Anesth Pain Med.
2020 Jul;15(3):314-318. 10.17085/apm.19051.
Successful management of uncontrolled postpartum hemorrhage due to morbidly adherent placenta with Resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta during emergency cesarean section - A case report -
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea
- KMID: 2504893
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.19051
Abstract
- Background
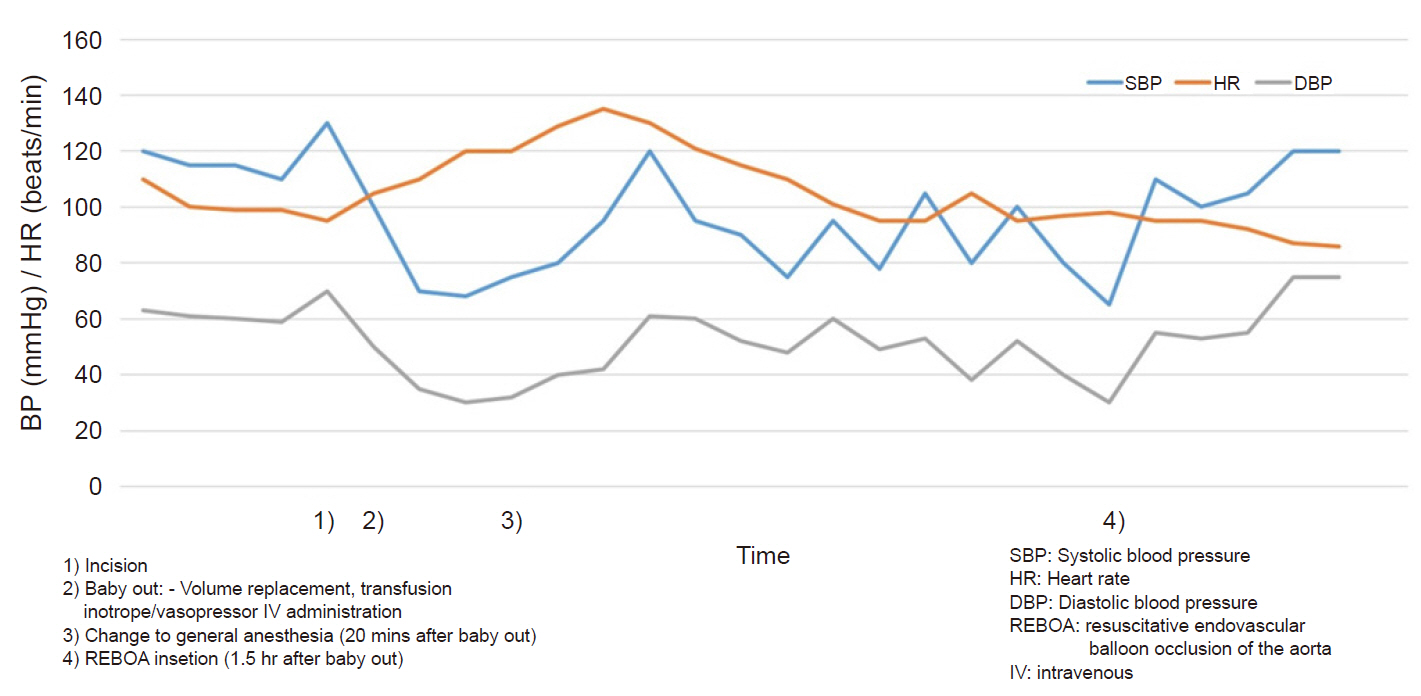
Morbidly adherent placenta (MAP) may cause life-threatening postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) requiring massive transfusions. Furthermore, it could endanger the lives of both mother and baby. Despite various efforts, such as adjuvant endovascular embolization and hysterectomy, massive PPH due to MAP still occurs and is difficult to overcome. Case: Herein, we described the case of a 40-year-old woman with placenta previa totalis who experienced massive bleeding during a cesarean section. We used resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta (REBOA) and it improved the condition of the surgical field and the hemodynamic stability of the patient temporarily. The patient was successfully managed without further complications.
Conclusions
REBOA can be used as a rescue procedure for uncontrolled bleeding situations in patients with MAPs. Anesthesiologists should consider and recommend REBOA as another resuscitative therapeutic option in the case of massive PPH.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bauer ST, Bonanno C. Abnormal placentation. Semin Perinatol. 2009; 33:88–96.2. Wu S, Kocherginsky M, Hibbard JU. Abnormal placentation: twenty-year analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005; 192:1458–61.3. Committee on Obstetric Practice. Committee opinion no. 529: placenta accreta. Obstet Gynecol. 2012; 120:207–11.4. Hudon L, Belfort MA, Broome DR. Diagnosis and management of placenta percreta: a review. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1998; 53:509–17.5. Lau TK, Leung TY. Prenatal diagnosis of morbidly adherent placenta. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2011; 20:107–9.6. Woodring TC, Klauser CK, Bofill JA, Martin RW, Morrison JC. Prediction of placenta accreta by ultrasonography and color Doppler imaging. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011; 24:118–21.7. Eller AG, Porter TF, Soisson P, Silver RM. Optimal management strategies for placenta accreta. BJOG. 2009; 116:648–54.8. Gonsalves M, Belli A. The role of interventional radiology in obstetric hemorrhage. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010; 33:887–95.9. Biffl WL, Fox CJ, Moore EE. The role of REBOA in the control of exsanguinating torso hemorrhage. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015; 78:1054–8.10. Manzano-Nunez R, Escobar-Vidarte MF, Orlas CP, Herrera-Escobar JP, Galvagno SM, Melendez JJ, et al. Resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta deployed by acute care surgeons in patients with morbidly adherent placenta: a feasible solution for two lives in peril. World J Emerg Surg. 2018; 13:44.11. Eller AG, Bennett MA, Sharshiner M, Masheter C, Soisson AP, Dodson M, et al. Maternal morbidity in cases of placenta accreta managed by a multidisciplinary care team compared with standard obstetric care. Obstet Gynecol. 2011; 117(2 Pt 1):331–7.12. Ordoñez CA, Manzano-Nunez R, Parra MW, Rasmussen TE, Nieto AJ, Herrera-Escobar JP, et al. Prophylactic use of resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta in women with abnormal placentation: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and case series. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018; 84:809–18.13. Manzano-Nunez R, Escobar-Vidarte MF, Naranjo MP, Rodriguez F, Ferrada P, Casallas JD, et al. Expanding the field of acute care surgery: a systematic review of the use of resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta (REBOA) in cases of morbidly adherent placenta. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2018; 44:519–26.14. Cui S, Zhi Y, Cheng G, Zhang K, Zhang L, Shen L. Retrospective analysis of placenta previa with abnormal placentation with and without prophylactic use of abdominal aorta balloon occlusion. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2017; 137:265–70.15. Wu Q, Liu Z, Zhao X, Liu C, Wang Y, Chu Q, et al. Outcome of pregnancies after balloon occlusion of the infrarenal abdominal aorta during caesarean in 230 patients with placenta praevia accreta. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2016; 39:1573–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intraoperative Use of Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta for Hemorrhage Control in Woman with Placenta Percreta Involving the Bladder
- Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta in a Trauma Patient with Hypovolemic Shock
- Management of massive hemorrhage in pregnant women with placenta previa
- Transsplenic Ultrasound-Guided Balloon Positioning During a Zone 1 Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta: A Case Report
- Positioning of Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta Catheter: A Case of an Elderly Patient with Concomitant Chest and Pelvic Injury after Blunt Trauma