Ann Rehabil Med.
2020 Aug;44(4):320-326. 10.5535/arm.19091.
Flat Foot and Postural Harmony in 6-Year-Old Caucasians: What is Their Relationship?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Unit of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Department of Medical and Oral Sciences and Biotechnologies, University G. D’Annunzio Chieti-Pescara, Chieti, Italy
- 2Department of Public Health and Infectious Diseases, Sapienza University of Rome, Rome, Italy
- 3Department of Biomolecular Sciences, University of Study of Urbino Carlo Bo, Urbino, Italy
- KMID: 2505392
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.19091
Abstract
Objective
To determine whether asymptomatic flexible flat feet show specific postural assessment with respect to neutral feet in 6-year-old children.
Methods
In this cross-sectional observational study, 164 subjects were observed and divided into two groups: 57 with flexible flat feet and 107 with neutral feet. A non-quantitative inspection by podoscopy and baropodometry were performed to evaluate plantar support, and a clinical examination to assess postural setting.
Results
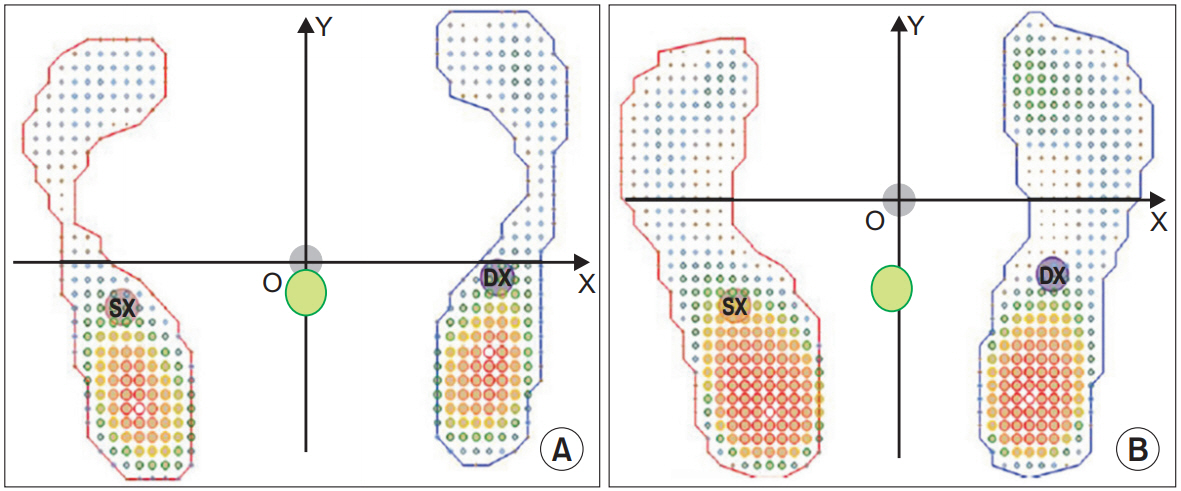
The prevalence of flexible flat feet was 34.8%. The differenceinthe mean centre of pressure (CoP) between the two groups was significant (p=0.028), regarding the antero-posterior direction of CoP only. There was no significant differencein the presence of postural growth disharmony between the neutral and flat-feet groups.
Conclusion
The flattening of the plantar archseems to be linked to a displacement of CoP Y, more posterior in flat feet than in neutral feet; on the other hand, postural harmony in 6-year-old children during growth is not influenced by flat feet.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pfeiffer M, Kotz R, Ledl T, Hauser G, Sluga M. Prevalence of flat foot in preschool-aged children. Pediatrics. 2006; 118:634–9.
Article2. Yin J, Zhao H, Zhuang G, Liang X, Hu X, Zhu Y, et al. Flexible flatfoot of 6-13-year-old children: a cross-sectional study. J Orthop Sci. 2018; 23:552–6.
Article3. Balague F, Troussier B, Salminen JJ. Non-specific low back pain in children and adolescents: risk factors. Eur Spine J. 1999; 8:429–38.4. Wojtkow M, Szkoda-Poliszuk K, Szotek S. Influence of body posture on foot load distribution in young school-age children. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2018; 20:101–7.5. Penha PJ, Joao SM, Casarotto RA, Amino CJ, Penteado DC. Postural assessment of girls between 7 and 10 years of age. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2005; 60:9–16.
Article6. Shumway-Cook A, Woollacott MH. The growth of stability: postural control from a development perspective. J Mot Behav. 1985; 17:131–47.7. PLOS Medicine Editors. Observational studies: getting clear about transparency. PLoS Med. 2014; 11:e1001711.8. Cacciari E, Milani S, Balsamo A, Spada E, Bona G, Cavallo L, et al. Italian cross-sectional growth charts for height, weight and BMI (2 to 20 yr). J Endocrinol Invest. 2006; 29:581–93.
Article9. Kerr CM, Stebbins J, Theologis T, Zavatsky AB. Static postural differences between neutral and flat feet in children with and without symptoms. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2015; 30:314–7.
Article10. Viladot Perice A. New method of statistical investigation of the feet; photopodography. Clin Lab (Zaragoza). 1954; 57:114–7.11. Garcia-Rodriguez A, Martin-Jimenez F, Carnero-Varo M, Gomez-Gracia E, Gomez-Aracena J, Fernandez-Crehuet J. Flexible flat feet in children: a real problem? Pediatrics. 1999; 103:e84.12. Brzezinski M, Czubek Z, Niedzielska A, Jankowski M, Kobus T, Ossowski Z. Relationship between lower-extremity defects and body mass among polish children: a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019; 20:84.
Article13. Sadeghi-Demneh E, Melvin JM, Mickle K. Prevalence of pathological flatfoot in school-age children. Foot (Edinb). 2018; 37:38–44.
Article14. Paolucci T, Piccinini G, Iosa M, Piermattei C, De Angelis S, Zangrando F, et al. The importance of trunk perception during brace treatment in moderate juvenile idiopathic scoliosis: what is the impact on self-image? J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2017; 30:203–10.
Article15. Zaina F, Atanasio S, Ferraro C, Fusco C, Negrini A, Romano M, et al. Review of rehabilitation and orthopedic conservative approach to sagittal plane diseases during growth: hyperkyphosis, junctional kyphosis, and Scheuermann disease. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2009; 45:595–603.16. Bricot B. Total postural reprogramming. 4th ed. Santa Monica, CA: Dux Lucis Books;2014.17. Ministry of Health. National classification guidelines: classification and measurement of posture and related dysfunctions [Internet]. Rome, Italy: Ministry of Health;2017. [cited 2020 Jul 7]. Available from: http://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pubblicazioni_2717_allegato.pdf.18. Chang HW, Chieh HF, Lin CJ, Su FC, Tsai MJ. The relationships between foot arch volumes and dynamic plantar pressure during midstance of walking in preschool children. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e94535.
Article19. Iodice P, Bellomo RG, Migliorini M, Megna M, Saggini R. Flexible flatfoot treatment in children with mechanical sound vibration therapy. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2012; 25:9S–15S.
Article20. Holowka NB, Wallace IJ, Lieberman DE. Foot strength and stiffness are related to footwear use in a comparison of minimally-vs. conventionally-shod populations. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:3679.
Article21. Kim JA, Lim OB, Yi CH. Difference in static and dynamic stability between flexible flatfeet and neutral feet. Gait Posture. 2015; 41:546–50.
Article22. Youn KJ, Ahn SY, Kim BO, Park IS, Bok SK. Long-term effect of rigid foot orthosis in children older than six years with flexible flat foot. Ann Rehabil Med. 2019; 43:224–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long Term Effect of Custom-Molded Foot Orthoses on Foot Pain and Balance in Children with Symptomatic Flexible Flat Feet
- Effect of Custom-Molded Foot Orthoses on Foot Pain and Balance in Children With Symptomatic Flexible Flat Feet
- Flat Foot Survey in 8 Year Old Primary School Children
- Effects of an Interpersonal Relationship Harmony Program on Nursing Students
- The Effect of Insole to Flexible Flat Foot on Dynamic Balance and Ankle Muscle Activity during the Y-Balance Test