J Korean Med Sci.
2020 Jul;35(28):e230. 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e230.
Clinical Perspectives of Parkinson's Disease for Ophthalmologists, Otorhinolaryngologists, Cardiologists, Dentists, Gastroenterologists, Urologists, Physiatrists, and Psychiatrists
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 3Department of Dentistry, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 5Department of Urology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 6Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 7Department of Neuropsychiatry, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 8Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 9Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- KMID: 2504364
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e230
Abstract
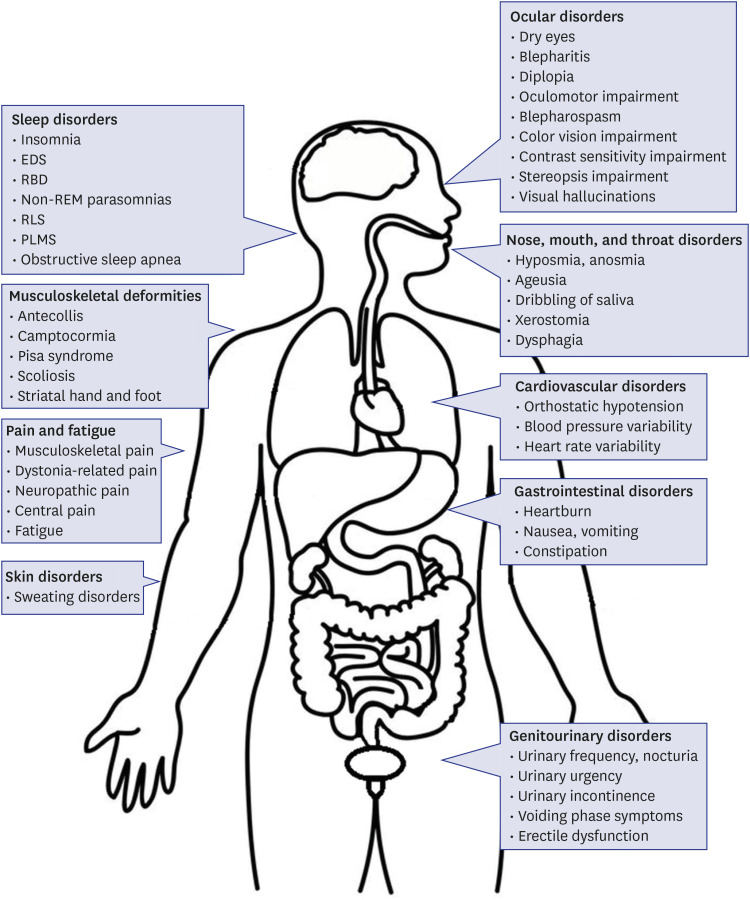
- Parkinson's disease (PD) is a multisystemic disorder characterized by various non-motor symptoms (NMS) in addition to motor dysfunction. NMS include sleep, ocular, olfactory, throat, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, or musculoskeletal disorders. A range of NMS, particularly hyposmia, sleep disturbances, constipation, and depression, can even appear prior to the motor symptoms of PD. Because NMS can affect multiple organs and result in major disabilities, the recognition and multidisciplinary and collaborative management of NMS by physicians is essential for patients with PD. Therefore, the aim of this review article is to provide an overview of the organs that are affected by NMS in PD together with a brief review of pathophysiology and treatment options.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Louis ED, Ferreira JJ. How common is the most common adult movement disorder? Update on the worldwide prevalence of essential tremor. Mov Disord. 2010; 25(5):534–541. PMID: 20175185.
Article2. Tanner CM, Goldman SM. Epidemiology of Parkinson's disease. Neurol Clin. 1996; 14(2):317–335. PMID: 8827174.
Article3. Kim JM, Kim JS, Kim KW, Lee SB, Park JH, Lee JJ, et al. Study of the prevalence of Parkinson's disease using dopamine transporter imaging. Neurol Res. 2010; 32(8):845–851. PMID: 20021740.
Article4. Oh ES, Kim JM, Kim YE, Yun JY, Kim JS, Kim SE, et al. The prevalence of essential tremor in elderly Koreans. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29(12):1694–1698. PMID: 25469072.
Article5. Postuma RB, Aarsland D, Barone P, Burn DJ, Hawkes CH, Oertel W, et al. Identifying prodromal Parkinson's disease: pre-motor disorders in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2012; 27(5):617–626. PMID: 22508280.
Article6. Barone P, Antonini A, Colosimo C, Marconi R, Morgante L, Avarello TP, et al. The PRIAMO study: a multicenter assessment of nonmotor symptoms and their impact on quality of life in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2009; 24(11):1641–1649. PMID: 19514014.
Article7. Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2003; 24(2):197–211. PMID: 12498954.
Article8. Forno LS. Neuropathology of Parkinson's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1996; 55(3):259–272. PMID: 8786384.9. Chaudhuri KR, Healy DG, Schapira AH. National Institute for Clinical Excellence. Non-motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease: diagnosis and management. Lancet Neurol. 2006; 5(3):235–245. PMID: 16488379.
Article10. Rana AQ, Ahmed US, Chaudry ZM, Vasan S. Parkinson's disease: a review of non-motor symptoms. Expert Rev Neurother. 2015; 15(5):549–562. PMID: 25936847.
Article11. Seppi K, Ray Chaudhuri K, Coelho M, Fox SH, Katzenschlager R, Perez Lloret S, et al. Update on treatments for nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson's disease-an evidence-based medicine review. Mov Disord. 2019; 34(2):180–198. PMID: 30653247.
Article12. Han JW, Ahn YD, Kim WS, Shin CM, Jeong SJ, Song YS, et al. Psychiatric manifestation in patients with Parkinson's disease. J Korean Med Sci. 2018; 33(47):e300. PMID: 30450025.
Article13. Garcia-Borreguero D, Larrosa O, Bravo M. Parkinson's disease and sleep. Sleep Med Rev. 2003; 7(2):115–129. PMID: 12628213.
Article14. Bonnet AM, Jutras MF, Czernecki V, Corvol JC, Vidailhet M. Nonmotor symptoms in Parkinson's disease in 2012: relevant clinical aspects. Parkinsons Dis. 2012; 2012:198316. PMID: 22888466.
Article15. French IT, Muthusamy KA. A review of sleep and its disorders in patients with Parkinson's disease in relation to various brain structures. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016; 8:114. PMID: 27242523.
Article16. Salawu F, Olokoba A. Excessive daytime sleepiness and unintended sleep episodes associated with Parkinson's disease. Oman Med J. 2015; 30(1):3–10. PMID: 25829994.
Article17. Gjerstad MD, Wentzel-Larsen T, Aarsland D, Larsen JP. Insomnia in Parkinson's disease: frequency and progression over time. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007; 78(5):476–479. PMID: 17098844.
Article18. Riemann D, Spiegelhalder K, Feige B, Voderholzer U, Berger M, Perlis M, et al. The hyperarousal model of insomnia: a review of the concept and its evidence. Sleep Med Rev. 2010; 14(1):19–31. PMID: 19481481.
Article19. Suzuki K, Miyamoto M, Miyamoto T, Iwanami M, Hirata K. Sleep disturbances associated with Parkinson's disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2011; 2011:219056. PMID: 21876839.
Article20. Arnulf I, Konofal E, Merino-Andreu M, Houeto JL, Mesnage V, Welter ML, et al. Parkinson's disease and sleepiness: an integral part of PD. Neurology. 2002; 58(7):1019–1024. PMID: 11940685.
Article21. Tandberg E, Larsen JP, Karlsen K. Excessive daytime sleepiness and sleep benefit in Parkinson's disease: a community-based study. Mov Disord. 1999; 14(6):922–927. PMID: 10584665.
Article22. Abbott RD, Ross GW, White L. Excessive daytime sleepiness and the future risk of Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2005; 20:S101.23. Pirker W, Happe S. Sleep attacks in Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2000; 356(9229):597–598.
Article24. Gjerstad MD, Alves G, Wentzel-Larsen T, Aarsland D, Larsen JP. Excessive daytime sleepiness in Parkinson disease: is it the drugs or the disease? Neurology. 2006; 67(5):853–858. PMID: 16966550.
Article25. Ferreira JJ, Galitzky M, Thalamas C, Tiberge M, Montastruc JL, Sampaio C, et al. Effect of ropinirole on sleep onset: a randomized, placebo-controlled study in healthy volunteers. Neurology. 2002; 58(3):460–462. PMID: 11839850.
Article26. Olson EJ, Boeve BF, Silber MH. Rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder: demographic, clinical and laboratory findings in 93 cases. Brain. 2000; 123(Pt 2):331–339. PMID: 10648440.
Article27. Schenck CH, Boeve BF, Mahowald MW. Delayed emergence of a parkinsonian disorder or dementia in 81% of older men initially diagnosed with idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder: a 16-year update on a previously reported series. Sleep Med. 2013; 14(8):744–748. PMID: 23347909.
Article28. Schenck CH, Bundlie SR, Mahowald MW. Delayed emergence of a parkinsonian disorder in 38% of 29 older men initially diagnosed with idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder. Neurology. 1996; 46(2):388–393. PMID: 8614500.29. Shouse MN, Siegel JM. Pontine regulation of REM sleep components in cats: integrity of the pedunculopontine tegmentum (PPT) is important for phasic events but unnecessary for atonia during REM sleep. Brain Res. 1992; 571(1):50–63. PMID: 1611494.
Article30. Lai YY, Siegel JM. Muscle tone suppression and stepping produced by stimulation of midbrain and rostral pontine reticular formation. J Neurosci. 1990; 10(8):2727–2734. PMID: 2388085.
Article31. Ratti PL, Sierra-Peña M, Manni R, Simonetta-Moreau M, Bastin J, Mace H, et al. Distinctive features of NREM parasomnia behaviors in Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy. PLoS One. 2015; 10(3):e0120973. PMID: 25756280.
Article32. Liu Y, Zhu XY, Zhang XJ, Kuo SH, Ondo WG, Wu YC. Clinical features of Parkinson's disease with and without rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. Transl Neurodegener. 2017; 6:35. PMID: 29296278.
Article33. Bohnen NI, Kanel P, Müller ML. Chapter seven - molecular imaging of the cholinergic system in Parkinson's disease. In : Politis M, editor. International Review of Neurobiology. Boston, MA: Academic Press;2018. p. 211–250.34. Mahowald MW, Schenck CH, Bornemann MA. Pathophysiologic mechanisms in REM sleep behavior disorder. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2007; 7(2):167–172. PMID: 17355839.
Article35. Garcia-Borreguero D, Odin P, Serrano C. Restless legs syndrome and PD: a review of the evidence for a possible association. Neurology. 2003; 61(6):Suppl 3. S49–S55.
Article36. Winkelman JW. Considering the causes of RLS. Eur J Neurol. 2006; 13(Suppl 3):8–14. PMID: 16930377.
Article37. Rye DB. Parkinson's disease and RLS: the dopaminergic bridge. Sleep Med. 2004; 5(3):317–328. PMID: 15165542.
Article38. Ferini-Strambi L, Carli G, Casoni F, Galbiati A. Restless legs syndrome and Parkinson disease: a causal relationship between the two disorders? Front Neurol. 2018; 9:551. PMID: 30087647.
Article39. Happe S, Pirker W, Klösch G, Sauter C, Zeitlhofer J. Periodic leg movements in patients with Parkinson's disease are associated with reduced striatal dopamine transporter binding. J Neurol. 2003; 250(1):83–86. PMID: 12527997.
Article40. Cochen De Cock V, Abouda M, Leu S, Oudiette D, Roze E, Vidailhet M, et al. Is obstructive sleep apnea a problem in Parkinson's disease? Sleep Med. 2010; 11(3):247–252. PMID: 19628429.
Article41. Loddo G, Calandra-Buonaura G, Sambati L, Giannini G, Cecere A, Cortelli P, et al. The treatment of sleep disorders in Parkinson's disease: from research to clinical practice. Front Neurol. 2017; 8:42. PMID: 28261151.
Article42. Todorova A, Jenner P, Ray Chaudhuri K. Non-motor Parkinson's: integral to motor Parkinson's, yet often neglected. Pract Neurol. 2014; 14(5):310–322. PMID: 24699931.
Article43. Diederich NJ, McIntyre DJ. Sleep disorders in Parkinson's disease: many causes, few therapeutic options. J Neurol Sci. 2012; 314(1-2):12–19. PMID: 22118862.
Article44. Büchele F, Hackius M, Schreglmann SR, Omlor W, Werth E, Maric A, et al. Sodium oxybate for excessive daytime sleepiness and sleep disturbance in Parkinson disease: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2018; 75(1):114–118. PMID: 29114733.45. Neikrug AB, Liu L, Avanzino JA, Maglione JE, Natarajan L, Bradley L, et al. Continuous positive airway pressure improves sleep and daytime sleepiness in patients with Parkinson disease and sleep apnea. Sleep (Basel). 2014; 37(1):177–185.
Article46. Biousse V, Skibell BC, Watts RL, Loupe DN, Drews-Botsch C, Newman NJ. Ophthalmologic features of Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 2004; 62(2):177–180. PMID: 14745050.
Article47. Borm CD, Smilowska K, de Vries NM, Bloem BR, Theelen T. How I do it: the neuro-ophthalmological assessment in Parkinson's disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2019; 9(2):427–435. PMID: 30958314.48. Karson CN, LeWitt PA, Calne DB, Wyatt RJ. Blink rates in parkinsonism. Ann Neurol. 1982; 12(6):580–583. PMID: 7159063.
Article49. Taylor JR, Elsworth JD, Lawrence MS, Sladek JR Jr, Roth RH, Redmond DE Jr. Spontaneous blink rates correlate with dopamine levels in the caudate nucleus of MPTP-treated monkeys. Exp Neurol. 1999; 158(1):214–220. PMID: 10448434.
Article50. Tamer C, Melek IM, Duman T, Oksüz H. Tear film tests in Parkinson's disease patients. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112(10):1795. PMID: 16095705.
Article51. Ekker MS, Janssen S, Seppi K, Poewe W, de Vries NM, Theelen T, et al. Ocular and visual disorders in Parkinson's disease: common but frequently overlooked. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2017; 40:1–10. PMID: 28284903.
Article52. Shibasaki H, Tsuji S, Kuroiwa Y. Oculomotor abnormalities in Parkinson's disease. Arch Neurol. 1979; 36(6):360–364. PMID: 454234.
Article53. Shaikh AG, Xu-Wilson M, Grill S, Zee DS. ‘Staircase’ square-wave jerks in early Parkinson's disease. Br J Ophthalmol. 2011; 95(5):705–709. PMID: 20693560.
Article54. Gitchel GT, Wetzel PA, Baron MS. Pervasive ocular tremor in patients with Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol. 2012; 69(8):1011–1017. PMID: 22490323.
Article55. Rana AQ, Kabir A, Dogu O, Patel A, Khondker S. Prevalence of blepharospasm and apraxia of eyelid opening in patients with parkinsonism, cervical dystonia and essential tremor. Eur Neurol. 2012; 68(5):318–321. PMID: 23075668.
Article56. Yoon WT, Chung EJ, Lee SH, Kim BJ, Lee WY. Clinical analysis of blepharospasm and apraxia of eyelid opening in patients with parkinsonism. J Clin Neurol. 2005; 1(2):159–165. PMID: 20396463.
Article57. Pieri V, Diederich NJ, Raman R, Goetz CG. Decreased color discrimination and contrast sensitivity in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Sci. 2000; 172(1):7–11. PMID: 10620653.
Article58. Weil RS, Schrag AE, Warren JD, Crutch SJ, Lees AJ, Morris HR. Visual dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Brain. 2016; 139(11):2827–2843. PMID: 27412389.
Article59. Archibald NK, Clarke MP, Mosimann UP, Burn DJ. The retina in Parkinson's disease. Brain. 2009; 132(Pt 5):1128–1145. PMID: 19336464.
Article60. Koh SB, Suh SI, Kim SH, Kim JH. Stereopsis and extrastriate cortical atrophy in Parkinson's disease: a voxel-based morphometric study. Neuroreport. 2013; 24(5):229–232. PMID: 23376833.61. Sun L, Zhang H, Gu Z, Cao M, Li D, Chan P. Stereopsis impairment is associated with decreased color perception and worse motor performance in Parkinson's disease. Eur J Med Res. 2014; 19(1):29. PMID: 24886673.
Article62. Gibson G, Mottram PG, Burn DJ, Hindle JV, Landau S, Samuel M, et al. Frequency, prevalence, incidence and risk factors associated with visual hallucinations in a sample of patients with Parkinson's disease: a longitudinal 4-year study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013; 28(6):626–631. PMID: 22927195.
Article63. Goetz CG, Stebbins GT, Ouyang B. Visual plus nonvisual hallucinations in Parkinson's disease: development and evolution over 10 years. Mov Disord. 2011; 26(12):2196–2200. PMID: 21755536.
Article64. Fénelon G, Mahieux F, Huon R, Ziégler M. Hallucinations in Parkinson's disease: prevalence, phenomenology and risk factors. Brain. 2000; 123(Pt 4):733–745. PMID: 10734005.65. Barnes J, David AS. Visual hallucinations in Parkinson's disease: a review and phenomenological survey. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001; 70(6):727–733. PMID: 11385004.
Article66. Bares M, Brázdil M, Kanovský P, Jurák P, Daniel P, Kukleta M, et al. The effect of apomorphine administration on smooth pursuit ocular movements in early Parkinsonian patients. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2003; 9(3):139–144. PMID: 12573868.67. Büttner T, Kuhn W, Patzold T, Przuntek H. L-Dopa improves colour vision in Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm Park Dis Dement Sect. 1994; 7(1):13–19. PMID: 8579766.
Article68. Doty RL. Olfactory dysfunction in Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2012; 8(6):329–339. PMID: 22584158.
Article69. Rodríguez-Violante M, Lees AJ, Cervantes-Arriaga A, Corona T, Silveira-Moriyama L. Use of smell test identification in Parkinson's disease in Mexico: a matched case-control study. Mov Disord. 2011; 26(1):173–176. PMID: 20842690.
Article70. Jellinger KA. The pathomechanisms underlying Parkinson's disease. Expert Rev Neurother. 2014; 14(2):199–215. PMID: 24471711.
Article71. Jankovic J. Parkinson's disease: clinical features and diagnosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008; 79(4):368–376. PMID: 18344392.
Article72. Tarakad A, Jankovic J. Chapter seventeen - anosmia and ageusia in Parkinson's disease. In : Chaudhuri KR, Titova N, editors. International Review of Neurobiology. Boston, MA: Academic Press;2017. p. 541–556.73. Kashihara K, Hanaoka A, Imamura T. Frequency and characteristics of taste impairment in patients with Parkinson's disease: results of a clinical interview. Intern Med. 2011; 50(20):2311–2315. PMID: 22001456.
Article74. Garcia-Esparcia P, Schlüter A, Carmona M, Moreno J, Ansoleaga B, Torrejón-Escribano B, et al. Functional genomics reveals dysregulation of cortical olfactory receptors in Parkinson disease: novel putative chemoreceptors in the human brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2013; 72(6):524–539. PMID: 23656994.
Article75. Rana AQ, Yousuf MS, Awan N, Fattah A. Impact of progression of Parkinson's disease on drooling in various ethnic groups. Eur Neurol. 2012; 67(5):312–314. PMID: 22517489.
Article76. Zlotnik Y, Balash Y, Korczyn AD, Giladi N, Gurevich T. Disorders of the oral cavity in Parkinson's disease and parkinsonian syndromes. Parkinsons Dis. 2015; 2015:379482. PMID: 25685594.
Article77. Hanaoka A, Kashihara K. Increased frequencies of caries, periodontal disease and tooth loss in patients with Parkinson's disease. J Clin Neurosci. 2009; 16(10):1279–1282. PMID: 19570683.
Article78. Cersosimo MG, Raina GB, Calandra CR, Pellene A, Gutiérrez C, Micheli FE, et al. Dry mouth: an overlooked autonomic symptom of Parkinson's disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2011; 1(2):169–173. PMID: 23939300.
Article79. Del Tredici K, Hawkes CH, Ghebremedhin E, Braak H. Lewy pathology in the submandibular gland of individuals with incidental Lewy body disease and sporadic Parkinson's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2010; 119(6):703–713. PMID: 20229352.
Article80. Cersósimo MG, Perandones C, Micheli FE, Raina GB, Beron AM, Nasswetter G, et al. Alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity in minor salivary gland biopsies of Parkinson's disease patients. Mov Disord. 2011; 26(1):188–190. PMID: 20836135.
Article81. Coates C, Bakheit AM. Dysphagia in Parkinson's disease. Eur Neurol. 1997; 38(1):49–52. PMID: 9252799.
Article82. Leopold NA, Kagel MC. Prepharyngeal dysphagia in Parkinson's disease. Dysphagia. 1996; 11(1):14–22. PMID: 8556872.
Article83. Haehner A, Tosch C, Wolz M, Klingelhoefer L, Fauser M, Storch A, et al. Olfactory training in patients with Parkinson's disease. PLoS One. 2013; 8(4):e61680. PMID: 23613901.
Article84. Yagi T, Asakawa A, Ueda H, Ikeda S, Miyawaki S, Inui A. The role of zinc in the treatment of taste disorders. Recent Pat Food Nutr Agric. 2013; 5(1):44–51. PMID: 23305423.
Article85. Hobson P, Islam W, Roberts S, Adhiyman V, Meara J. The risk of bladder and autonomic dysfunction in a community cohort of Parkinson's disease patients and normal controls. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2003; 10(2):67–71. PMID: 14643995.
Article86. Pfeiffer RF. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2011; 17(1):10–15. PMID: 20829091.
Article87. Kim JS, Lee SH, Oh YS, Park JW, An JY, Park SK, et al. Cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction in mild and advanced Parkinson's disease. J Mov Disord. 2016; 9(2):97–103. PMID: 27020456.
Article88. Oh YS, Kim JS, Kim YI, Yang DW, Koo J, Jung HO, et al. Circadian blood pressure and heart rate variations in de novo Parkinson's disease. Biol Rhythm Res. 2014; 45(3):335–343.89. Senard JM, Raï S, Lapeyre-Mestre M, Brefel C, Rascol O, Rascol A, et al. Prevalence of orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997; 63(5):584–589. PMID: 9408097.
Article90. Goldstein DS, Holmes CS, Dendi R, Bruce SR, Li ST. Orthostatic hypotension from sympathetic denervation in Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 2002; 58(8):1247–1255. PMID: 11971094.
Article91. Jain S, Goldstein DS. Cardiovascular dysautonomia in Parkinson disease: from pathophysiology to pathogenesis. Neurobiol Dis. 2012; 46(3):572–580. PMID: 22094370.
Article92. Allcock LM, Kenny RA, Burn DJ. Clinical phenotype of subjects with Parkinson's disease and orthostatic hypotension: autonomic symptom and demographic comparison. Mov Disord. 2006; 21(11):1851–1855. PMID: 16958096.
Article93. Sharabi Y, Goldstein DS. Mechanisms of orthostatic hypotension and supine hypertension in Parkinson disease. J Neurol Sci. 2011; 310(1-2):123–128. PMID: 21762927.
Article94. Swinn L, Schrag A, Viswanathan R, Bloem BR, Lees A, Quinn N. Sweating dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2003; 18(12):1459–1463. PMID: 14673882.
Article95. Leta V, van Wamelen DJ, Rukavina K, Jaakkola E, Sportelli C, Wan YM, et al. Sweating and other thermoregulatory abnormalities in Parkinson's disease: a review. Ann Mov Disord. 2019; 2(2):39–47.
Article96. Coon EA, Low PA. Thermoregulation in Parkinson disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018; 157:715–725. PMID: 30459035.
Article97. Pursiainen V, Haapaniemi TH, Korpelainen JT, Sotaniemi KA, Myllylä VV. Sweating in Parkinsonian patients with wearing-off. Mov Disord. 2007; 22(6):828–832. PMID: 17357129.
Article98. Wang N, Gibbons CH, Lafo J, Freeman R. α-Synuclein in cutaneous autonomic nerves. Neurology. 2013; 81(18):1604–1610. PMID: 24089386.
Article99. Donadio V, Incensi A, Leta V, Giannoccaro MP, Scaglione C, Martinelli P, et al. Skin nerve α-synuclein deposits: a biomarker for idiopathic Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2014; 82(15):1362–1369. PMID: 24634456.
Article100. Pfeiffer RF. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol. 2003; 2(2):107–116. PMID: 12849267.
Article101. Cersosimo MG, Benarroch EE. Pathological correlates of gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2012; 46(3):559–564. PMID: 22048068.
Article102. Asai H, Udaka F, Hirano M, Minami T, Oda M, Kubori T, et al. Increased gastric motility during 5-HT4 agonist therapy reduces response fluctuations in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2005; 11(8):499–502. PMID: 16263322.103. Shin CM, Lee YJ, Kim JM, Lee JY, Kim KJ, Choi YJ, et al. DA-9701 on gastric motility in patients with Parkinson's disease: a randomized controlled trial. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2018; 54:84–89. PMID: 29705555.
Article104. Shin HW, Chung SJ. Drug-induced parkinsonism. J Clin Neurol. 2012; 8(1):15–21. PMID: 22523509.
Article105. Salat-Foix D, Suchowersky O. The management of gastrointestinal symptoms in Parkinson's disease. Expert Rev Neurother. 2012; 12(2):239–248. PMID: 22288679.
Article106. Araki I, Kuno S. Assessment of voiding dysfunction in Parkinson's disease by the international prostate symptom score. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000; 68(4):429–433. PMID: 10727477.
Article107. Lemack GE, Dewey RB Jr, Roehrborn CG, O'Suilleabhain PE, Zimmern PE. Questionnaire-based assessment of bladder dysfunction in patients with mild to moderate Parkinson's disease. Urology. 2000; 56(2):250–254. PMID: 10925088.
Article108. Campos-Sousa RN, Quagliato E, da Silva BB, de Carvalho RM Jr, Ribeiro SC, de Carvalho DF. Urinary symptoms in Parkinson's disease: prevalence and associated factors. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2003; 61(2B):359–363. PMID: 12894267.
Article109. Seki S, Igawa Y, Kaidoh K, Ishizuka O, Nishizawa O, Andersson KE. Role of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the micturition reflex in conscious rats. Neurourol Urodyn. 2001; 20(1):105–113. PMID: 11135387.
Article110. Yoshimura N, Kuno S, Chancellor MB, De Groat WC, Seki S. Dopaminergic mechanisms underlying bladder hyperactivity in rats with a unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) lesion of the nigrostriatal pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 2003; 139(8):1425–1432. PMID: 12922929.
Article111. Sakakibara R, Uchiyama T, Yamanishi T, Kishi M. Genitourinary dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2010; 25(1):2–12. PMID: 20077468.
Article112. Kim KJ, Jeong SJ, Kim JM. Neurogenic bladder in progressive supranuclear palsy: a comparison with Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy. Neurourol Urodyn. 2018; 37(5):1724–1730. PMID: 29356135.
Article113. Brown RG, Jahanshahi M, Quinn N, Marsden CD. Sexual function in patients with Parkinson's disease and their partners. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990; 53(6):480–486. PMID: 2380728.
Article114. Basson R. Sexuality and Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 1996; 2(4):177–185. PMID: 18591038.
Article115. Jacobs H, Vieregge A, Vieregge P. Sexuality in young patients with Parkinson's disease: a population based comparison with healthy controls. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000; 69(4):550–552. PMID: 10990524.
Article116. Papatsoris AG, Deliveliotis C, Singer C, Papapetropoulos S. Erectile dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Urology. 2006; 67(3):447–451. PMID: 16504269.
Article117. Langston JW, Forno LS. The hypothalamus in Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol. 1978; 3(2):129–133. PMID: 350130.
Article118. Nakum S, Cavanna AE. The prevalence and clinical characteristics of hypersexuality in patients with Parkinson's disease following dopaminergic therapy: a systematic literature review. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016; 25:10–16. PMID: 26923525.
Article119. Gomes CM, Sammour ZM, de Bessa Junior J, Barbosa ER, Lopes RI, Sallem FS, et al. Neurological status predicts response to alpha-blockers in men with voiding dysfunction and Parkinson's disease. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2014; 69(12):817–822. PMID: 25627993.
Article120. Ashour R, Jankovic J. Joint and skeletal deformities in Parkinson's disease, multiple system atrophy, and progressive supranuclear palsy. Mov Disord. 2006; 21(11):1856–1863. PMID: 16941460.
Article121. Kim YE, Jeon BS. Musculoskeletal problems in Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2013; 120(4):537–542. PMID: 23420172.
Article122. Pandey S, Kumar H. Assessment of striatal & postural deformities in patients with Parkinson's disease. Indian J Med Res. 2016; 144(5):682–688. PMID: 28361820.123. Kim YE, Kim HJ, Yun JY, Lee WW, Yang HJ, Kim JM, et al. Musculoskeletal problems affect the quality of life of patients with Parkinson's disease. J Mov Disord. 2018; 11(3):133–138. PMID: 30304926.
Article124. Srivanitchapoom P, Hallett M. Camptocormia in Parkinson's disease: definition, epidemiology, pathogenesis and treatment modalities. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2016; 87(1):75–85. PMID: 25896683.
Article125. Barone P, Santangelo G, Amboni M, Pellecchia MT, Vitale C. Pisa syndrome in Parkinson's disease and parkinsonism: clinical features, pathophysiology, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2016; 15(10):1063–1074. PMID: 27571158.
Article126. Finsterer J, Strobl W. Presentation, etiology, diagnosis, and management of camptocormia. Eur Neurol. 2010; 64(1):1–8. PMID: 20634620.
Article127. Gerton BK, Theeler B, Samii A. Backpack treatment for camptocormia. Mov Disord. 2010; 25(2):247–248. PMID: 20077473.
Article128. Schroeteler FE, Fietzek UM, Ziegler K, Ceballos-Baumann AO. Upright posture in parkinsonian camptocormia using a high-frame walker with forearm support. Mov Disord. 2011; 26(8):1560–1561. PMID: 21520281.
Article129. de Sèze MP, Creuzé A, de Sèze M, Mazaux JM. An orthosis and physiotherapy programme for camptocormia: a prospective case study. J Rehabil Med. 2008; 40(9):761–765. PMID: 18843430.
Article130. Bartolo M, Serrao M, Tassorelli C, Don R, Ranavolo A, Draicchio F, et al. Four-week trunk-specific rehabilitation treatment improves lateral trunk flexion in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2010; 25(3):325–331. PMID: 20131386.
Article131. Capecci M, Serpicelli C, Fiorentini L, Censi G, Ferretti M, Orni C, et al. Postural rehabilitation and Kinesio taping for axial postural disorders in Parkinson's disease. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014; 95(6):1067–1075. PMID: 24508531.
Article132. Bonanni L, Thomas A, Varanese S, Scorrano V, Onofrj M. Botulinum toxin treatment of lateral axial dystonia in Parkinsonism. Mov Disord. 2007; 22(14):2097–2103. PMID: 17685467.
Article133. Tassorelli C, De Icco R, Alfonsi E, Bartolo M, Serrao M, Avenali M, et al. Botulinum toxin type A potentiates the effect of neuromotor rehabilitation of Pisa syndrome in Parkinson disease: a placebo controlled study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014; 20(11):1140–1144. PMID: 25175601.
Article134. Dupeyron A, Viollet E, Coroian F, Gagnard C, Renard D, Castelnovo G. Botulinum toxin-A for treatment of Pisa syndrome: a new target muscle. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2015; 21(6):669–670. PMID: 25899457.
Article135. von Coelln R, Raible A, Gasser T, Asmus F. Ultrasound-guided injection of the iliopsoas muscle with botulinum toxin in camptocormia. Mov Disord. 2008; 23(6):889–892. PMID: 18307265.
Article136. Colosimo C, Salvatori FM. Injection of the iliopsoas muscle with botulinum toxin in camptocormia. Mov Disord. 2009; 24(2):316–317. PMID: 18973251.
Article137. Fietzek UM, Schroeteler FE, Ceballos-Baumann AO. Goal attainment after treatment of parkinsonian camptocormia with botulinum toxin. Mov Disord. 2009; 24(13):2027–2028. PMID: 19645067.
Article138. Galbusera F, Bassani T, Stucovitz E, Martini C, Ismael Aguirre MF, Berjano PL, et al. Surgical treatment of spinal disorders in Parkinson's disease. Eur Spine J. 2018; 27(Suppl 1):101–108.
Article139. Poewe WH, Lees AJ. The pharmacology of foot dystonia in parkinsonism. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1987; 10(1):47–56. PMID: 3545460.
Article140. Umemura A, Oka Y, Ohkita K, Yamawaki T, Yamada K. Effect of subthalamic deep brain stimulation on postural abnormality in Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg. 2010; 112(6):1283–1288. PMID: 19895200.
Article141. Ha AD, Jankovic J. Pain in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2012; 27(4):485–491. PMID: 21953990.
Article142. Rana AQ, Kabir A, Jesudasan M, Siddiqui I, Khondker S. Pain in Parkinson's disease: analysis and literature review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013; 115(11):2313–2317. PMID: 24075714.
Article143. Ford B. Pain in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2010; 25(Suppl 1):S98–S103. PMID: 20187254.
Article144. Beiske AG, Loge JH, Rønningen A, Svensson E. Pain in Parkinson's disease: prevalence and characteristics. Pain. 2009; 141(1-2):173–177. PMID: 19100686.
Article145. Wallace VC, Chaudhuri KR. Unexplained lower limb pain in Parkinson's disease: a phenotypic variant of “painful Parkinson's disease”. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014; 20(1):122–124. PMID: 24139891.
Article146. Brefel-Courbon C, Payoux P, Thalamas C, Ory F, Quelven I, Chollet F, et al. Effect of levodopa on pain threshold in Parkinson's disease: a clinical and positron emission tomography study. Mov Disord. 2005; 20(12):1557–1563. PMID: 16078219.147. Friedman J, Friedman H. Fatigue in Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 1993; 43(10):2016–2018. PMID: 8413960.
Article148. Abe K, Takanashi M, Yanagihara T. Fatigue in patients with Parkinson's disease. Behav Neurol. 2000; 12(3):103–106. PMID: 11455047.
Article149. Herlofson K, Larsen JP. Measuring fatigue in patients with Parkinson's disease - the Fatigue Severity Scale. Eur J Neurol. 2002; 9(6):595–600. PMID: 12453074.
Article150. Kang SY, Ma HI, Lim YM, Hwang SH, Kim YJ. Fatigue in drug-naïve Parkinson's disease. Eur Neurol. 2013; 70(1-2):59–64. PMID: 23796615.
Article151. Chaudhuri A, Behan PO. Fatigue and basal ganglia. J Neurol Sci. 2000; 179(S 1-2):34–42. PMID: 11054483.
Article152. Chaudhuri A, Condon BR, Gow JW, Brennan D, Hadley DM. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of basal ganglia in chronic fatigue syndrome. Neuroreport. 2003; 14(2):225–228. PMID: 12598734.
Article153. Yamamoto S, Ouchi Y, Onoe H, Yoshikawa E, Tsukada H, Takahashi H, et al. Reduction of serotonin transporters of patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Neuroreport. 2004; 15(17):2571–2574. PMID: 15570154.
Article154. Pavese N, Metta V, Bose SK, Chaudhuri KR, Brooks DJ. Fatigue in Parkinson's disease is linked to striatal and limbic serotonergic dysfunction. Brain. 2010; 133(11):3434–3443. PMID: 20884645.
Article155. Lou JS, Kearns G, Oken B, Sexton G, Nutt J. Exacerbated physical fatigue and mental fatigue in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2001; 16(2):190–196. PMID: 11295769.
Article156. Hagell P, Brundin L. Towards an understanding of fatigue in Parkinson disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009; 80(5):489–492. PMID: 19204024.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Electroconvulsive Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease with Depression and Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome: A Case Report
- Overdenture with magnetic attachments for a patient with Parkinson's disease: a case report
- Evaluating patients with abdominal pain originating in the abdominal wall
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson's Disease
- Comparison of Musculoskeletal Disorders between Pediatric Dentists and General Dentists