J Korean Med Sci.
2020 Aug;35(33):e302. 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e302.
[Secondary Publication] Standard Operating Procedure for Post-mortem Inspection in a Focus on Coronavirus Disease-19: the Korean Society for Legal Medicine
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
- 2Department of Forensic Medicine, Jeonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea
- 3Division of Forensic Medicine, National Forensic Service Seoul Institute, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Forensic Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2505597
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e302
Abstract
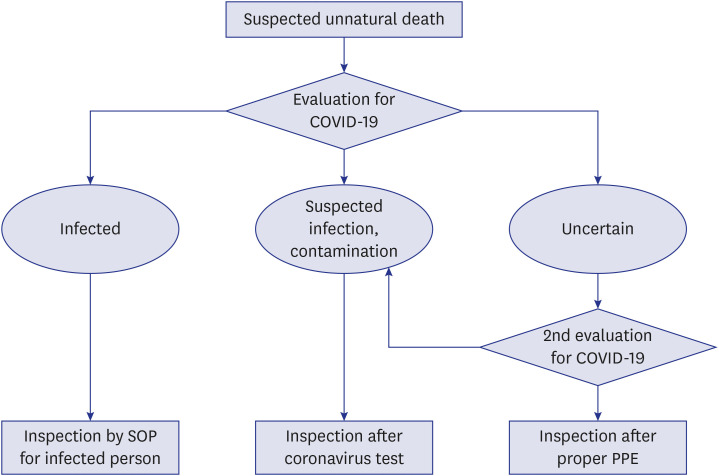
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a respiratory syndrome caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and emerged in Wuhan, China, in late 2019. It resulted in a worldwide pandemic, and spread through community transmission in the Republic of Korea (ROK). In the ROK, SARS-CoV-2 is categorized as a first-degree infectious disease of the legal communicable disease present. The Korean Society for Legal Medicine (KSLM) is the sole official academic association of forensic professionals in the ROK. As such, this society has played an important role in forensic medicine and science in the ROK. Therefore, KSLM suggests a standard operating procedure for the postmortem inspection in a focus on COVID-19. This article includes the background of this suggested standard operation procedure, basic principles for postmortem inspections of individuals suggested of having an infectious disease, and specific procedures according to the probability level of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nolte KB, Taylor DG, Richmond JY. Biosafety considerations for autopsy. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2002; 23(2):107–122. PMID: 12040252.
Article2. van Doremalen N, Bushmaker T, Morris DH, Holbrook MG, Gamble A, Williamson BN, et al. Aerosol and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 as compared with SARS-CoV-1. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382(16):1564–1567. PMID: 32182409.
Article3. Zhang W, Du RH, Li B, Zheng XS, Yang XL, Hu B, et al. Molecular and serological investigation of 2019-nCoV infected patients: implication of multiple shedding routes. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020; 9(1):386–389. PMID: 32065057.
Article4. Wang XW, Li JS, Jin M, Zhen B, Kong QX, Song N, et al. Study on the resistance of severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus. J Virol Methods. 2005; 126(1-2):171–177. PMID: 15847934.
Article5. Mahallawi WH. Case report: Detection of the Middle East respiratory syndrome corona virus (MERS-CoV) in nasal secretions of a dead human. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2017; 13(3):302–304. PMID: 31435338.
Article6. Kampf G, Todt D, Pfaender S, Steinmann E. Persistence of coronaviruses on inanimate surfaces and their inactivation with biocidal agents. J Hosp Infect. 2020; 104(3):246–251. PMID: 32035997.
Article7. World Health Organization. Infection prevention and control for the safe management of a dead body in the context of COVID-19 (Interim guidance). Updated 2020. Accessed March 30, 2020. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/331538.8. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Collection and submission of postmortem specimens from deceased persons with known or suspected COVID-19. Updated 2020. Accessed August 11, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/guidance-postmortem-specimens.html.9. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Considerations related to the safe handling of bodies of deceased persons with suspected or confirmed COVID-19. Updated 2020. Accessed March 30, 2020. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/considerations-related-safe-handling-bodies-deceased-persons-suspected-or.10. Finegan O, Fonseca S, Guyomarc’h P, Morcillo Mendez MD, Rodriguez Gonzalez J, Tidball-Binz M, et al. International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC): General guidance for the management of the dead related to COVID-19. Forensic Sci Int. 2020; 2:129–137.
Article11. International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, International Committee of the Red Cross, World Health Organization. COVID-19 Interim Guidance for the Management of the Dead in Humanitarian Settings. Updated 2020. Accessed August 11, 2020. https://reliefweb.int/report/world/covid-19-interim-guidance-management-dead-humanitarian-settings-july-2020.12. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 guidelines (for local government). Appendix 9th-1 ed. 23-5. Updated 2020. Accessed August 11, 2020. http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/upload/viewer/skin/doc.html?fn=1594339429555_20200710090350.pdf&rs=/upload/viewer/result/202008/.13. National Law Information Center. Enforcement Decree of Infectious Disease Control and Prevention Act. Updated 2020. Accessed May 1, 2020. http://www.law.go.kr/.14. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 guidelines for funeral of the dead. Updated 2020. Accessed March 1, 2020. http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/upload/viewer/skin/doc.html?fn=1583134848272_20200302164048.hwp&rs=/upload/viewer/result/202005/.15. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 guidelines (for local government). Appendix 9th-1 ed. 49-53. Updated 2020. Accessed August 11, 2020. http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/upload/viewer/skin/doc.html?fn=1594339391392_20200710090312.pdf&rs=/upload/viewer/result/202008/.16. National Law Information Center. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Test Request Regulation. Updated 2020. Accessed May 1, 2020. http://www.law.go.kr/.17. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 guidelines (for local government). Appendix 9th-1 ed. 33-41. Updated 2020. Accessed August 11, 2020. http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/upload/viewer/skin/doc.html?fn=1594339429555_20200710090350.pdf&rs=/upload/viewer/result/202008/.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Standard Operating Procedure for Postmortem Inspection in a Focus on Coronavirus Disease-19: The Korean Society for Legal Medicine
- The Forensic Pathology in Scotland and the Analysis of Post-mortem Examinations at Glasgow
- Evaluation of the Usefulness of Cardiac Marker Analysis for Postmortem Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Differences in the Determination of Cause and Manner of 127 Natural Death Cases by Postmortem Inspection and Autopsy
- The interpretation of post-mortem vaginal acid phosphatase determination