Prog Med Phys.
2020 Jun;31(2):29-34. 10.14316/pmp.2020.31.2.29.
Verification of Secondary Electron Generated by Head Screw in Gamma Knife Using Monte Carlo N-Particle Simulation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Convergent Medical Physics, Graduate School of Engineering, Konkuk University, Korea
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2503940
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2020.31.2.29
Abstract
- Purpose
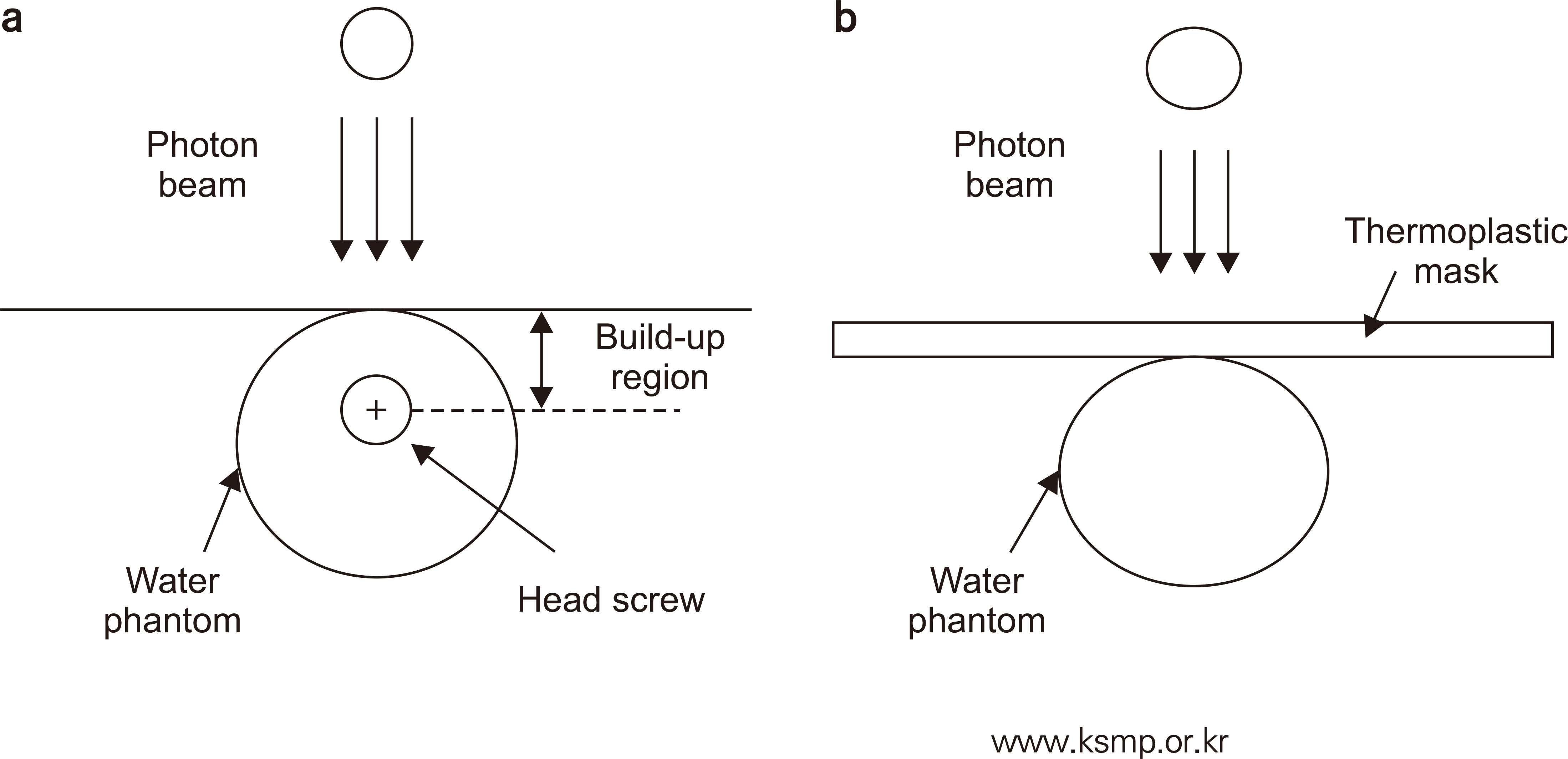
The interaction of various substances inserted into the human body and radiation can confirm the radiation enhancement effect. A Leksell frame inserted into the human body for gamma knife treatment will cause not only pain and inconvenience to the patient, but also additional exposure to the patient’s normal tissues. In this study, we attempt to confirm the additional exposure caused by the interaction of the Leksell frame and thermoplastic mask, and 60Co used for gamma knife treatment.
Methods
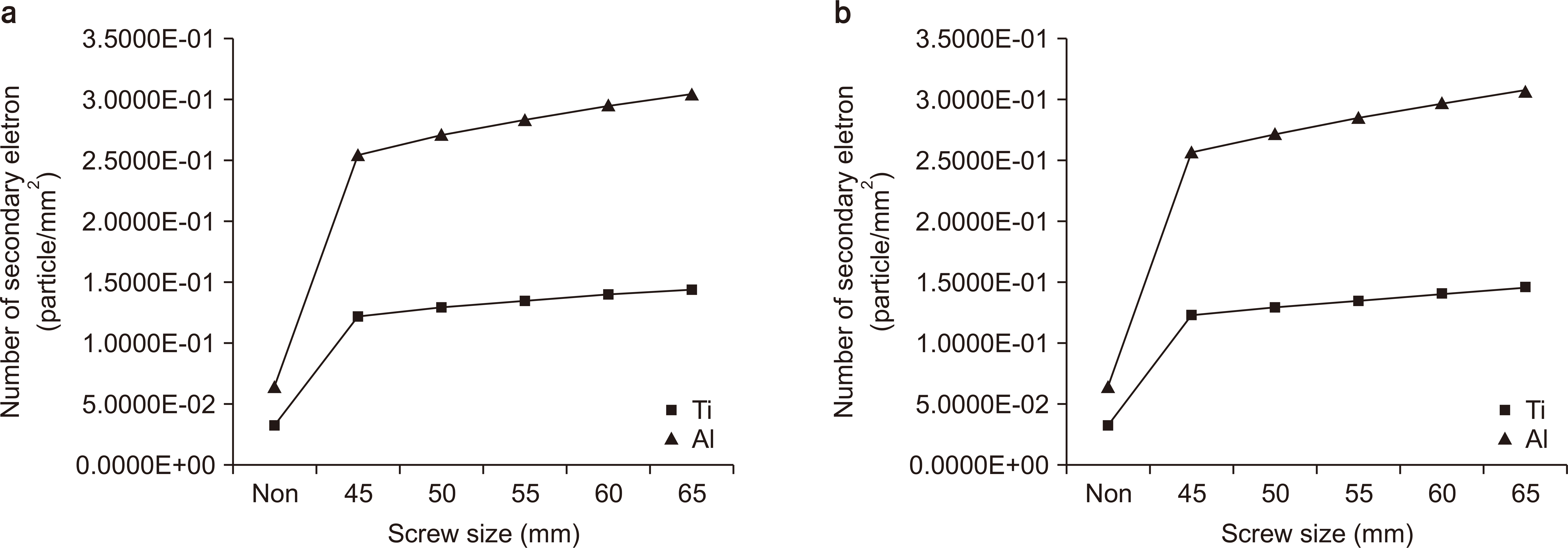
A 60Co energy of 1.17, 1.33 MeV is applied using Monte Carlo simulation, and fixation screws and thermoplastic mask are fabricated using aluminum and titanium alloy, and Carbon compounds.
Results
Results show a dose enhancement of up to 396.27% higher compared with that without a Leksell frame and up to 391.25% in thermoplastic mask.
Conclusions
Hence, appropriate treatment methods and materials must be used to reduce additional exposure to normal tissues.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kim YB, Suh CH. 2008; Evolution of radiotherapy: high-precision radiotherapy. J Korean Med Assoc. 51:604–611. DOI: 10.5124/jkma.2008.51.7.604.
Article2. Chung HT, Kim DG. 2008; Introduction to radiosurgery. J Korean Med Assoc. 51:5–15. DOI: 10.5124/jkma.2008.51.1.5.
Article3. Jeon SR, Lee DJ, Kim JH, Kim CJ, Kwon Y, Lee JK, et al. 2000; Outcome of gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 28:1228–1232.4. Choi EJ, Ro HW, Cho JS, Park MH, Yoon JH, Jegal YJ. 2009; Gamma Knife Surgery for brain metastases from breast carcinoma. J Korean Surg Soc. 76:81–85. DOI: 10.4174/jkss.2009.76.2.81.
Article5. Young RF. 1998; The role of the gamma knife in the treatment of malignant primary and metastatic brain tumors. CA Cancer J Clin. 48:177–188. DOI: 10.3322/canjclin.48.3.177. PMID: 9594920.
Article6. Young RF. 1998; Radiosurgery for the treatment of brain metastases. Semin Surg Oncol. 14:70–78. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2388(199801/02)14:1<70::AID-SSU9>3.0.CO;2-#.
Article7. Kwon YM, Park YS, Ha Y, Chang JH, Chang JW, Park GY. 2004; Factor related to occurrence of radiation necrosis following gamma knife radiosurgery for metastatic brain tumors. Brain Tumor Res Treat. 3:103–108.8. Lim SM, Lee R, Suh HS. 2010; Clinical results from single-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) of brain arteriovenous malformation: single center experience. Korean J Med Phys. 23:274–280.9. Kossert K, Marganiec-Ga©©ązka J, Mougeot X, Nähle OJ. 2018; Activity determination of 60Co and the importance of its beta spectrum. Appl Radiat Isot. 134:212–218. DOI: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2017.06.015. PMID: 28629654.10. Evans LT, Andre K, De R, Henning R, Morgan ED. 2009; Reconstruction of a radiation point source¡¯s radial location using goodness-of-fit test on spectra obtained from an HPGe detector. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B. 267:3688–3693. DOI: 10.1016/j.nimb.2009.09.003.
Article11. Kuntner C, Auffray E, Lecoq P, Pizzolotto C, Schneegans M. 2002; Schneegans M. Intrinsic energy resolution and light output of the Lu0.7Y0.3AP:Ce scintillator. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res A. 493:131–136. DOI: 10.1016/S0168-9002(02)01559-0.12. Choi TJ, Kim OB, Joo YK, Suh SJ, Son EI. 1996; Determination of stereotactic target position with MR localizer. Korean J Med Phys. 7:67–77.13. Seo WS, Shin DO, Ji YH, Lim YJ. 2003; A study on quality assurance for gamma knife. Korean J Med Phys. 14:184–188.14. Baek SY, Choi JY. 2012; Associated factors with pin-fixing & pin removal pain among patients undergoing gamma knife radiosurgery. Asian Oncol Nurs. 12:323–330. DOI: 10.5388/aon.2012.12.4.323.15. Hwang CH, Im IC, Kim JH. 2017; A Monte Carlo study of dose enhancement with kilovoltage and megavoltage photons. J Korean Soc Radiol. 11:87–94. DOI: 10.7742/jksr.2017.11.2.87.
Article16. Hwang CH, Kang SS, Kim JH. 2016; A Monte Carlo study of secondary electron production from gold nanoparticle in kilovoltage and megavoltage X-rays. J Korean Soc Radiol. 10:152–159. DOI: 10.7742/jksr.2016.10.3.153.
Article17. Mesbahi A, Jamali F, Garehaghaji N. 2013; Effect of photon beam energy, gold nanoparticle size and concentration on the dose enhancement in radiation therapy. Bioimpacts. 3:29–35.18. Cheung JY, Yu KN, Chan JF, Ho RT, Yu CP. 2003; Dose distribution close to metal implants in Gamma Knife Radiosurgery: a Monte Carlo study. Med Phys. 30:1812–1815. DOI: 10.1118/1.1582811. PMID: 12906199.
Article19. Nakazawa H, Mori Y, Yamamuro O, Komori M, Shibamoto Y, Uchiyama Y, et al. 2014; Geometric accuracy of 3D coordinates of the Leksell stereotactic skull frame in 1.5 Tesla- and 3.0 Tesla-magnetic resonance imaging: a comparison of three different fixation screw materials. J Radiat Res. 55:1184–1191. DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rru064. PMID: 25034732. PMCID: PMC4229929.
Article20. ICRU Report 44. 1989. Tissue substitutes in radiation dosimetry and measurement. ICRU Report. 44:ICRU;Bethesda:21. Al-Dweri FMO, Lallena AM. 2004; A simplified model of the source channel of the Leksell Gamma Knife¢ç: testing multisource configurations with PENELOPE. Phys Med Biol. 49:3441–3453. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/49/15/009. PMID: 15379024.
Article22. Moskvin V, Timmerman R, DesRosiers C, Randall M, DesRosiers P, Dittmer P, et al. 2004; Monte Carlo simulation of the Leksell Gamma Knife¢ç: II. Effects of heterogeneous versus homogeneous media for stereotactic radiosurgery. Phys Med Biol. 49:4879–4895. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/49/21/003. PMID: 15584525.
Article23. Ballester F, Granero D, Pérez-Calatayud J, Casal E, Agramunt S, Cases R. 2005; Monte Carlo dosimetric study of the BEBIG Co-60 HDR source. Phys Med Biol. 50:N309–N316. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/50/21/N03. PMID: 16237230.
Article24. Vijande J, Granero D, Perez-Calatayud J, Ballester F. 2012; Monte Carlo dosimetric study of the Flexisource Co-60 high dose rate source. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 4:34–44. DOI: 10.5114/jcb.2012.27950. PMID: 23346138. PMCID: PMC3551374.
Article25. Kang JK, Lee DJ. 2012; Development of Monte Carlo simulation code for the dose calculation of the stereotactic radiosurgery. Korean J Med Phys. 23:303–308.26. Khan FM. 2012. Physics of radiation therapy. 4th ed. Wolters Kluwer Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;Philadelphia:27. Zeverino M, Jaccard M, Patin D, Ryckx N, Marguet M, Tuleasca C, et al. 2017; Commissioning of the Leksell Gamma Knife¢ç IconTM . Med Phys. 44:355–363. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12052. PMID: 28133748.28. Wright G, Harrold N, Hatfield P, Bownes P. 2017; Validity of the use of nose tip motion as a surrogate for intracranial motion in mask-fixated frameless Gamma Knife¢ç IconTM therapy. J Radiosurg SBRT. 4:289–301.29. AlDahlawi I, Prasad D, Podgorsak MB. 2017; Evaluation of stability of stereotactic space defined by cone-beam CT for the Leksell Gamma Knife Icon. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 18:67–72. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12073. PMID: 28419781. PMCID: PMC5689865.
Article30. Li W, Bootsma G, Von Schultz O, Carlsson P, Laperriere N, Millar BA, et al. 2016; Preliminary evaluation of a novel thermoplastic mask system with intra-fraction motion monitoring for future use with image-guided gamma knife. Cureus. 8:e531. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.531. PMID: 27081592. PMCID: PMC4829406.
Article31. Kang KM, Chai GY, Jeong BG, Ha IB, Park KB, Jung JM, et al. 2012; An analysis of intra-fractional movement during image-guided frameless radiosurgery for brain tumor using cyberKnife. Korean J Med Phys. 23:169–176.32. Ji Y, Chang KH, Cho B, Kwak J, Song SY, Choi EK, et al. 2015; Evaluation of set-up accuracy for frame-based and frameless lung stereotactic body radiation therapy. Korean J Med Phys. 26:286–293. DOI: 10.14316/pmp.2015.26.4.286.
Article33. Lindtner RA, Schmid R, Nydegger T, Konschake M, Schmoelz W. 2018; Pedicle screw anchorage of carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK screws under cyclic loading. Eur Spine J. 27:1775–1784. DOI: 10.1007/s00586-018-5538-8. PMID: 29497852.
Article34. Ringel F, Ryang YM, Kirschke JS, Müller BS, Wilkens JJ, Brodard J, et al. 2017; Radiolucent carbon fiber-reinforced pedicle screws for treatment of spinal tumors: advantages for radiation planning and follow-up imaging. World Neurosurg. 105:294–301. DOI: 10.1016/j.wneu.2017.04.091. PMID: 28478252.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Monte Carlo Photon and Electron Dose Calculation Time Reduction Using Local Least Square Denoising Filters
- A Monte Carlo Simulation Study of a Therapeutic Proton Beam Delivery System Using the Geant4 Code
- Monte Carlo Simulation Codes for Nuclear Medicine Imaging
- Reference based Simulation Study of Detector Comparison for BNCT-SPECT Imaging
- Development of DICOM Convert Program for the Geant4 Monte Carlo Simulation of the Radiotherapy