J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2020 Jul;63(4):532-538. 10.3340/jkns.2019.0233.
Endovascular Treatment of Traumatic Arteriovenous Fistula in Young Adults with Pulsatile Tinnitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang, Korea
- KMID: 2504648
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2019.0233
Abstract
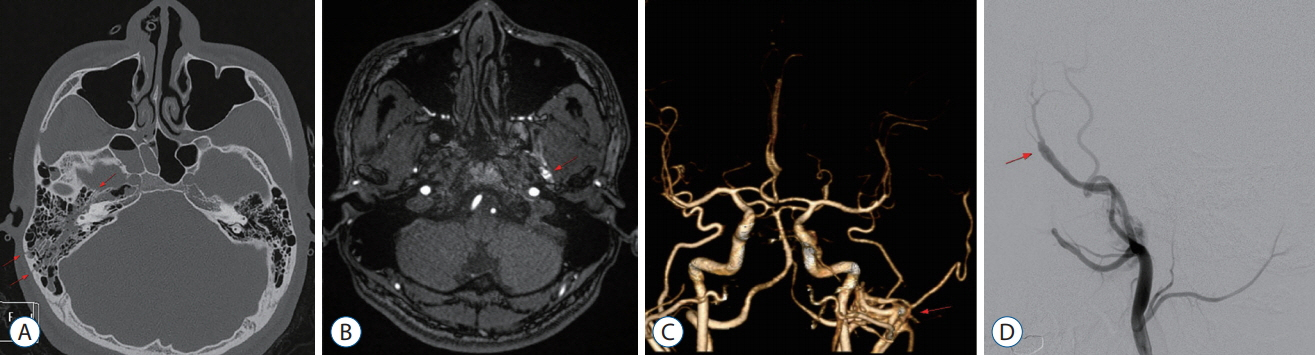
- Traumatic arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs) involving the external carotid artery are exceedingly rare in young adults. Since an AVF is the most common life-threatening cause for pulsatile tinnitus (PT), meticulous evaluation and treatment of patients with PT is crucial. Here, we present two traumatic AVF cases treated with coil embolization leading to no residual fistulous connections followed by an immediate and complete resolution of PT. A 20-year-old man developed left ear tinnitus three months after a traumatic brain injury involving the right temporal bone fracture. Cerebral angiography demonstrated an enlarged left middle meningeal artery (MMA) and a fistular point at the posterior branch of the MMA draining to the middle meningeal vein (MMV) and the left pterygoid plexus, suggesting an AVF. Another 18-year-old girl developed left tinnitus, left exophthalmos, and conjunctival injection 6 months after a traffic accident involving no demonstrable abnormal findings in the radiologic exam. Magnetic resonance angiography demonstrated a markedly dilated left MMA draining to the MMV, left cavernous sinus, and left superior ophthalmic vein. In both cases, coil embolization was performed with total obliteration of the fistular point.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. An YH, Han S, Lee M, Rhee J, Kwon OK, Hwang G, et al. Dural arteriovenous fistula masquerading as pulsatile tinnitus: radiologic assessment and clinical implications. Sci Rep. 6:36601. 2016.
Article2. Borden JA, Wu JK, Shucart WA. A proposed classification for spinal and cranial dural arteriovenous fistulous malformations and implications for treatment. J Neurosurg. 82:166–179. 1995.
Article3. Cognard C, Gobin YP, Pierot L, Bailly AL, Houdart E, Casasco A, et al. Cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas: clinical and angiographic correlation with a revised classification of venous drainage. Radiology. 194:671–680. 1995.
Article4. Deuschl C, Göricke S, Gramsch C, Özkan N, Lehnerdt G, Kastrup O, et al. Value of DSA in the diagnostic workup of pulsatile tinnitus. PLoS One. 10:e0117814. 2015.
Article5. Fincher EF. Arteriovenous fistula between the middle meningeal artery and the greater petrosal sinus; case report. Ann Surg. 133:886–888. 1951.
Article6. Freckmann N, Sartor K, Herrmann HD. Traumatic arteriovenous fistulae of the middle meningeal artery and neighbouring veins or dural sinuses. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 55:273–281. 1981.
Article7. Gandhi D, Chen J, Pearl M, Huang J, Gemmete JJ, Kathuria S. Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: classification, imaging findings, and treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 33:1007–1013. 2012.
Article8. Geibprasert S, Pongpech S, Armstrong D, Krings T. Dangerous extracranial-intracranial anastomoses and supply to the cranial nerves: vessels the neurointerventionalist needs to know. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 30:1459–1468. 2009.
Article9. Kiyosue H, Hori Y, Okahara M, Tanoue S, Sagara Y, Matsumoto S, et al. Treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: current strategies based on location and hemodynamics, and alternative techniques of transcatheter embolization. Radiographics. 24:1637–1653. 2004.
Article10. Letourneau-Guillon L, Krings T. Simultaneous arteriovenous shunting and venous congestion identification in dural arteriovenous fistulas using susceptibility-weighted imaging: initial experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 33:301–307. 2012.
Article11. Lockwood AH, Salvi RJ, Burkard RF. Tinnitus. N Engl J Med. 347:904–910. 2002.
Article12. Martinez M, Pergami P, Murnick J, Pearl MS. Embolization of a traumatic arteriovenous fistula between the middle meningeal artery and middle meningeal vein in a child with pulsatile tinnitus. Childs Nerv Syst. 34:571–575. 2018.
Article13. Noguchi K, Kuwayama N, Kubo M, Kamisaki Y, Kameda K, Tomizawa G, et al. Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula with retrograde cortical venous drainage: use of susceptibility-weighted imaging in combination with dynamic susceptibility contrast imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 3:1903–1910. 2010.
Article14. Pakarinen S. Arteriovenous fistula betwwen the middle meningeal artery and the sphenoparietal sinus. A case report. J Neurosurgery. 23:438–439. 1965.
Article15. Remley KB, Coit WE, Harnsberger HR, Smoker WR, Jacobs JM, McIff EB. Pulsatile tinnitus and the vascular tympanic membrane: CT, MR, and angiographic findings. Radiology. 174:383–389. 1990.
Article16. Saini J, Thomas B, Bodhey NK, Periakaruppan A, Babulal JM. Susceptibility-weighted imaging in cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 30:E6. 2009.17. Sila CA, Furlan AJ, Little JR. Pulsatile tinnitus. Stroke. 18:252–256. 1987.
Article18. Sismanis A, Smoker WR. Pulsatile tinnitus: recent advances in diagnosis. Laryngoscope. 104(6 Pt 1):681–688. 1994.19. Söderman M, Pavic L, Edner G, Holmin S, Andersson T. Natural history of dural arteriovenous shunts. Stroke. 39:1735–1739. 2008.
Article20. Song JJ, Kim YJ, Kim SY, An YS, Kim K, Lee SY, et al. Sinus wall resurfacing for patients with temporal bone venous sinus diverticulum and ipsilateral pulsatile tinnitus. Neurosurgery. 77:709–717. discussion 717. 2015.
Article21. Stouffer JL, Tyler RS. Characterization of tinnitus by tinnitus patients. J Speech Hear Disord. 55:439–453. 1990.
Article22. Takeuchi S, Takasato Y, Masaoka H, Hayakawa T, Otani N, Yoshino Y, et al. A case of traumatic middle meningeal arteriovenous fistula on the side of the head opposite to the injured side. No Shinkei Geka. 37:983–986. 2009.23. Unterhofer C, Chemelli A, Waldenberger P, Bauer R, Ortler M. Traumatic fistula between the middle meningeal artery and the sphenoparietal sinus. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 151:1301–1304. 2009.
Article24. Vassilyadi M, Mehrotra N, Shamji MF, Michaud J. Pediatric traumatic dural arteriovenous fistula. Can J Neurol Sci. 36:751–756. 2009.
Article25. Waldvogel D, Mattle HP, Sturzenegger M, Schroth G. Pulsatile tinnitus--a review of 84 patients. J Neurol. 245:137–142. 1998.26. Wee JH, Song JJ, Koo JW, Kim CS. Increased intracranial pressure after surgical treatment of pulsatile tinnitus from a prominent sigmoid sinus. Otol Neurotol. 33:e41–e42. 2012.
Article27. Yu J, Guo Y, Wu Z, Xu K. Traumatic arteriovenous fistula between the extracranial middle meningeal artery and the pterygoid plexus: a case report and literature review. Interv Neuroradiol. 23:90–96. 2017.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pulsatile Tinnitus Caused by Arteriovenous Fistula of External Carotid Artery
- Tinnitus Caused by Traumatic Posterior Auricular Artery-Internal Jugular Vein Fistula
- A Case of the Pulsatile Tinnitus due to Post-traumatic Arteriovenous Fistula Involving Superficial Temporal Artery Treated with Percutaneous Embolization
- A Case of Therapeutic Percutaneous Embolization of Spontaneous Arteriovenous Fistulas with Pulsatile Tinnitus Involving the Branches of the Left External Carotid Artery
- Multiple Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Presenting as Pulsatile Tinnitus Treated with External Manual Compression