Korean J Gastroenterol.
2020 Aug;76(2):78-82. 10.4166/kjg.2020.76.2.78.
Eosinophilic Esophagitis with Angina Pectoris
- Affiliations
-
- 1Divisions of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Divisions of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 3Divisions of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2505814
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2020.76.2.78
Abstract
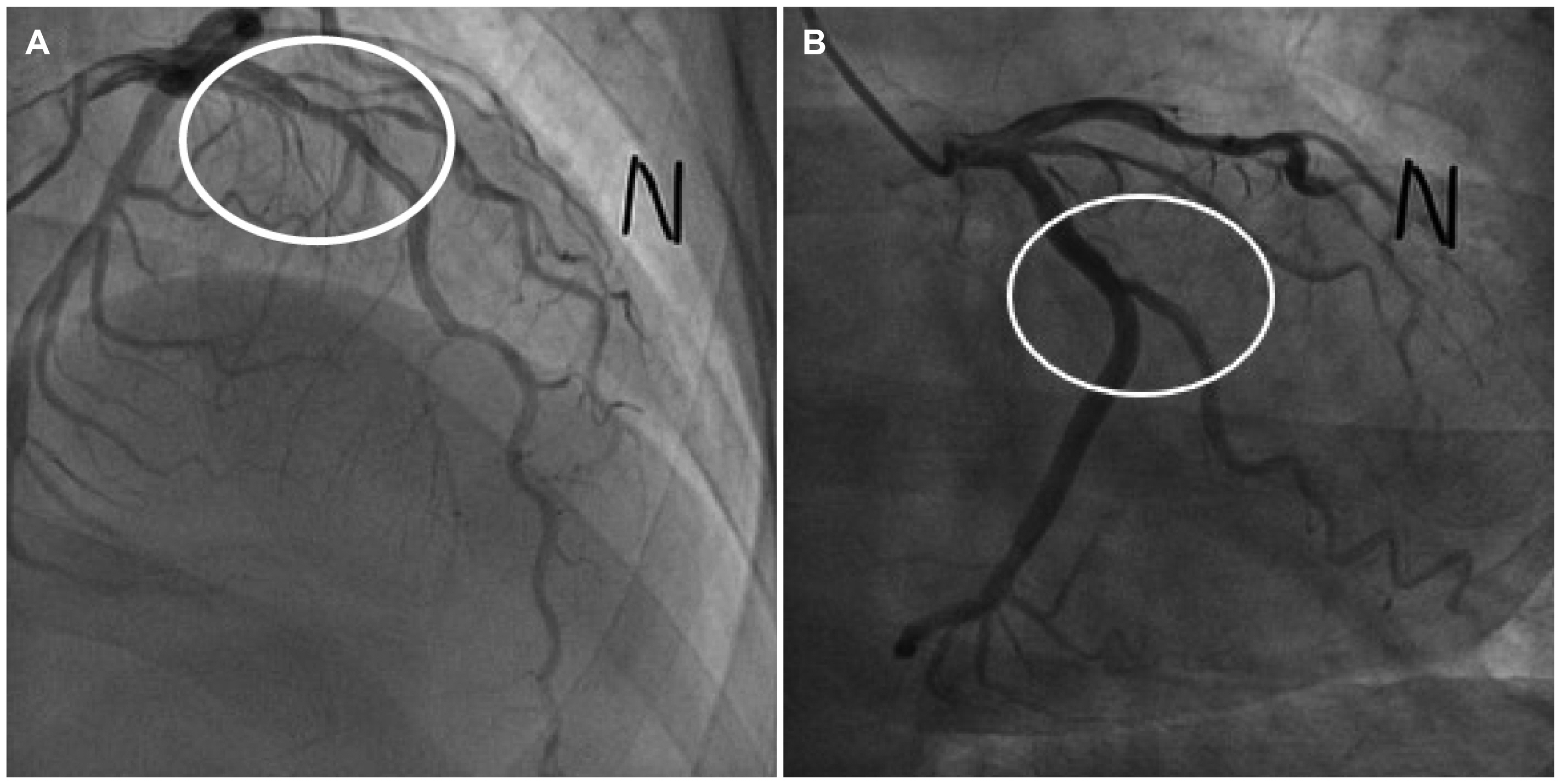
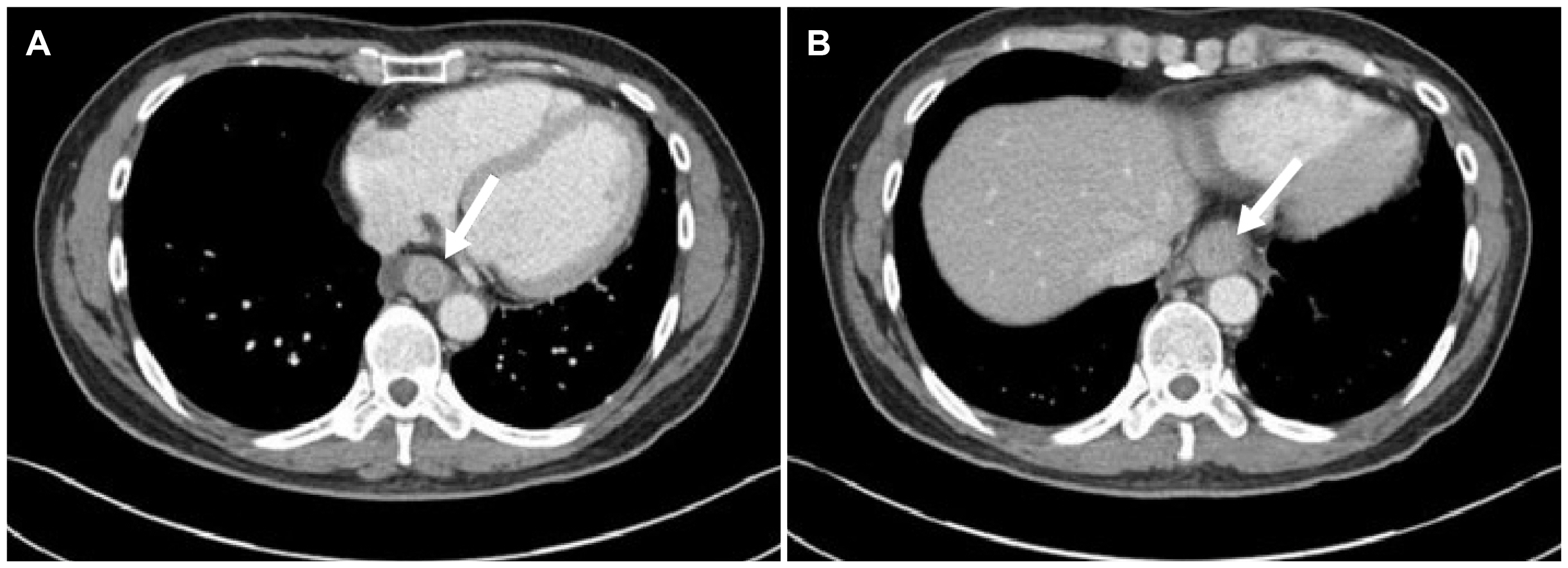
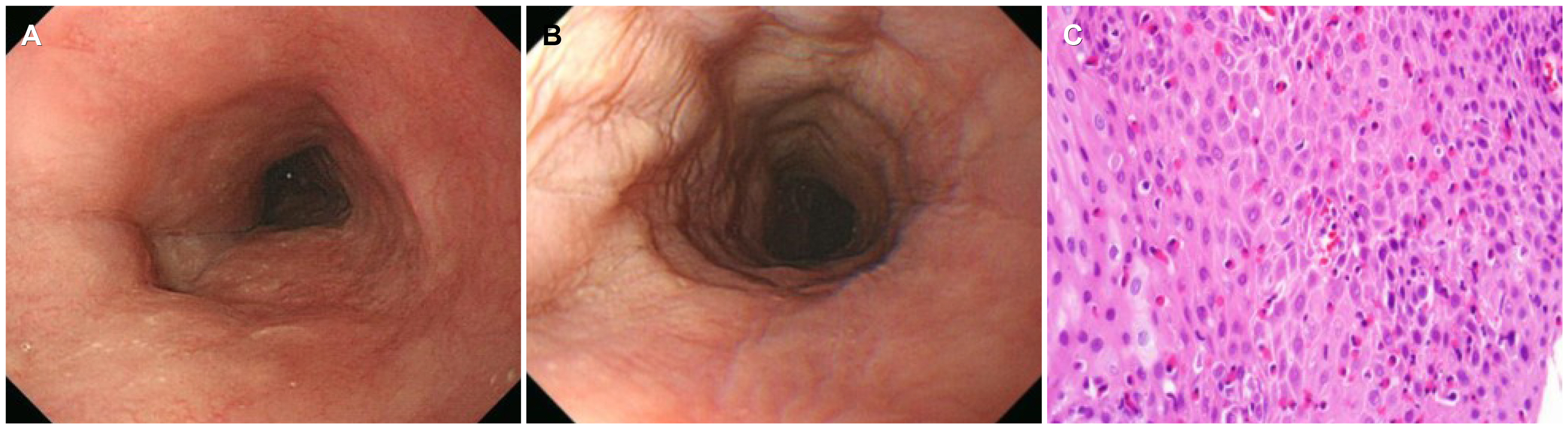
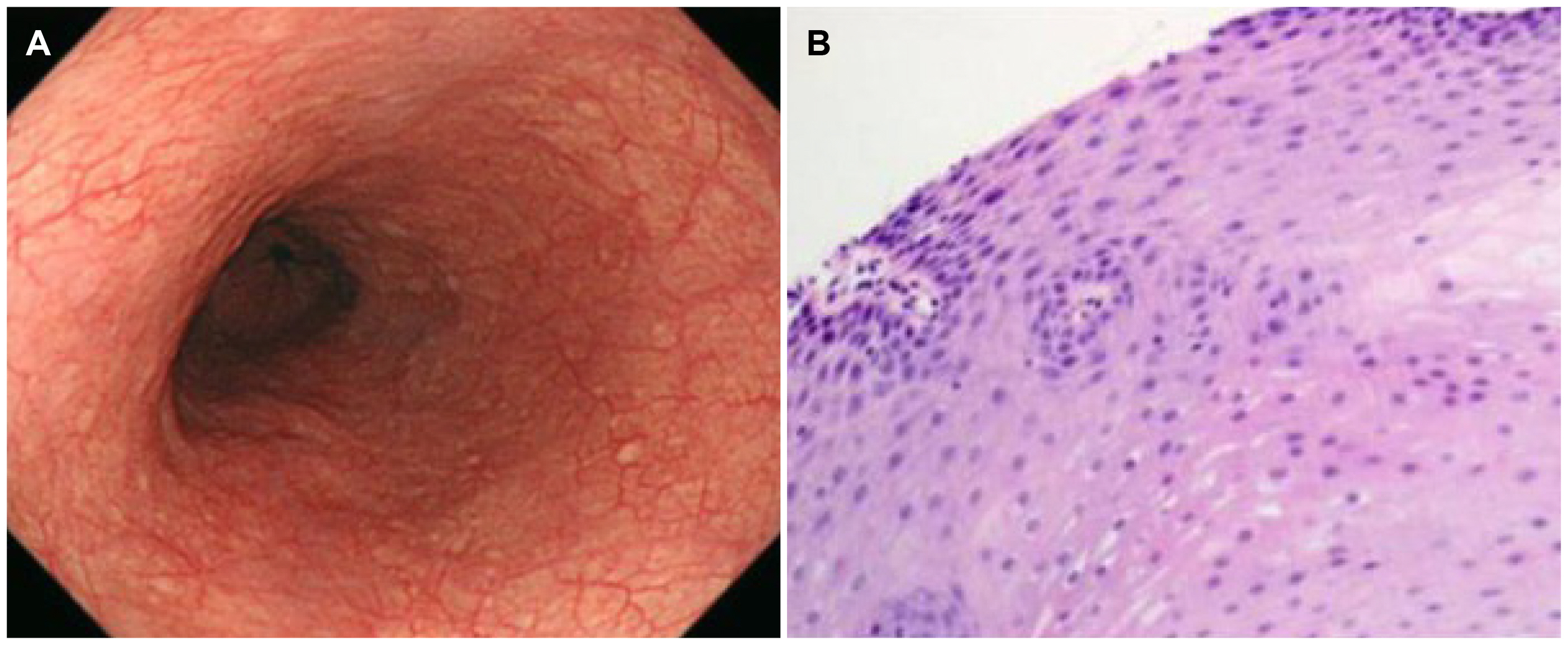
- Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an immune or antigen-mediated chronic inflammatory esophageal disorder that is relatively rarein Asian countries. The main symptoms of EoE are dysphagia and food impaction. Although chest pain is a symptom of EoE, it isalso a symptom of coronary heart disease. This paper reports a case of EoE with angina pectoris in a 45-year-old male who wasreferred to the authors’ hospital for chest pain. He was diagnosed with angina pectoris because of mild stenosis in the left coronaryartery on coronary angiography. On the other hand, the symptoms did not improve with angina medication therapy.Therefore, he underwent a chest CT scan, which revealed esophageal thickening. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy was performed.His endoscopic findings showed linear furrows with edema, and >90 eosinophils existed per high-power field on the histologyfindings. He was diagnosed with EoE. Through additional examinations, he was also diagnosed with asthma. The patient wastreated with a proton pump inhibitor and a fluticasone inhaler. His symptoms and abnormal endoscopic findings disappeared aftereight weeks of treatment. This case shows that physicians should consider the possibility of the symptoms for EoE when unexplainedchest pain persists.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Furuta GT, Katzka DA. 2015; Eosinophilic esophagitis. N Engl J Med. 373:1640–1648. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1502863. PMID: 26488694. PMCID: PMC4905697.
Article2. Kim GH, Park YS, Jung KW, et al. 2019; An increasing trend of eosinophilic esophagitis in Korea and the clinical implication of the biomarkers to determine disease activity and treatment response in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 25:525–533. DOI: 10.5056/jnm19066. PMID: 31587544. PMCID: PMC6786448.
Article3. Moawad FJ. 2018; Eosinophilic esophagitis: incidence and prevalence. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 28:15–25. DOI: 10.1016/j.giec.2017.07.001. PMID: 29129296.4. Sgouros SN, Bergele C, Mantides A. 2006; Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: a systematic review. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:211–217. DOI: 10.1097/00042737-200602000-00015. PMID: 16394804.
Article5. Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, et al. 2007; Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology. 133:1342–1363. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.08.017. PMID: 17919504.
Article6. Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, et al. 2011; Eosinophilic esophagitis:updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 128:3–22. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.02.040. PMID: 21477849.7. Kahrilas PJ, Bredenoord AJ, Fox M, et al. 2015; The Chicago classification of esophageal motility disorders, v3. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 27:160–174. DOI: 10.1111/nmo.12477. PMID: 25469569. PMCID: PMC4308501.8. Dellon ES, Liacouras CA, Molina-Infante J, et al. 2018; Updated international consensus diagnostic criteria for eosinophilic esophagitis:proceedings of the AGREE conference. Gastroenterology. 155:1022–1033. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.07.009. PMID: 30009819. PMCID: PMC6174113.9. Hirano I, Moy N, Heckman MG, Thomas CS, Gonsalves N, Achem SR. 2013; Endoscopic assessment of the oesophageal features of eosinophilic oesophagitis: validation of a novel classification and grading system. Gut. 62:489–495. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301817. PMID: 22619364.
Article10. Dellon ES, Hirano I. 2018; Epidemiology and natural history of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 154:319–332.e3. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.06.067. PMID: 28774845. PMCID: PMC5794619.
Article11. Kim JW, Park JS, Kim YH, et al. 2002; Secondary achalasia by eosinophilic esophagitis. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 25:198–202.12. Lee BJ, Park HJ, Yoon HS, Kim HK, Kim HS. 2008; Three cases of eosinophilic esophagitis with dysphagia as a chief complaint. Clin Endosc. 36:145–149.13. Park SB, Kim GH, Choi MK, et al. 2009; A case of eosinophilic esophagitis found incidentally during the evaluation of a gastric submucosal tumor. Clin Endosc. 39:212–216.14. Arora AS, Yamazaki K. 2004; Eosinophilic esophagitis: asthma of the esophagus? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2:523–530. DOI: 10.1016/S1542-3565(04)00236-8. PMID: 15224275.
Article15. Hogan SP, Mishra A, Brandt EB, et al. 2001; A pathological function for eotaxin and eosinophils in eosinophilic gastrointestinal inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2:353–360. DOI: 10.1038/86365. PMID: 11276207.
Article16. Kinoshita Y, Ishimura N, Oshima N, Ishihara S. 2015; Systematic review:eosinophilic esophagitis in Asian countries. World J Gastroenterol. 21:8433–8440. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8433. PMID: 26217096. PMCID: PMC4507114.17. Achem SR, Almansa C, Krishna M, et al. 2011; Oesophageal eosinophilic infiltration in patients with noncardiac chest pain. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 33:1194–1201. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04652.x. PMID: 21466568.
Article18. Kahn J, Bussmann C, Beglinger C, Straumann A, Hruz P. 2015; Exercise-induced chest pain: an atypical manifestation of eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Med. 128:196–199. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.08.007. PMID: 25261012.
Article19. Lucendo AJ, Molina-Infante J, Arias Á, et al. 2017; Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United European Gastroenterol J. 5:335–358. DOI: 10.1177/2050640616689525. PMID: 28507746. PMCID: PMC5415218.
Article20. Cheng E, Zhang X, Huo X, et al. 2013; Omeprazole blocks eotaxin-3 expression by oesophageal squamous cells from patients with eosinophilic oesophagitis and GORD. Gut. 62:824–832. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302250. PMID: 22580413. PMCID: PMC3552049.
Article