Clinical Course and Outcomes of 3,060 Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Korea, January–May 2020
- Affiliations
-
- 1National Emergency Medical Center, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Incheon Medical Center, Incheon, Korea
- 3Department of Pulmonology, Busan Medical Center, Busan, Korea
- 4Department of Tuberculosis, Seoul Metropolitan Seobuk Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul Metropolitan Seonam Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chungju Medical Center, Chungju, Korea
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeonggi Provincial Medical Center Ansung Hospital, Anseong, Korea
- 8Department of Infection Control, Chungcheongnam-do Gongju Medical Center, Gongju, Korea
- 9Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Internal Medicine, Armed Forces Capital Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 10Department of Infection Control, Chungcheongnam-do Seosan Medical Center, Seosan, Korea
- 11Department of Infectious Diseases, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea
- 12Department of Nursing, Yeongju Red Cross Hospital, Yeongju, Korea
- 13Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 14Department of Surgery, Gyeonggi Provincial Medical Center Uijeongbu Hospital, Uijeongbu, Korea
- 15Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 16Department of Internal Medicine, Korea Workers’ Compensation & Welfare Services Daegu Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 17Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 18Department of Internal Medicine, Chungcheongnam-do Cheonan Medical Center, Cheonan, Korea
- 19Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 20Department of Internal Medicine, Jeonllanam-do Suncheon Medical Center, Suncheon, Korea
- 21Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 22Infection Control Team, Cheongju Medical Center, Cheongju, Korea
- 23Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
- 24Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 25Intensive Care Team, Gyeonggi Provincial Medical Center Paju Hospital, Paju, Korea
- 26Infection Control Team, Gyeonggi Provincial Medical Center Icheon Hospital, Icheon, Korea
- 27Infection Control Team, Korea Worker's Compensation & Welfare Service Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea
- 28National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 29Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2505195
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e280
Abstract
- Background
The fatality rate of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) varies among countries owing to demographics, patient comorbidities, surge capacity of healthcare systems, and the quality of medical care. We assessed the clinical outcomes of patients with COVID-19 during the first wave of the epidemic in Korea.
Methods
Using a modified World Health Organization clinical record form, we obtained clinical data for 3,060 patients with COVID-19 treated at 55 hospitals in Korea. Disease severity scores were defined as: 1) no limitation of daily activities; 2) limitation of daily activities but no need for supplemental oxygen; 3) supplemental oxygen via nasal cannula; 4) supplemental oxygen via facial mask; 5) non-invasive mechanical ventilation; 6) invasive mechanical ventilation; 7) multi-organ failure or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy; and 8) death. Recovery was defined as a severity score of 1 or 2, or discharge and release from isolation.
Results
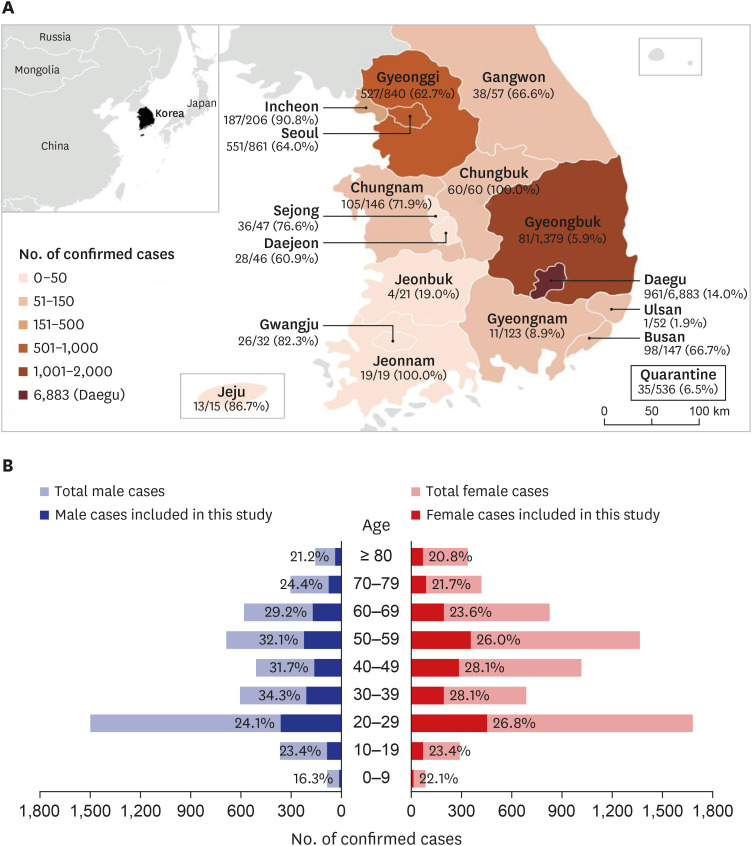
The median age of the patients was 43 years of age; 43.6% were male. The median time from illness onset to admission was 5 days. Of the patients with a disease severity score of 3–4 on admission, 65 (71.5%) of the 91 patients recovered, and 7 (7.7%) died due to illness by day 28. Of the patients with disease severity scores of 5–7, 7 (19.5%) of the 36 patients recovered, and 8 (22.2%) died due to illness by day 28. None of the 1,324 patients who were < 50 years of age died; in contrast, the fatality rate due to illness by day 28 was 0.5% (2/375), 0.9% (2/215), 5.8% (6/104), and 14.0% (7/50) for the patients aged 50–59, 60–69, 70–79, and ≥ 80 years of age, respectively.
Conclusion
In Korea, almost all patients of < 50 years of age with COVID-19 recovered without supplemental oxygen. In patients of ≥ 50 years of age, the fatality rate increased with age, reaching 14% in patients of ≥ 80 years of age.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 14 articles
-
Characteristics of Acute Stroke in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Challenges in Stroke Management during an Epidemic
Doo Hyuk Kwon, Youngrok Do, Mi-Yeon Eun, Jun Lee, Hyungjong Park, Sung-Il Sohn, Jeong-Ho Hong
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(35):e324. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e324.Letter to Editor: Strategy for Hospitalization and Discharge of COVID-19 Patients: Based on the Nationwide Clinical Course Analysis
Yeonjae Kim, Ho Kyung Sung, Ji Hwan Bang, Im-Seok Koh, Joon-Sung Joh, Young-Su Ju, Hye Sook Min, Bum Sik Chin, Ki-hyun Chung
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(38):e353. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e353.Operation and Management of Seoul Metropolitan City Community Treatment Center for Mild Condition COVID-19 Patients
Sun Young Lee, Kyoung Jun Song, Chun Soo Lim, Byeong Gwan Kim, Young Jun Chai, Jung-Kyu Lee, Su Hwan Kim, Hyouk Jae Lim
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(40):e367. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e367.Clinical Features of COVID-19 in Uzbekistan
KyungHee Kim, Jae Wook Choi, Juyoung Moon, Habibulla Akilov, Laziz Tuychiev, Bakhodir Rakhimov, Kwang Sung Min
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(45):e404. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e404.Establishment of a Nationwide Korean Imaging Cohort of Coronavirus Disease 2019
Soon Ho Yoon, Soo-Youn Ham, Bo Da Nam, Kum Ju Chae, Dabee Lee, Jin Young Yoo, So Hyeon Bak, Jin Young Kim, Jin Hwan Kim, Ki Beom Kim, Jung Im Jung, Jae-Kwang Lim, Jong Eun Lee, Myung Jin Chung, Young Kyung Lee, Young Seon Kim, Ji Eun Jo, Sang Min Lee, Woocheol Kwon, Chang Min Park, Yun-Hyeon Kim, Yeon Joo Jeong
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(46):e413. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e413.Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of COVID-19 Cohort Patients in Daegu Metropolitan City Outbreak in 2020
Shin-Woo Kim, Seung-Mee Kim, Yu Kyung Kim, Jong-yeon Kim, Yu-Mi Lee, Bong-Ok Kim, Suhyun Hwangbo, Taesung Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;36(1):e12. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e12.Clinical and Virologic Effectiveness of Remdesivir Treatment for Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea: a Nationwide Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
Eun-Jeong Joo, Jae-Hoon Ko, Seong Eun Kim, Seung-Ji Kang, Ji Hyeon Baek, Eun Young Heo, Hye Jin Shi, Joong Sik Eom, Pyoeng Gyun Choe, Seongman Bae, Sang Hyun Ra, Da Young Kim, Baek-Nam Kim, Yu Min Kang, Ji Yeon Kim, Jin-Won Chung, Hyun-Ha Chang, Sohyun Bae, Shinhyea Cheon, Yoonseon Park, Heun Choi, Eunjung Lee, Bo young Lee, Jung Wan Park, Yujin Sohn, Jung Yeon Heo, Sung-Han Kim, Kyong Ran Peck
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(11):e83. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e83.Risk Factors of Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients in Korea: Focus on Early Symptoms
Su Yeon Jang, Jeong-Yeon Seon, Baik-Lin Eun, Seong-Beom Koh, Jin-Hong Yoo, Woo Yong Lee, Ho-Kee Yum, Seok-Jun Yoon, In-Hwan Oh, Sang-Cheol Bae, Sung-Goo Chang
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(18):e132. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e132.Developing a Framework for Pandemic COVID-19 Vaccine Allocation: a Modified Delphi Consensus Study in Korea
Min Joo Choi, Won Suk Choi, Hye Seong, Jun Yong Choi, Jong-Hyun Kim, Yae-Jean Kim, Eun Young Cho, Dong-Hyun Kim, Hyesook Park, Heeyoung Lee, Nam Joong Kim, Joon Young Song, Hee Jin Cheong, Sang Il Kim, Kyong Ran Peck
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(23):e166. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e166.Comprehensive Laboratory Data Analysis to Predict the Clinical Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 1,952 Patients in Daegu, Korea
Eun-Hyung Yoo, Soon Hee Chang, Do-Young Song, Chae Hoon Lee, Gyu Young Cheong, Sunggyun Park, Jae Hee Lee, Sooin Lee, Sang-Gyu Kwak, Chang-Ho Jeon, Kyung Eun Song
Ann Lab Med. 2022;42(1):24-35. doi: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.1.24.National Academy of Medicine of Korea (NAMOK) Key Statements on COVID-19
Hyoung-Shik Shin, Hyesook Park, Jun Soo Kwon, Hyun Namgoong, Seong-Jun Kim, June Myung Kim, Kyong Ran Peck, Kyungwon Lee, Jong-koo Lee, JinHan Lee, Hee Chul Han, SungJin Hong, Byung-Joo Park, Tae Hwan Lim, Eung Soo Hwang, Jun Hee Woo,
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(41):e287. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e287.Predictors of Red Blood Cell Transfusion in Elderly COVID-19 Patients in Korea
Hye Ryun Lee
Ann Lab Med. 2022;42(6):659-667. doi: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.6.659.Comprehensive Rehabilitation in Severely Ill Inpatients With COVID-19: A Cohort Study in a Tertiary Hospital
Hyeonseong Woo, Sanghee Lee, Hyun Sung Lee, Hyun Jun Chae, Jongtak Jung, Myung Jin Song, Sung Yoon Lim, Yeon Joo Lee, Young-Jae Cho, Eu Suk Kim, Hong Bin Kim, Jae-Young Lim, Kyoung-Ho Song, Jaewon Beom
J Korean Med Sci. 2022;37(34):e262. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e262.Real-World Effectiveness of Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir and Its Acceptability in High-Risk COVID-19 Patients
Min-Kyung Kim, Kyung-Shin Lee, Sin Young Ham, Youn Young Choi, Eunyoung Lee, Seungjae Lee, Bora Lee, Jaehyun Jeon, BumSik Chin, Yeonjae Kim, Gayeon Kim, Hee-Chang Jang, Jae-Phil Choi, Sang-Won Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2023;38(35):e272. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e272.
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation report-143. Updated 2020. Accessed 15 June, 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports.2. Kim JY, Choe PG, Oh Y, Oh KJ, Kim J, Park SJ, et al. The First Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Imported into Korea from Wuhan, China: Implication for Infection Prevention and Control Measures. J Korean Med Sci. 2020; 35(5):e61. PMID: 32030925.
Article3. Korea Centers for Disease control and Prevention. Coronavirus disease-19 main website. Updated 2020. Accessed June 15, 2020. http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/en.4. Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in china: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020; 323(13):1239–1242.5. Grasselli G, Zangrillo A, Zanella A, Antonelli M, Cabrini L, Castelli A, et al. Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy region, Italy. JAMA. 2020; 323(16):1574–1581.
Article6. Petrilli CM, Jones SA, Yang J, Rajagopalan H, O'Donnell L, Chernyak Y, et al. Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2020; 369:m1966. PMID: 32444366.
Article7. World Health Organization. I.S.A.R.E.I.C., Global COVID-19: clinical platform: novel coronavius (COVID-19): rapid version. Geneva: World Health Organization;2020.8. Korea Centers for Disease control and Prevention. Press release. Coronavirus disease-19, Republic of Korea. Updated 2020. Accessed June 12, 2020. http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/en/tcmBoardList.do?brdId=12&brdGubun=125&dataGubun=&ncvContSeq=&contSeq=&board_idhttp://ncov.mohw.go.kr/en/tcmBoardList.do?brdId=12&brdGubun=125&dataGubun=&ncvContSeq=&contSeq=&board_id=.9. WHO Working Group on the Clinical Characterisation and Management of COVID-19 Infection. A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research. Lancet Infect Dis. Forthcoming. 2020; DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7.10. Kim ES, Chin BS, Kang CK, Kim NJ, Kang YM, Choi JP, et al. Clinical course and outcomes of patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection: a preliminary report of the first 28 patients from the Korean cohort study on COVID-19. J Korean Med Sci. 2020; 35(13):e142. PMID: 32242348.
Article11. Kim NJ, Choe PG, Park SJ, Lim J, Lee WJ, Kang CK, et al. A cluster of tertiary transmissions of 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) in the community from infectors with common cold symptoms. Korean J Intern Med. 2020; 35(4):758–764. PMID: 32506866.
Article12. World Health Organization. Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Geneva: World Health Organization;2020.13. Verity R, Okell LC, Dorigatti I, Winskill P, Whittaker C, Imai N, et al. Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: a model-based analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020; 20(6):669–677. PMID: 32240634.
Article14. Korean Society of Infectious Diseases. Korean Society of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. Korean Society of Epidemiology. Korean Society for Antimicrobial Therapy. Korean Society for Healthcare-associated Infection Control and Prevention. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Report on the epidemiological features of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in the Republic of Korea from January 19 to March 2, 2020. J Korean Med Sci. 2020; 35(10):e112. PMID: 32174069.15. Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M, Crawford JM, McGinn T, Davidson KW, et al. Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area. JAMA. 2020; 323(20):2052.
Article16. Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, Mehta AK, Zingman BS, Kalil AC, et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 - Preliminary report. N Engl J Med. Forthcoming. 2020; DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764.
Article17. Kang E, Lee SY, Jung H, Kim MS, Cho B, Kim YS. Operating protocols of a community treatment center for isolation of patients with coronavirus disease, South Korea. Emerging. Emerg Infect Dis. Forthcoming. 2020; DOI: 10.3201/eid2610.201460.18. Lee YH, Hong CM, Kim DH, Lee TH, Lee J. Clinical course of asymptomatic and mildly symptomatic patients with coronavirus disease admitted to community treatment centers, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis. Forthcoming. 2020; DOI: 10.3201/eid2610.201620.
Article19. Geleris J, Sun Y, Platt J, Zucker J, Baldwin M, Hripcsak G, et al. Observational study of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382(25):2411–2418. PMID: 32379955.
Article20. Cao B, Wang Y, Wen D, Liu W, Wang J, Fan G, et al. A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382(19):1787–1799. PMID: 32187464.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis on 54 Mortality Cases of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in the Republic of Korea from January 19 to March 10, 2020
- Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in the Early Stage of Outbreak
- Report on the Epidemiological Features of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in the Republic of Korea from January 19 to March 2, 2020
- Epidemiologic characteristics of early cases with 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) disease in Korea
- Vaccines and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019