J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2020 Jul;63(4):455-462. 10.3340/jkns.2020.0036.
Arachnoid Plasty to Prevent and Reduce Chronic Subdural Hematoma after Clipping Surgery for Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm : A Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2504639
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2020.0036
Abstract
Objective
: Recent studies have reported that arachnoid plasty (ARP) using gelatin sponges with fibrin glue reduced the occurrence of chronic subdural hematoma (CSDH) following clipping surgery for unruptured intracranial aneurysm (UIA). This metaanalysis was conducted to collate further evidence for the efficacy of ARP in preventing postoperative CSDH.
Methods
: Data of patients who underwent clipping surgery were extracted from PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials by two independent reviewers. A random effects model was used to investigate the efficacy of ARP by using odd ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). A meta-regression analysis for male sex was additionally preformed.
Results
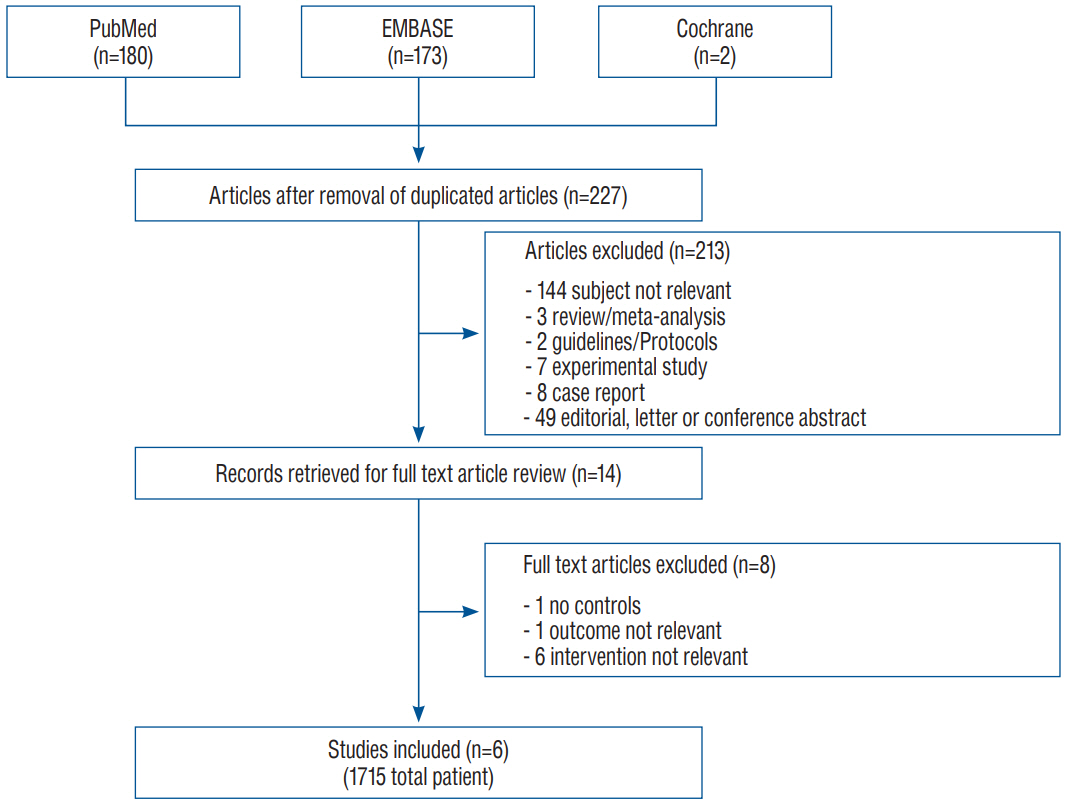
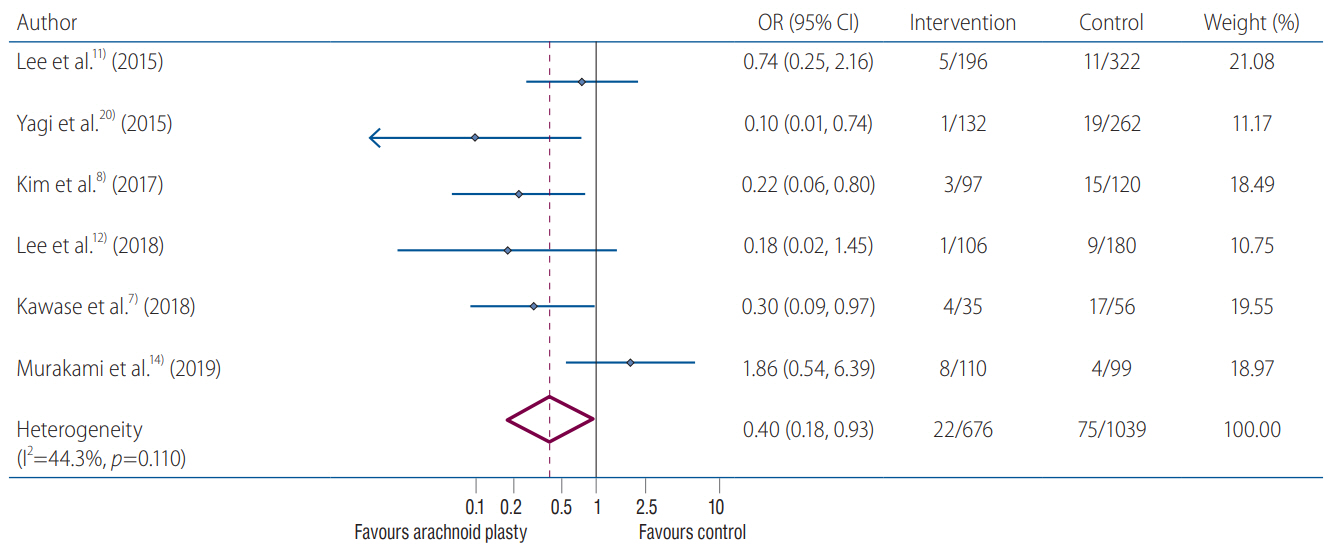
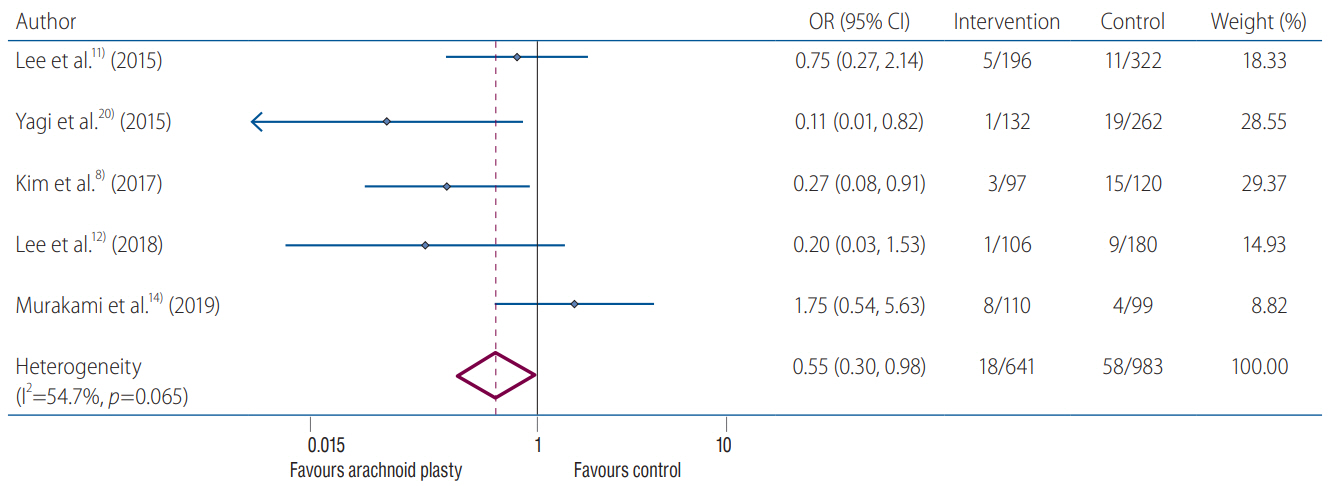
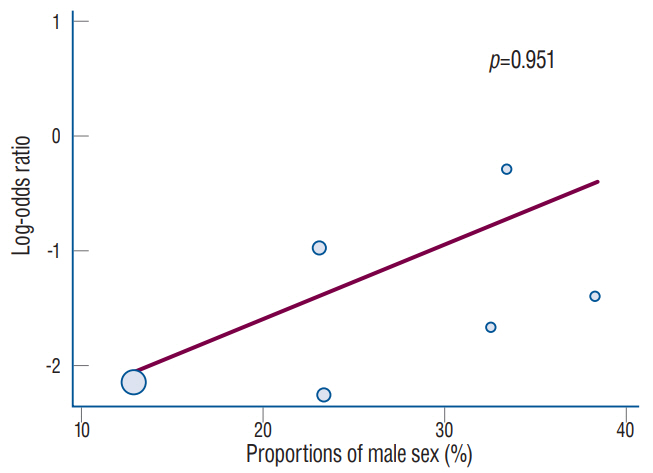
: Data from six studies with 1715 patients were consecutively included. Meta-analysis revealed that ARP was significantly associated with lower rates of CSDH development after surgical clipping for UIA (ARP group vs. control group : 3.2% vs. 7.2%; OR, 0.40; 95% CI, 0.18–0.93; I2 =44.3%; p=0.110). Meta-regression analysis did not highlight any modifying effect of the male sex on postoperative CSDH development (p=0.951).
Conclusion
: This meta-analysis indicated that ARP reduced the incidence rates of CSDH following clipping surgery for UIA. If feasible, ARP would be implemented as an additional surgical technique to prevent postoperative CSDH development during surgical clipping of UIA.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Desai VR, Scranton RA, Britz GW. Management of recurrent subdural hematomas. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 28:279–286. 2017.
Article2. Gazzeri R, Galarza M, Neroni M, Alfieri A, Giordano M. Hemostatic matrix sealant in neurosurgery: a clinical and imaging study. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 153:148–155. 2011.
Article3. Inamasu J, Watabe T, Ganaha T, Yamada Y, Nakae S, Ohmi T, et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of chronic subdural haematoma associated with clipping of unruptured cerebral aneurysms. J Clin Neurosci. 20:1095–1098. 2013.
Article4. Jung YJ, Ahn JS, Park ES, Kwon DH, Kwun BD, Kim CJ. Surgical results of unruptured intracranial aneurysms in the elderly : single center experience in the past ten years. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 49:329–333. 2011.
Article5. Kang JH, Huh SK, Kim J, Park KY, Chung J. Subdural fluid collection after the clipping of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: its clinical course and significance. World Neurosurg. 116:e266–e272. 2018.
Article6. Kawabata S, Tani S, Imamura H, Adachi H, Sakai N. Postoperative subdural air collection is a risk factor for chronic subdural hematoma after surgical clipping of cerebral aneurysms. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 58:247–253. 2018.
Article7. Kawase T, Bishnoi I, Tanaka R, Dash C, Kato Y, Yamada Y. Study of incidence and factors: risk and preventive, of chronic subdural hematoma/hygroma in clipped patients of unruptured intracranial aneurysms - an institutional experience. Asian J Neurosurg. 13:707–713. 2018.
Article8. Kim JH, Kim CH, Lee CY. Efficacy of arachnoid-plasty on chronic subdural hematoma following surgical clipping of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. World neurosurgery. 104:303–310. 2017.
Article9. Kwon MY, Kim CH, Lee CY. Predicting factors of chronic subdural hematoma following surgical clipping in unruptured and ruptured intracranial aneurysm. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 59:458–465. 2016.
Article10. Lee KS. The pathogenesis and clinical significance of traumatic subdural hygroma. Brain Inj. 12:595–603. 1998.
Article11. Lee WJ, Jo KI, Yeon JY, Hong SC, Kim JS. Incidence and risk factors of chronic subdural hematoma after surgical clipping for unruptured anterior circulation aneurysms. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 57:271–275. 2015.
Article12. Lee WJ, Nam TM, Jo KI, Yeon JY, Hong SC, Kim JS. Modified arachnoid plasty reduces chronic subdural hematoma after unruptured aneurysm clipping : technical note. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 61:761–766. 2018.
Article13. Mino Y, Hirashima Y, Hamada H, Masuoka T, Yamatani K, Takeda S, et al. Effect of arachnoid plasty using fibrin glue membrane after clipping of ruptured aneurysm on the occurrence of complications and outcome in the elderly patients. Acta neurochirurgica (Wien). 148:627–631. discussion 631. 2006.
Article14. Murakami T, Nakagawa I, Park HS, Kotsugi M, Takamura Y, Takeshima Y, et al. Extensive postoperative subdural fluid volume affects the onset of chronic subdural hematoma after unruptured aneurysmal clipping surgery. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 187:105533. 2019.
Article15. Ohno T, Iihara K, Takahashi JC, Nakajima N, Satow T, Hishikawa T, et al. Incidence and risk factors of chronic subdural hematoma after aneurysmal clipping. World Neurosurg. 80:534–537. 2013.
Article16. Park J, Cho JH, Goh DH, Kang DH, Shin IH, Hamm IS. Postoperative subdural hygroma and chronic subdural hematoma after unruptured aneurysm surgery: age, sex, and aneurysm location as independent risk factors. J Neurosurg. 124:310–317. 2016.
Article17. Schardt C, Adams MB, Owens T, Keitz S, Fontelo P. Utilization of the PICO framework to improve searching PubMed for clinical questions. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 7:16. 2007.
Article18. Sundstrøm T, Helland CA, Aarhus M, Wester K. What is the pressure in chronic subdural hematomas? A prospective, population-based study. J Neurotrauma. 29:137–142. 2012.
Article19. Tsuruno T. An arachnoid plasty technique using a collagen seat and fibrin glue. Jpn J Neurosurg (Tokyo). 4:193–195. 1995.
Article20. Yagi K, Irie S, Inagaki T, Ishii Y, Saito O, Lee T, et al. Intraoperative arachnoid plasty has possibility to prevent chronic subdural hematoma after surgery for unruptured cerebral aneurysms. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 55:493–497. 2015.
Article21. Yamamoto H, Hirashima Y, Hamada H, Hayashi N, Origasa H, Endo S. Independent predictors of recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma: results of multivariate analysis performed using a logistic regression model. J Neurosurg. 98:1217–1221. 2003.
Article22. Yoshimoto Y, Wakai S, Hamano M. External hydrocephalus after aneurysm surgery: paradoxical response to ventricular shunting. J Neurosurg. 88:485–489. 1998.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Modified Arachnoid Plasty Reduces Chronic Subdural Hematoma after Unruptured Aneurysm Clipping : Technical Note
- Treatment of Chronic Subdural Hematoma with Arachnoid Cyst
- Predicting Factors of Chronic Subdural Hematoma Following Surgical Clipping in Unruptured and Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysm
- Incidence and Risk Factors of Chronic Subdural Hematoma after Surgical Clipping for Unruptured Anterior Circulation Aneurysms
- Two Cases of Posterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm Complicated by Massive Subdural Hematoma