J Korean Med Sci.
2020 Sep;35(36):e329. 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e329.
The Impact of COVID-19 on the Conduct of Clinical Trials for Medical Products in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Project Leadership, IQVIA, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2506549
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e329
Abstract
- Background
The number of clinical trials conducted in Korea continues to increase and an increasing proportion focus on severe and rare incurable diseases. After the start of the severe acute respiratory syndrome, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC) developed guidelines to prevent the spread of infection. This study evaluated the impact of COVID-19 and the KCDC guideline on the conduct of clinical research in Korea. The purpose was to develop recommendations on how to minimize the risk of infection while enabling subjects to take part in the trials if no better alternative treatment options were available.
Methods
The impact on subject's scheduled visits and major milestones of clinical trials in Korea were measured by conducting a survey among clinical project manager (CPMs) working at global clinical research organization. The policy on monitor's access to hospital and site initiation meetings was investigated through correspondence with clinical trial center of 39 hospitals. The Top 25 pharmaceutical companies' official press and public clinical trial registry database were used to analyze companies' trial strategy during the pandemic and COVID-19 clinical research status, respectively.
Results
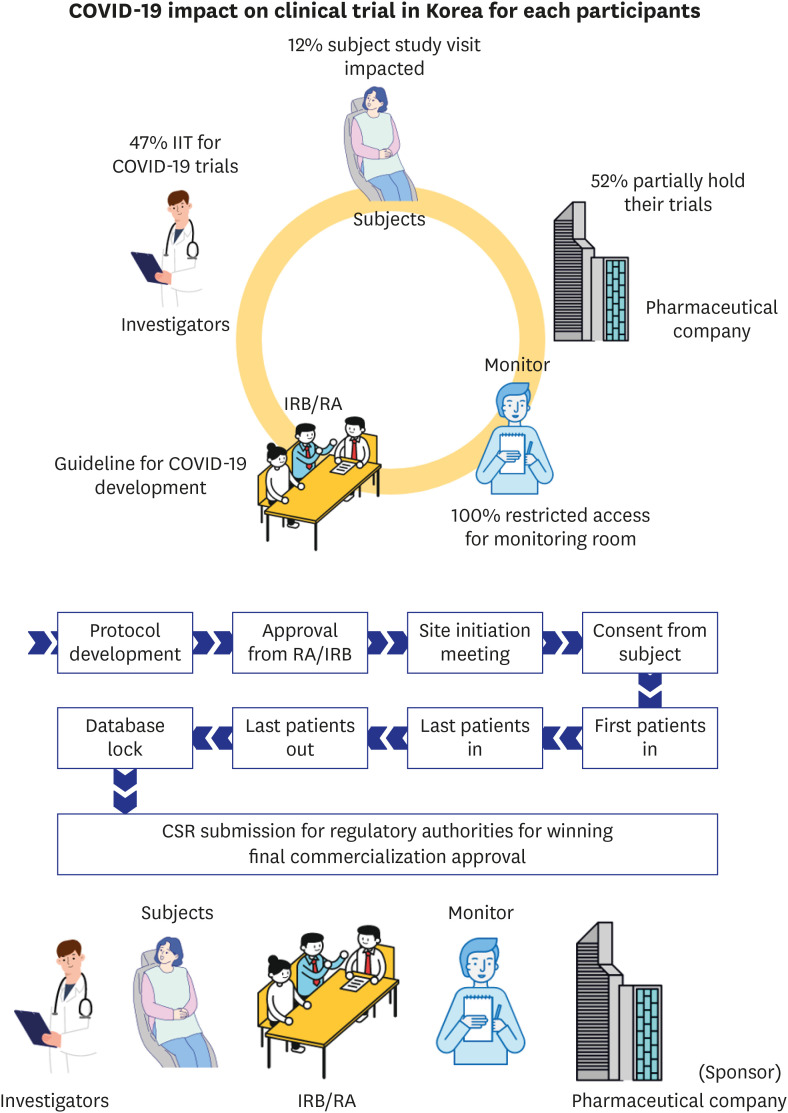
Of 85 CPMs, 12% reported that trial subjects' scheduled visits had been affected in their project. Monitors' access to hospital for source data verification was restricted at all sites in February 2020. Accordingly, 43% of 105 CPMs reported that the COVID-19 epidemic had an effect on study major milestones and data cleaning and database lock accounted for > 60% of milestones affected. In addition, 87% sites advised not to have site initiation meetings and 52% pharmaceutical companies suspended recruitment or new study startup due to the pandemic. On the other hands, the number of COVID-19 related clinical trials increased rapidly in Korea and worldwide, with investigator-initiated trials accounting for 47% and 63% of all trials locally and globally, respectively. Most trials were phase 2 and were in the recruitment stage.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 and the KCDC guideline influenced all parties involved in clinical trials in Korea. In order to ensure the safety and well-being of trial subjects during the pandemic, new approaches are required for clinical trials to respond to the impact actively. Method of non-contact is developed to replace and supplement the face-to-face contact and alternatives to reduce the travel is introduced to decrease the risk of infection for all trial participants in whole trial process. The relevant regulations should be developed and the guidelines for foreign countries need to be adopted in accordance with the situation in Korea. COVID-19 trial is rapidly increasing worldwide and continuous support of health authorities, regulation, and facilities is required for developing the treatments with protecting all trial participants.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Reporting Survey Based Studies – a Primer for Authors
Prithvi Sanjeevkumar Gaur, Olena Zimba, Vikas Agarwal, Latika Gupta
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(45):e398. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e398.
Reference
-
1. Korea Clinical Trials Information Center. Updated 2020. Accessed June 29, 2020. https://www.koreaclinicaltrials.org/kr/contents/datainfo_data_01_tab03/view.do.2. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Presentation of the results of approval of clinical trials for medicines in Korea in 2018. Updated 2019. Accessed May 4, 2020. https://www.mfds.go.kr/brd/m_99/view.do?seq=43284.3. ICH GCP. ICH harmonized guideline integrated addendum to ICH E6(R1): Guideline for Good Clinical Practice ICH E6(R2) ICH Consensus Guideline. Updated 2017. Accessed June 29, 2020. https://ichgcp.net/.4. Korean Society of Infectious Diseases. Korean Society of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. Korean Society of Epidemiology. Korean Society for Antimicrobial Therapy. Korean Society for Healthcare-associated Infection Control and Prevention. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Report on the epidemiological features of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in the Republic of Korea from January 19 to March 2, 2020. J Korean Med Sci. 2020; 35(10):e112. PMID: 32174069.5. Ministry of Health. Daily status of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome, MERS. Updated 2018. Accessed June 29, 2020. http://www.mohw.go.kr/react/al/sal0301ls.jsp?PAR_MENU_ID=04&MENU_ID=0403.6. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 response guideline 9th edition by Central Disaster Management Headquarters · Central Disease Control Headquarters. Updated 2020. Accessed June 29, 2020. https://www.cdc.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a20507020000&bid=0019.7. Korea Pharmaceutical and Bio-Pharma Manufacturers' Association. 2019 Pharmaceutical Industry Database Book Statistical Information. Updated 2019. Accessed June 29, 2020. http://www.kpbma.or.kr.8. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Integrated drug information system. Updated 2020. Accessed June 24, 2020. https://nedrug.mfds.go.kr/searchClinic.9. U.S National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated 2020. Accessed June 28, 2020. https://clinicaltrials.gov/.10. Ministry Health and Welfare. Daily status of COVID-19. Updated 2020. Accessed March 20, 2020. http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/bdBoardList_Real.do.11. Korean Hospital Association. Updated 2020. Accessed June 28, 2020. https://www.kha.or.kr.12. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Considerations for clinical trials in a situation of COVID-19. Updated 2020. Accessed March 27, 2020. https://www.mfds.go.kr/index.do.13. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Notice of training considerations for clinical trial workers according to corona 19 situation. Updated 2020. Accessed June 28, 2020. https://www.mfds.go.kr/index.do.14. United Kingdom Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency. Synopsis of MHRA advice on management of clinical trials in relation to coronavirus. Updated 2020. Accessed March 27, 2020. https://www.gov.uk/government/collections/mhra-guidance-on-coronavirus-covid-19.15. Korea National Enterprise for Clinical Trials. Analysis of domestic and international clinical trials. Updated 2020. Accessed June 28, 2020. https://www.koreaclinicaltrials.org/kr/board/covid19_smry/boardView.do?bbsIdx=888&pageIndex=1&searchCondition=&searchKeyword=.16. Korea National Enterprise for Clinical Trials. KoNECT brief. Ed1. Updated 2020. Accessed March 27, 2020. https://www.konect.or.kr/.17. Food and Drug Administration. Guidance on Conduct of Clinical Trials of Medical Products during COVID-19 Public Health Emergency. Updated 2020. Accessed June 28, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/fda-guidance-conduct-clinical-trials-medical-products-during-covid-19-public-health-emergency.18. European Medicines Agency. Guidance on the management of clinical trials during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Updated 2020. Accessed June 28, 2020. https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/files/eudralex/vol-10/guidanceclinicaltrials_covid19_en.pdf.19. Korea Ministry of Government Legislation. Korea Pharmaceutical Affairs Act. Updated 2020. Accessed June 28, 2020. http://law.go.kr/%EB%B2%95%EB%A0%B9/%EC%95%BD%EC%82%AC%EB%B2%95/%EC%A0%9C50%EC%A1%B0.20. Association of Clinical Research Organizations. ACRO's considerations on monitoring during COVID-19. Updated 2020. Accessed June 28, 2020. https://www.acrohealth.org/acro-considerations-on-monitoring-during-covid-19/.21. The Italian Medicines Agency (AIFA). Clinical trials' management in Italy during the COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 19) emergency. Updated 2020. Accessed June 28, 2020. https://www.aifa.gov.it/documents/20142/871583/Comunicato_gestione_studi_clinici_in_emergenza_COVID-19_EN_12.03.2020.pdf/ee1f33e3-bb3e-9ce9-2a93-b33e88eea94d.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Small Molecule Drug Candidates for Managing the Clinical Symptoms of COVID-19: a Narrative Review
- Excluding Participants With Mycobacteria Infections From Clinical Trials: A Critical Consideration in Evaluating the Efficacy of BCG Against COVID-19
- The coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic and chronic diseases
- COVID-19 and Aviation Medical Examination
- The Impact of COVID-19 on Dysphagia in a Steroid-Responsive Dermatomyositis Patient: A Case Report