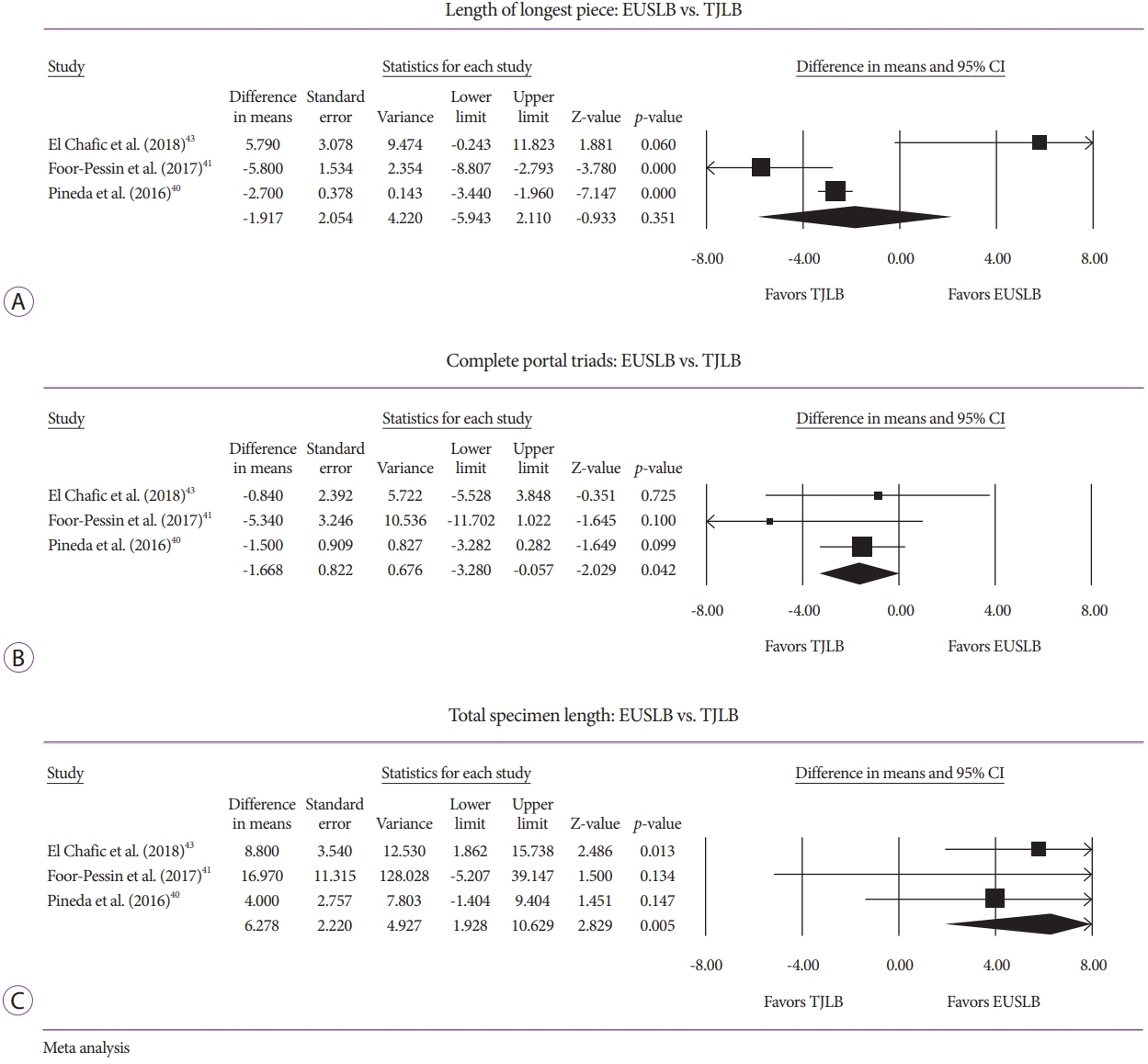
Five studies (EUSLB [n=301]; PCLB [n=176]; and TJLB [n=179]) were included. Biopsy cumulative adequacy rates for EUSLB, PCLB, and TJLB were 93.51%, 98.27%, and 97.61%, respectively. Based on the subgroup analysis limited to EUS biopsy needles in current clinical practice, there was no difference in biopsy adequacy or adverse events for EUSLB compared to PCLB and TJLB (all p>0.050). A comparison of EUSLB and PCLB revealed no difference between specimens regarding both CPT (p=0.079) and LLP (p=0.085); however, a longer TSL (p<0.001) was observed. Compared to TJLB, EUSLB showed no difference in LLP (p=0.351), fewer CPT (p=0.042), and longer TSL (p=0.005).
Conclusions
EUSLB appears to be a safe, minimally invasive procedure that is comparable to PCLB and TJLB regarding biopsy specimens obtained and rate of adverse events associated with each method.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Editors' Choice of Noteworthy Clinical Endoscopy Publications in the First Decade
Gwang Ha Kim, Kwang An Kwon, Do Hyun Park, Jimin Han
Clin Endosc. 2021;54(5):633-640. doi: 10.5946/ce.2021.216.
Reference
-
1. Bravo AA, Sheth SG, Chopra S. Liver biopsy. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:495–500.
Article2. Tapper EB, Lok AS. Use of liver imaging and biopsy in clinical practice. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:756–768.
Article3. Menghini G. One-second needle biopsy of the liver. Gastroenterology. 1958; 35:190–199.
Article4. van Leeuwen DJ, Wilson L, Crowe DR. Liver biopsy in the mid-1990s: questions and answers. Semin Liver Dis. 1995; 15:340–359.
Article5. Kirley K, Qato DM, Kornfield R, Stafford RS, Alexander GC. National trends in oral anticoagulant use in the United States, 2007 to 2011. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2012; 5:615–621.
Article6. Grant A, Neuberger J. Guidelines on the use of liver biopsy in clinical practice. British Society of Gastroenterology. Gut. 1999; 45(Suppl 4):IV1–IV11.7. Dotter CT. Catheter biopsy. Experimental technic for transvenous liver biopsy. Radiology. 1964; 82:312–314.
Article8. Rockey DC, Caldwell SH, Goodman ZD, Nelson RC, Smith AD. Liver biopsy. Hepatology. 2009; 49:1017–1044.
Article9. Sheela H, Seela S, Caldwell C, Boyer JL, Jain D. Liver biopsy: evolving role in the new millennium. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005; 39:603–610.10. Kalambokis G, Manousou P, Vibhakorn S, et al. Transjugular liver biopsy--indications, adequacy, quality of specimens, and complications--a systematic review. J Hepatol. 2007; 47:284–294.11. Schwarzer R, Ferlitsch A. Liver biopsy-transjugular. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2014; 4:113–115.
Article12. Dewitt J, McGreevy K, Cummings O, et al. Initial experience with EUS-guided Tru-cut biopsy of benign liver disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69(3 Pt 1):535–542.
Article13. Hollerbach S, Willert J, Topalidis T, Reiser M, Schmiegel W. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy of liver lesions: histological and cytological assessment. Endoscopy. 2003; 35:743–749.
Article14. Nakanishi Y, Mneimneh WS, Sey M, Al-Haddad M, DeWitt JM, Saxena R. One hundred thirteen consecutive transgastric liver biopsies for hepatic parenchymal diseases: a single-institution study. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015; 39:968–976.15. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 151:W65–W94.
Article16. Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA. 2000; 283:2008–2012.17. Schulman AR, Thompson CC, Odze R, Chan WW, Ryou M. Optimizing EUS-guided liver biopsy sampling: comprehensive assessment of needle types and tissue acquisition techniques. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85:419–426.
Article18. Mok SRS, Diehl DL. The role of EUS in liver biopsy. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019; 21:6.
Article19. Hirano T, Manabe T, Imanishi K, Ando K. Direct surface cooling of the exocrine pancreas in the rat. Br J Surg. 1992; 79:803–806.
Article20. Mohan BP, Shakhatreh M, Garg R, Ponnada S, Adler DG. Efficacy and safety of EUS-guided liver biopsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019; 89:238–246.e3.
Article21. Standish RA, Cholongitas E, Dhillon A, Burroughs AK, Dhillon AP. An appraisal of the histopathological assessment of liver fibrosis. Gut. 2006; 55:569–578.
Article22. Colloredo G, Guido M, Sonzogni A, Leandro G. Impact of liver biopsy size on histological evaluation of chronic viral hepatitis: the smaller the sample, the milder the disease. J Hepatol. 2003; 39:239–244.
Article23. Cholongitas E, Senzolo M, Standish R, et al. A systematic review of the quality of liver biopsy specimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006; 125:710–721.
Article24. DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986; 7:177–188.
Article25. Stuart A, Ord K. Kendall’s advanced theory of statistics. 6th ed. London: Edward Arnold;1994.26. McCarty TR, Itidiare M, Njei B, Rustagi T. Efficacy of transoral incisionless fundoplication for refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2018; 50:708–725.
Article27. McCarty TR, Njei B. Self-expanding metal stents for acute refractory esophageal variceal bleeding: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Endosc. 2016; 28:539–547.
Article28. Riley RD, Higgins JP, Deeks JJ. Interpretation of random effects meta-analyses. BMJ. 2011; 342:d549.
Article29. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003; 327:557–560.
Article30. Overton RC. A comparison of fixed-effects and mixed (random-effects) models for meta-analysis tests of moderator variable effects. Psychol Methods. 1998; 3:354–379.
Article31. Inoue T, Nishida T, Maekawa A, et al. Clinical features of post-polypectomy bleeding associated with heparin bridge therapy. Dig Endosc. 2014; 26:243–249.
Article32. Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996; 17:1–12.
Article33. Gage BF, Waterman AD, Shannon W, Boechler M, Rich MW, Radford MJ. Validation of clinical classification schemes for predicting stroke: results from the national registry of atrial fibrillation. JAMA. 2001; 285:2864–2870.
Article34. Borenstein M, Higgins JP, Hedges LV, Rothstein HR. Basics of meta-analysis: I2 is not an absolute measure of heterogeneity. Res Synth Methods. 2017; 8:5–18.35. Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JPT, Rothstein HR. Introduction to meta-analysis. Hoboken (NJ): Wiley;2011.36. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Spiegelhalter DJ. A re-evaluation of random-effects meta-analysis. J R Stat Soc Ser A Stat Soc. 2009; 172:137–159.
Article37. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315:629–634.
Article38. Easterbrook PJ, Berlin JA, Gopalan R, Matthews DR. Publication bias in clinical research. Lancet. 1991; 337:867–872.
Article39. Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. 2000; 56:455–463.
Article40. Pineda JJ, Diehl DL, Miao CL, et al. EUS-guided liver biopsy provides diagnostic samples comparable with those via the percutaneous or transjugular route. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:360–365.41. Foor-Pessin C, Bittner K, Kothari S, et al. Histologic yield of endoscopic ultrasound guided liver biopsy compared to percutaneous and transjugular approaches: a single-center retrospective review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85(5 Suppl):AB485–AB486.42. Shahshahan M, Gertz H, Fakhreddine AY, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided liver biopsy versus percutaneous and trans-jugular liver biopsy for evaluation of liver parenchyma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85(5 Suppl):AB490.43. El Chafic AH, Mubarak MF, Shah J, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided liver biopsy compared to percutaneous and transjugular liver biopsy: a tertiary center experience: category award (interventional endoscopy). Am J Gastroenterol. 2018; 113:S421.
Article44. Diehl DL, Johal AS, Khara HS, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided liver biopsy: a multicenter experience. Endosc Int Open. 2015; 3:E210–E215.
Article45. Maharaj B, Maharaj RJ, Leary WP, et al. Sampling variability and its influence on the diagnostic yield of percutaneous needle biopsy of the liver. Lancet. 1986; 1:523–525.
Article46. Gilmore IT, Burroughs A, Murray-Lyon IM, Williams R, Jenkins D, Hopkins A. Indications, methods, and outcomes of percutaneous liver biopsy in England and Wales: an audit by the British Society of Gastroenterology and the Royal College of Physicians of London. Gut. 1995; 36:437–441.
Article47. Singh P, Mukhopadhyay P, Bhatt B, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound versus CT scan for detection of the metastases to the liver: results of a prospective comparative study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2009; 43:367–373.48. Mathew A. EUS-guided routine liver biopsy in selected patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:2354–2355.
Article49. Diehl DL, Mok SRS, Khara HS, Johal AS, Kirchner HL, Lin F. Heparin priming of EUS-FNA needles does not adversely affect tissue cytology or immunohistochemical staining. Endosc Int Open. 2018; 6:E356–E362.
Article50. Mok SRS, Diehl DL, Johal AS, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy in chronic liver disease: a randomized comparison of 19-G FNA and 22-G FNB needles. Endosc Int Open. 2019; 7:E62–E71.
Article51. Schulman AR, Thompson CC, Ryou M. EUS-guided portal pressure measurement using a digital pressure wire with real-time remote display: a novel, minimally invasive technique for direct measurement in an animal model. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:817–820.52. Schulman AR, Thompson CC, Ryou M. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided direct portal pressure measurement using a digital pressure wire with real-time remote display: a survival study. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2017; 27:1051–1054.
Article53. Huang JY, Samarasena JB, Tsujino T, et al. EUS-guided portal pressure gradient measurement with a simple novel device: a human pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85:996–1001.
Article54. Samarasena JB, Huang JY, Tsujino T, et al. EUS-guided portal pressure gradient measurement with a simple novel device: a human pilot study. VideoGIE. 2018; 3:361–363.
Article55. Mohan BP, Adler DG. Heterogeneity in systematic review and meta-analysis: how to read between the numbers. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019; 89:902–903.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mucosal incision-assisted biopsy versus endoscopic ultrasound-assisted tissue acquisition for subepithelial lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Usefulness of Ultrasound for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Proven in Meta-Analysis Studies
- Intrahepatic Pseudoaneurysms Complicating Transjugular Liver Biopsy in Liver Transplantation Patients: Three Case Reports
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Vascular Procedures: A Review
- Fine-Needle Biopsy: Should This Be the First Choice in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition?