Cancer Res Treat.
2020 Jul;52(3):973-986. 10.4143/crt.2019.726.
RON and MET Co-overexpression Are Significant Pathological Characteristics of Poor Survival and Therapeutic Targets of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1State Key Laboratory for Diagnosis & Treatment of Infectious Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Zhejiang, China
- 2National Clinical Research Center for Infectious Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Zhejiang, China
- 3Department of Breast Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
- 4Department of Colorectal Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
- 5Department of Stormotologry, Wenzhou Medical University Renji College, Wenzhou, China
- 6Cancer Biology Research Center, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center School of Pharmacy, Amarillo, TX, USA
- 7Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center School of Pharmacy, Amarillo, TX, USA
- KMID: 2504475
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2019.726
Abstract
- Purpose
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is highly malignant and has poor prognosis and a high mortality rate. The lack of effective therapy has spurred our investigation of new targets for treating this malignant cancer. Here, we identified RON (macrophage-stimulating 1 receptor) and MET (MET proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase) as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic targets for potential TNBC treatment.
Materials and Methods
We analyzed RON and MET expression in 187 primary TNBC clinical samples with immunohistochemistry. We validated the targeted therapeutic effects of RON and MET in TNBC using three tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs): BMS-777607, INCB28060, and tivantinib. The preclinical therapeutic efficacy of the TKIs was mainly estimated using a TNBC xenograft model.
Results
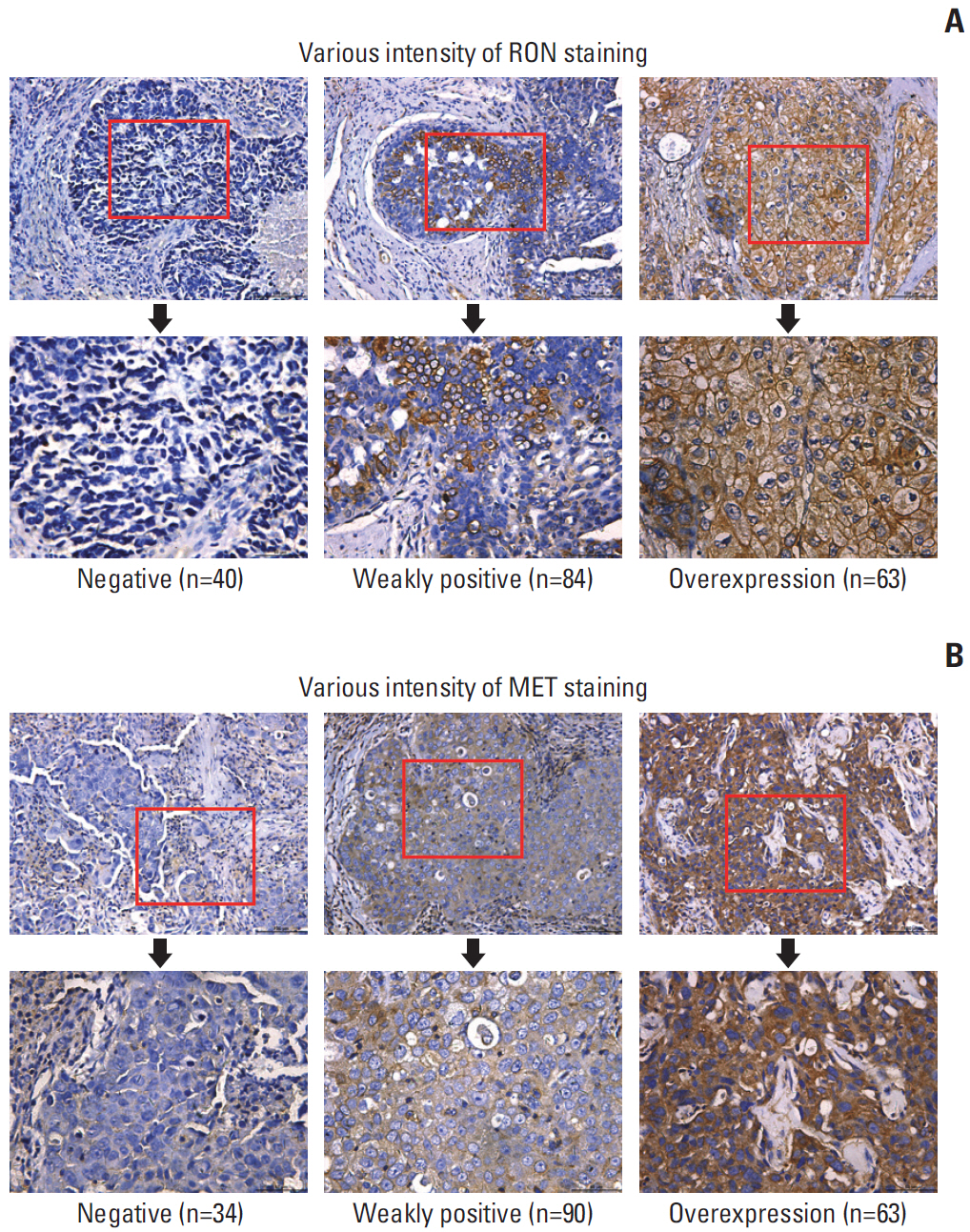
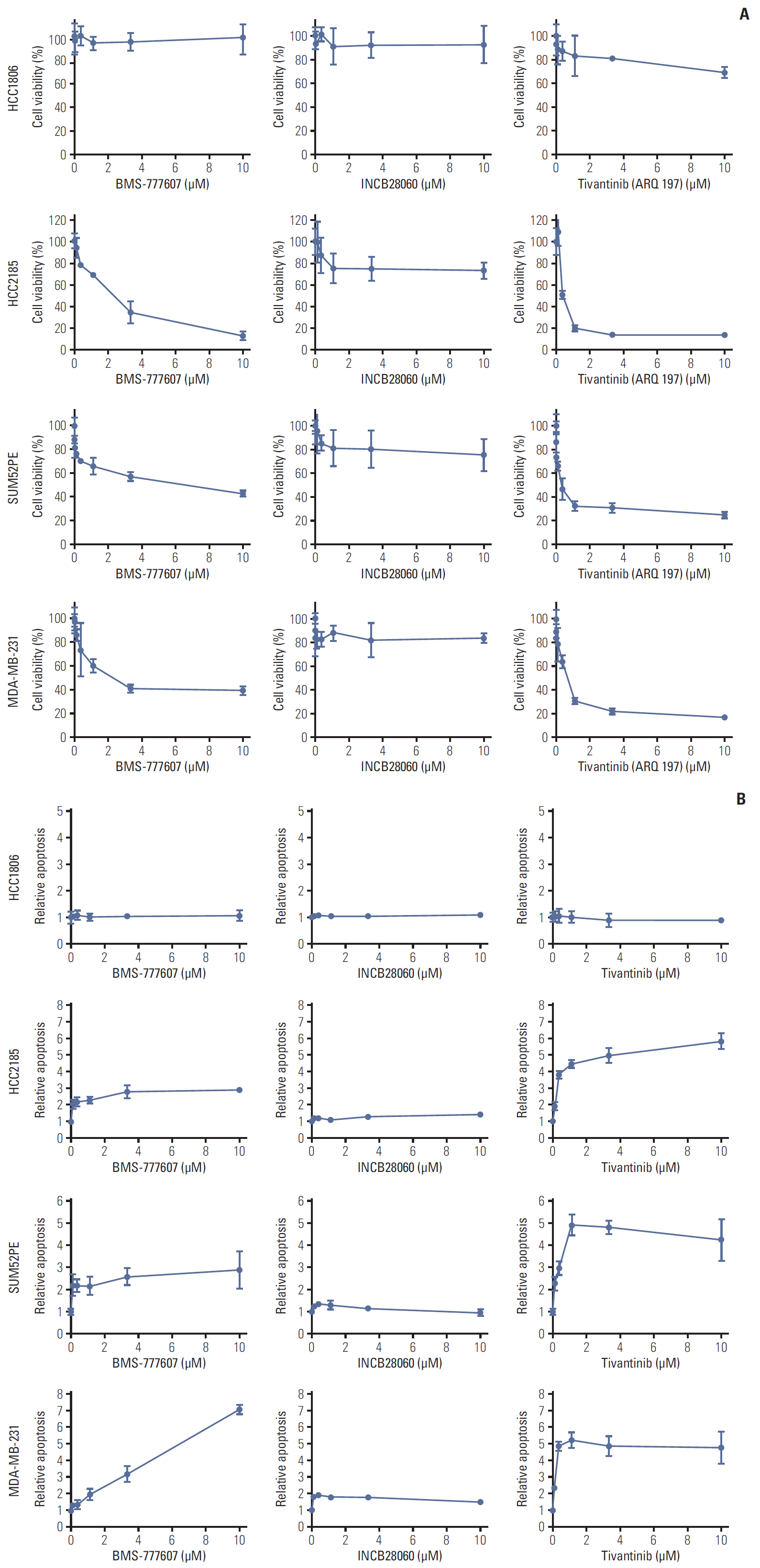
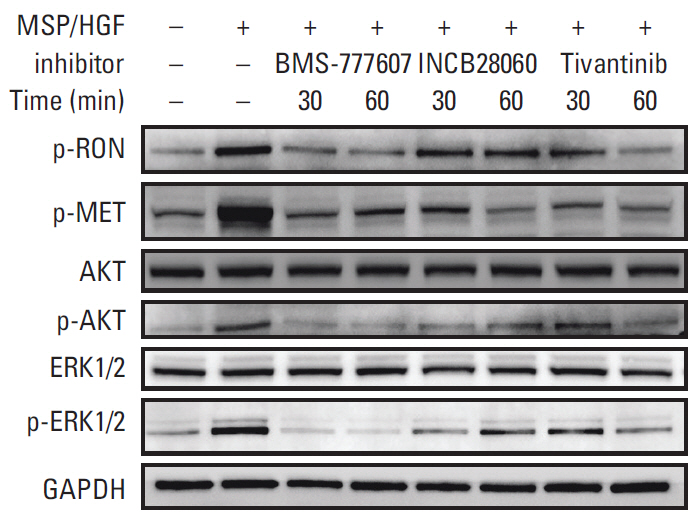
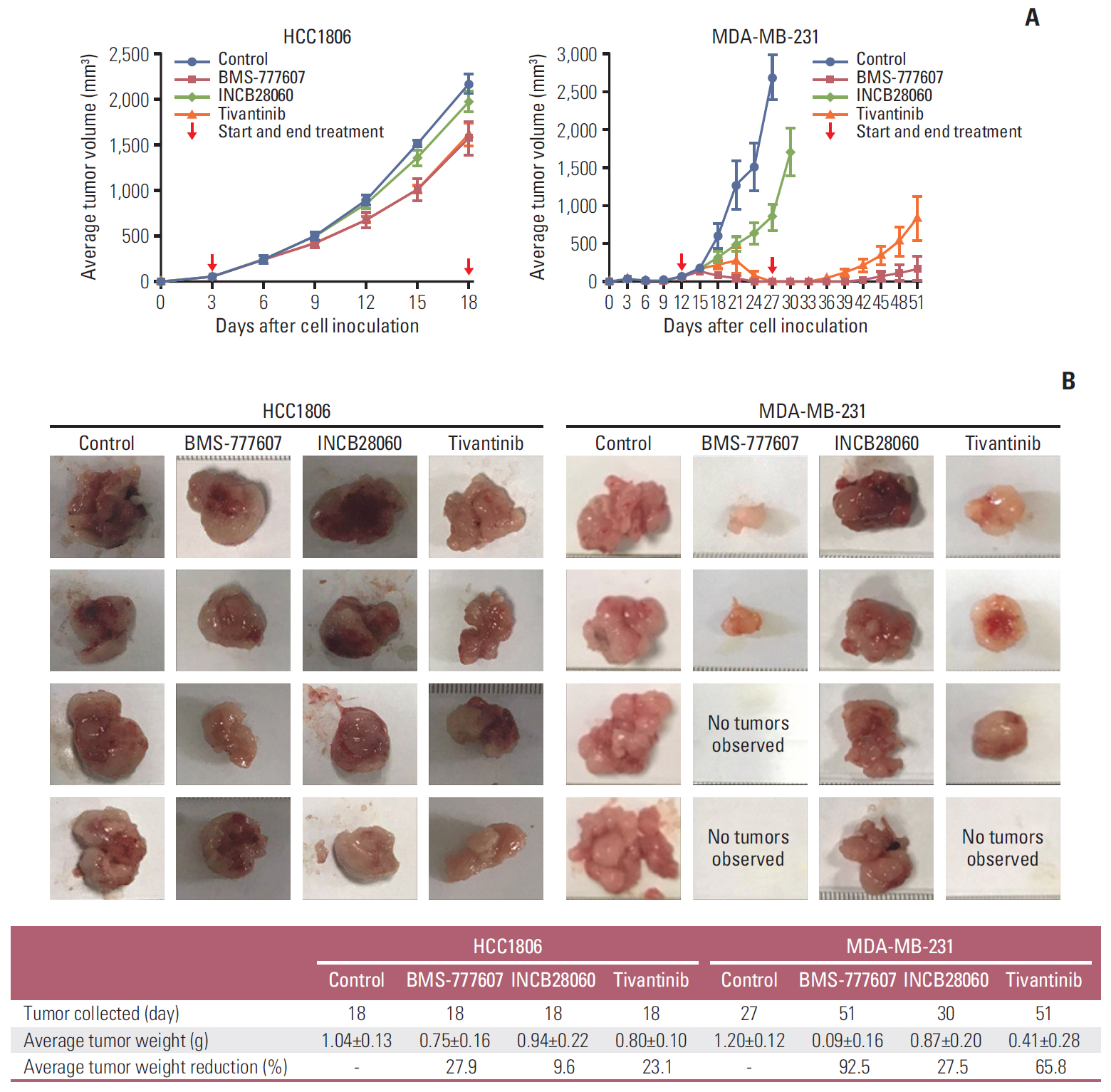
Patients with TNBC had widespread, abnormal expression of RON and MET. There was RON overexpression, MET overexpression, and RON and MET co-overexpression in 63 (33.7%), 63 (33.7%), and 43 cases (23.0%), respectively, which had poor prognosis and short survival. In vivo, the TKI targeting RON ant MET inhibited the activation of the downstream signaling molecules, inhibited TNBC cell migration and proliferation, and increased TNBC cell apoptosis; in the xenograft model, they significantly inhibited tumor growth and shrank tumor volumes. The TKI targeting RON and Met, such as BMS-777607 and tivantinib, yielded stronger anti-tumor effects than INCB28060.
Conclusion
RON and MET co-overexpression can be significant pathological characteristics in TNBC for poor prognosis. TKIs targeting RON and MET have stronger drug development potential for treating TNBC.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Bianchini G, Balko JM, Mayer IA, Sanders ME, Gianni L. Triple-negative breast cancer: challenges and opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016; 13:674–90.
Article2. Liao HY, Zhang WW, Sun JY, Li FY, He ZY, Wu SG. The clinicopathological features and survival outcomes of different histological subtypes in triple-negative breast cancer. J Cancer. 2018; 9:296–303.
Article3. Robinson DR, Wu YM, Lin SF. The protein tyrosine kinase family of the human genome. Oncogene. 2000; 19:5548–57.
Article4. Ronsin C, Muscatelli F, Mattei MG, Breathnach R. A novel putative receptor protein tyrosine kinase of the met family. Oncogene. 1993; 8:1195–202.5. Lai AZ, Abella JV, Park M. Crosstalk in Met receptor oncogenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 2009; 19:542–51.
Article6. Yao HP, Zhou YQ, Zhang R, Wang MH. MSP-RON signalling in cancer: pathogenesis and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013; 13:466–81.
Article7. Gherardi E, Birchmeier W, Birchmeier C, Vande Woude G. Targeting MET in cancer: rationale and progress. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012; 12:89–103.
Article8. Yao HP, Zhuang CM, Zhou YQ, Zeng JY, Zhang RW, Wang MH. Oncogenic variant RON160 expression in breast cancer and its potential as a therapeutic target by small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013; 13:686–97.
Article9. Maggiora P, Marchio S, Stella MC, Giai M, Belfiore A, De Bortoli M, et al. Overexpression of the RON gene in human breast carcinoma. Oncogene. 1998; 16:2927–33.
Article10. Zhao H, Chen MS, Lo YH, Waltz SE, Wang J, Ho PC, et al. The Ron receptor tyrosine kinase activates c-Abl to promote cell proliferation through tyrosine phosphorylation of PCNA in breast cancer. Oncogene. 2014; 33:1429–37.
Article11. Cunha S, Lin YC, Goossen EA, DeVette CI, Albertella MR, Thomson S, et al. The RON receptor tyrosine kinase promotes metastasis by triggering MBD4-dependent DNA methylation reprogramming. Cell Rep. 2014; 6:141–54.
Article12. Kretschmann KL, Eyob H, Buys SS, Welm AL. The macrophage stimulating protein/Ron pathway as a potential therapeutic target to impede multiple mechanisms involved in breast cancer progression. Curr Drug Targets. 2010; 11:1157–68.
Article13. Sharma S, Zeng JY, Zhuang CM, Zhou YQ, Yao HP, Hu X, et al. Small-molecule inhibitor BMS-777607 induces breast cancer cell polyploidy with increased resistance to cytotoxic chemotherapy agents. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013; 12:725–36.
Article14. Bieniasz M, Radhakrishnan P, Faham N, De La OJ, Welm AL. Preclinical efficacy of Ron kinase inhibitors alone and in combination with PI3K inhibitors for treatment of sfRon-expressing breast cancer patient-derived xenografts. Clin Cancer Res. 2015; 21:5588–600.
Article15. Lee WY, Chen HH, Chow NH, Su WC, Lin PW, Guo HR. Prognostic significance of co-expression of RON and MET receptors in node-negative breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11:2222–8.
Article16. Lindemann K, Resau J, Nahrig J, Kort E, Leeser B, Annecke K, et al. Differential expression of c-Met, its ligand HGF/SF and HER2/neu in DCIS and adjacent normal breast tissue. Histopathology. 2007; 51:54–62.
Article17. Ponzo MG, Lesurf R, Petkiewicz S, O'Malley FP, Pinnaduwage D, Andrulis IL, et al. Met induces mammary tumors with diverse histologies and is associated with poor outcome and human basal breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106:12903–8.
Article18. Graveel CR, DeGroot JD, Su Y, Koeman J, Dykema K, Leung S, et al. Met induces diverse mammary carcinomas in mice and is associated with human basal breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106:12909–14.
Article19. Comoglio PM, Giordano S, Trusolino L. Drug development of MET inhibitors: targeting oncogene addiction and expedience. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008; 7:504–16.
Article20. Schroeder GM, An Y, Cai ZW, Chen XT, Clark C, Cornelius LA, et al. Discovery of N-(4-(2-amino-3-chloropyridin-4-yloxy)-3-fluorophenyl)-4-ethoxy-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridine-3-carboxamide (BMS-777607), a selective and orally efficacious inhibitor of the Met kinase superfamily. J Med Chem. 2009; 52:1251–4.
Article21. Lauter M, Weber A, Torka R. Targeting of the AXL receptor tyrosine kinase by small molecule inhibitor leads to AXL cell surface accumulation by impairing the ubiquitin-dependent receptor degradation. Cell Commun Signal. 2019; 17:59.
Article22. Liu X, Wang Q, Yang G, Marando C, Koblish HK, Hall LM, et al. A novel kinase inhibitor, INCB28060, blocks c-MET-dependent signaling, neoplastic activities, and cross-talk with EGFR and HER-3. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17:7127–38.
Article23. Munshi N, Jeay S, Li Y, Chen CR, France DS, Ashwell MA, et al. ARQ 197, a novel and selective inhibitor of the human c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase with antitumor activity. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010; 9:1544–53.
Article24. Wang MH, Lee W, Luo YL, Weis MT, Yao HP. Altered expression of the RON receptor tyrosine kinase in various epithelial cancers and its contribution to tumourigenic phenotypes in thyroid cancer cells. J Pathol. 2007; 213:402–11.
Article25. Suthe SR, Yao HP, Weng TH, Hu CY, Feng L, Wu ZG, et al. RON receptor tyrosine kinase as a therapeutic target for eradication of triple-negative breast cancer: efficacy of anti-RON ADC Zt/g4-MMAE. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018; 17:2654–64.
Article26. Tsimafeyeu I, Stepanova E, Khochenkov D, Murillo G, Lapina N, Gavrilova E, et al. Preclinical characterization of alofanib, a novel allosteric FGFR2 inhibitor. Ann Oncol. 2016; 27(Suppl 9):ix45–51.
Article27. Chaudhuri A, Xie MH, Yang B, Mahapatra K, Liu J, Marsters S, et al. Distinct involvement of the Gab1 and Grb2 adaptor proteins in signal transduction by the related receptor tyrosine kinases RON and MET. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286:32762–74.
Article28. Li BQ, Wang MH, Kung HF, Ronsin C, Breathnach R, Leonard EJ, et al. Macrophage-stimulating protein activates Ras by both activation and translocation of SOS nucleotide exchange factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995; 216:110–8.
Article29. Doehn U, Hauge C, Frank SR, Jensen CJ, Duda K, Nielsen JV, et al. RSK is a principal effector of the RAS-ERK pathway for eliciting a coordinate promotile/invasive gene program and phenotype in epithelial cells. Mol Cell. 2009; 35:511–22.
Article30. Wang MH, Montero-Julian FA, Dauny I, Leonard EJ. Requirement of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase for epithelial cell migration activated by human macrophage stimulating protein. Oncogene. 1996; 13:2167–75.31. Torka R, Penzes K, Gusenbauer S, Baumann C, Szabadkai I, Orfi L, et al. Activation of HER3 interferes with antitumor effects of Axl receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors: suggestion of combination therapy. Neoplasia. 2014; 16:301–18.
Article32. Xiang Q, Zhen Z, Deng DY, Wang J, Chen Y, Li J, et al. Tivantinib induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis by disrupting tubulin polymerization in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015; 34:118.
Article33. Follenzi A, Bakovic S, Gual P, Stella MC, Longati P, Comoglio PM. Cross-talk between the proto-oncogenes Met and Ron. Oncogene. 2000; 19:3041–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of Recepteur D'origine Nantais on Gastric Cancer Development and Progression
- Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Early Stage Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Comparison with Non-triple Negative Group
- Molecular Basis of Drug Resistance: Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitors
- The Cancer/Testis Antigen CT45A1 Promotes Transcription of Oncogenic Sulfatase-2 Gene in Breast Cancer Cells and Is Sensible Targets for Cancer Therapy
- The Expressions of Tyrosine Kinase Receptors, EphA2, c-met and c-erbB-2 in the Human Breast