Korean J Ophthalmol.
2020 Apr;34(2):166-167. 10.3341/kjo.2019.0066.
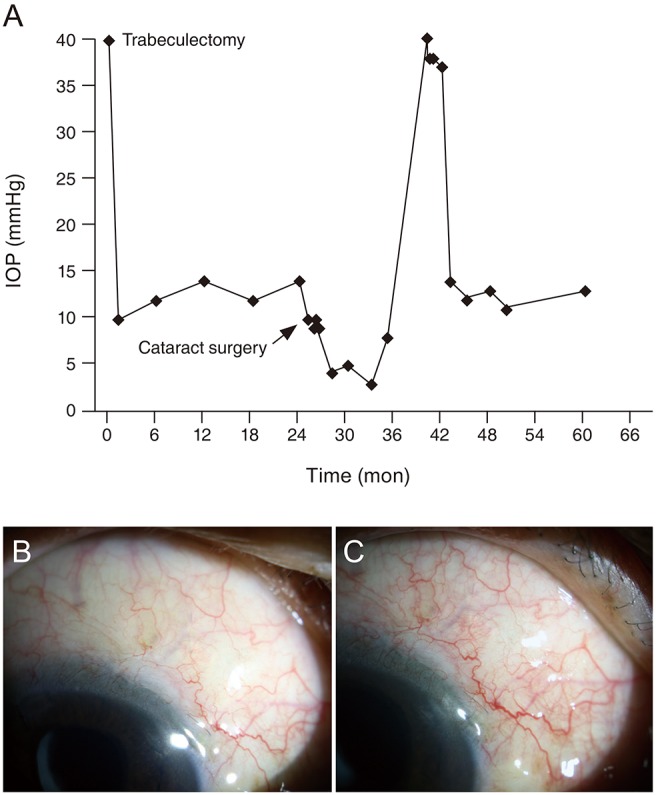
Ocular Hypotony after Cataract Surgery in an Eye with Prior Trabeculectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Myung-Gok Eye Research Institute, Kim's Eye Hospital, Konyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2507412
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2019.0066
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schubert HD. Postsurgical hypotony: relationship to fistulization, inflammation, chorioretinal lesions, and the vitreous. Surv Ophthalmol. 1996; 41:97–125. PMID: 8890437.
Article2. Mushtaq B, Chiang MY, Kumar V, et al. Phacoemulsification, persistent hypotony, and cyclodialysis clefts. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:1428–1432. PMID: 16105618.
Article3. Sen HN, Drye LT, Goldstein DA, et al. Hypotony in patients with uveitis: the Multicenter Uveitis Steroid Treatment (MUST) trial. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2012; 20:104–112. PMID: 22409563.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Cataract Operation on Ocular Hypotony after Trabeculectomy with Mitomycin C
- A Case of Ocular Siderosis with Cataract and Delayed-Onset Secondary Glaucoma
- Hypotony After Trabeculectomy with Mitomycin C
- Management of hypotony after trabeculectomy with mitomycin C
- Incidence of ptosis following trabeculectomy: a comparative study