Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2020 Aug;13(3):249-254. 10.21053/ceo.2019.01144.
A Retrospective Review of Temporal Bone Computed Tomography to Present Safe Guideline for Bone-Anchored Hearing Aids
- Affiliations
-
- 1Samsung Hearing Laboratory, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2504919
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2019.01144
Abstract
Objectives
. Bone-anchored hearing device (BAHD) is contraindicated in patients younger than 5 years because their calvarial bones are not thick enough to be implanted site. However, it has not been studied in the Korean population. This study was not only to establish a safe guideline for depth of implant device in all age groups who undergo BAHD implant surgery, but also to investigate whether implantation of currently used BAHDs could be done safely in Korean children, especially those younger than 5.
Methods
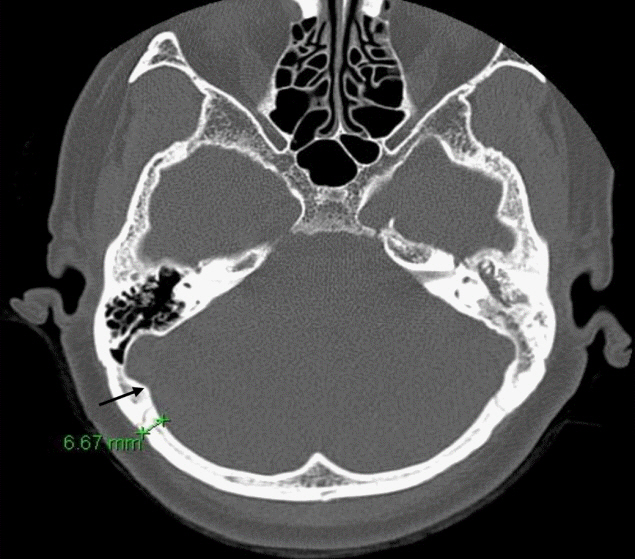
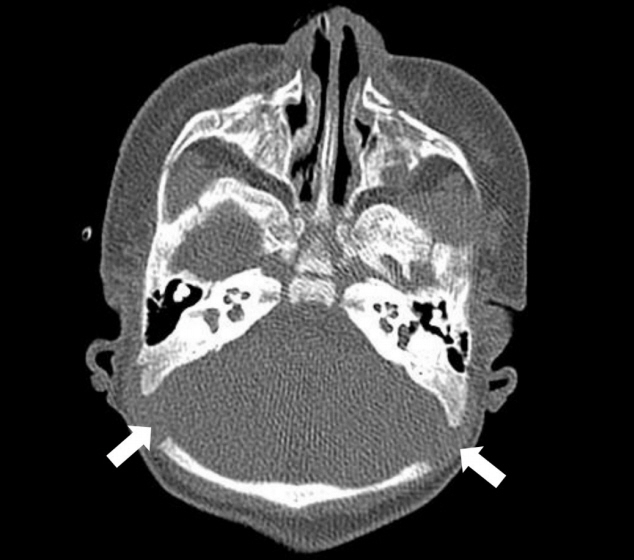
. Two hundred eighty patients, who underwent high-resolution temporal bone computed tomography (TBCT) images between August 2010 and October 2018 were randomly enrolled in all ages. We retrospectively reviewed TBCT imaging to measure skull bone thickness at the recommended BAHD implant site.
Results
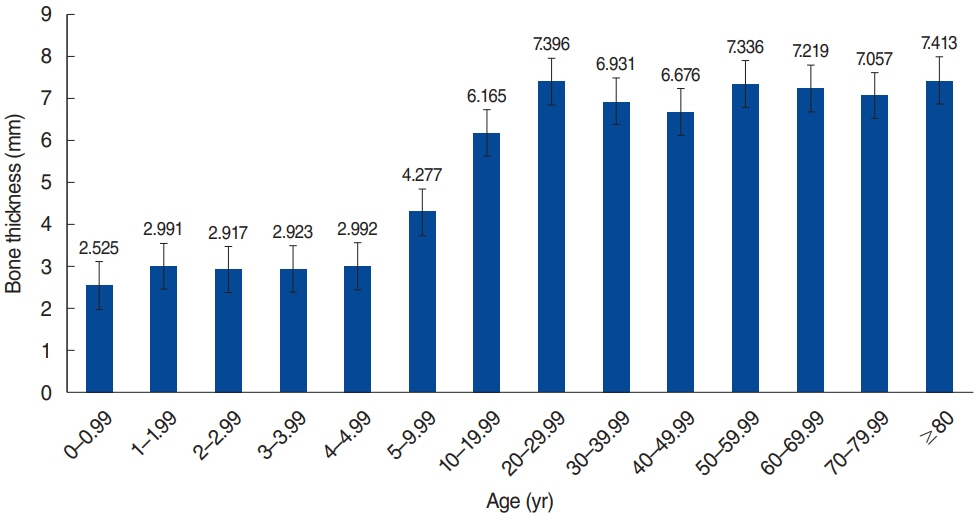
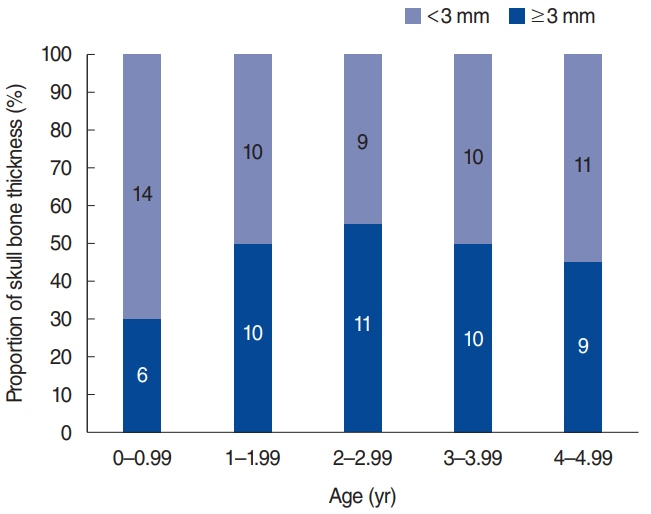
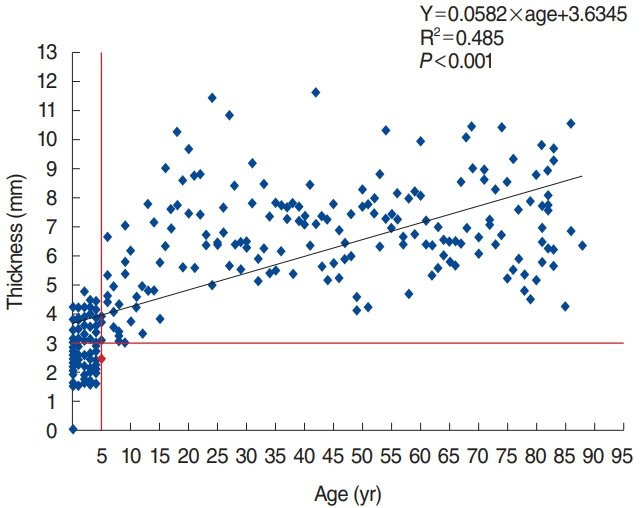
. The average skull bone thickness was 2.87 mm in patients younger than 5 years and 6.72 mm in patients older than 5 years, respectively, which conforms to the current guideline. The results indicate nearly 50% of calvarial bone thicknesses were less than 3 mm in patients under 5 years old, while 92.78% of the patients older than 5 years of age showed bone thickness greater than 4 mm. Of note, calvarial bone thickness was thicker than 3 mm in all patients who are older than 6 years.
Conclusion
. This study confirms that the currently approved BAHD implantation guideline is suitable in the Korean population. For safety, we suggest taking TBCTs prior to surgery, especially in pediatric patients. Besides, noninvasive applications are recommended for patients younger than 5.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Powell R, Wearden A, Pardesi SM, Green K. Understanding the low uptake of bone-anchored hearing aids: a review. J Laryngol Otol. 2017; Mar. 131(3):190–201.
Article2. Mudry A, Tjellstrom A. Historical background of bone conduction hearing devices and bone conduction hearing aids. In : Kompis M, Caversaccio MD, editors. Implantable bone conduction hearing aids. Basel: Karger Publishers;2011. p. 1–9.3. Tjellstrom A, Lindstrom J, Hallen O, Albrektsson T, Branemark PI. Osseointegrated titanium implants in the temporal bone: a clinical study on bone-anchored hearing aids. Am J Otol. 1981; Apr. 2(4):304–10.4. Reinfeldt S, Hakansson B, Taghavi H, Eeg-Olofsson M. New developments in bone-conduction hearing implants: a review. Med Devices (Auckl). 2015; Jan. 8:79–93.
Article5. Doshi J, McDermott AL. Bone anchored hearing aids in children. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2015; Jan. 12(1):73–82.
Article6. Kohan D, Ghossaini SN. Osseointegrated auditory devices-transcutaneous: Sophono and Baha attract. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2019; Apr. 52(2):253–63.7. Kim G, Ju HM, Lee SH, Kim HS, Kwon JA, Seo YJ. Efficacy of boneanchored hearing aids in single-sided deafness: a systematic review. Otol Neurotol. 2017; Apr. 38(4):473–83.
Article8. Svrakic M, Vambutas A. Medical and audiological indications for implantable auditory devices. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2019; Apr. 52(2):195–210.
Article9. Alzahrani M, Tabet P, Saliba I. Pediatric hearing loss: common causes, diagnosis and therapeutic approach. Minerva Pediatr. 2015; Feb. 67(1):75–90.10. Davids T, Gordon KA, Clutton D, Papsin BC. Bone-anchored hearing aids in infants and children younger than 5 years. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; Jan. 133(1):51–5.
Article11. Baker A, Fanelli D, Kanekar S, Isildak H. A review of temporal bone CT imaging with respect to pediatric bone-anchored hearing aid placement. Otol Neurotol. 2016; Oct. 37(9):1366–9.
Article12. Baker AR, Fanelli DG, Kanekar S, Isildak H. A retrospective review of temporal bone imaging with respect to bone-anchored hearing aid placement. Otol Neurotol. 2017; Jan. 38(1):86–8.
Article13. Priwin C, Granstrom G. The bone-anchored hearing aid in children: a surgical and questionnaire follow-up study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005; Apr. 132(4):559–65.
Article14. Granstrom G, Bergstrom K, Odersjo M, Tjellstrom A. Osseointegrated implants in children: experience from our first 100 patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001; Jul. 125(1):85–92.
Article15. Mierzwinski J, Konopka W, Drela M, Laz P, Smiechura M, Struzycka M, et al. Evaluation of bone conduction implant stability and soft tissue status in children in relation to age, bone thickness, and sound processor loading time. Otol Neurotol. 2015; Aug. 36(7):1209–15.16. McDermott AL, Williams J, Kuo M, Reid A, Proops D. The birmingham pediatric bone-anchored hearing aid program: a 15-year experience. Otol Neurotol. 2009; Feb. 30(2):178–83.17. Nelson KL, Cox MD, Richter GT, Dornhoffer JL. A comparative review of osseointegration failure between osseointegrated bone conduction device models in pediatric patients. Otol Neurotol. 2016; Mar. 37(3):276–80.
Article18. Zhang Y, Fan Y, Wang Y, Chen X. Efficacy of BAHA softband in young children with bilateral congenital aural atresia. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014; Feb. 94(6):420–3.19. Granstrom G, Tjellstrom A. Guided tissue generation in the temporal bone. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1999; Apr. 108(4):349–54.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Experience of BAHA(Bone Anchored Hearing Aid) Surgery
- Current Developments and Challenge of Implantable Bone Conduction Hearing Aids
- Hearing Rehabilitation Experiences With Osia®2 Bone Conduction Hearing Implant in Patients With Iatrogenic Unilateral Hearing Loss
- Hearing Rehabilitation with Bone Anchored Hearing Aid: Experience in 14 Patients
- A Case of Cochlear Implantation after Bilateral Temporal Bone Fracture