Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2020 Jul;24(4):319-328. 10.4196/kjpp.2020.24.4.319.
Activation of the renin-angiotensin system in high fructose-induced metabolic syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 41944, Korea
- 2Department of Cardiovascular Research Institute, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 41944, Korea
- 3Department of Biomedical Science, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 41944, Korea
- KMID: 2503325
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2020.24.4.319
Abstract
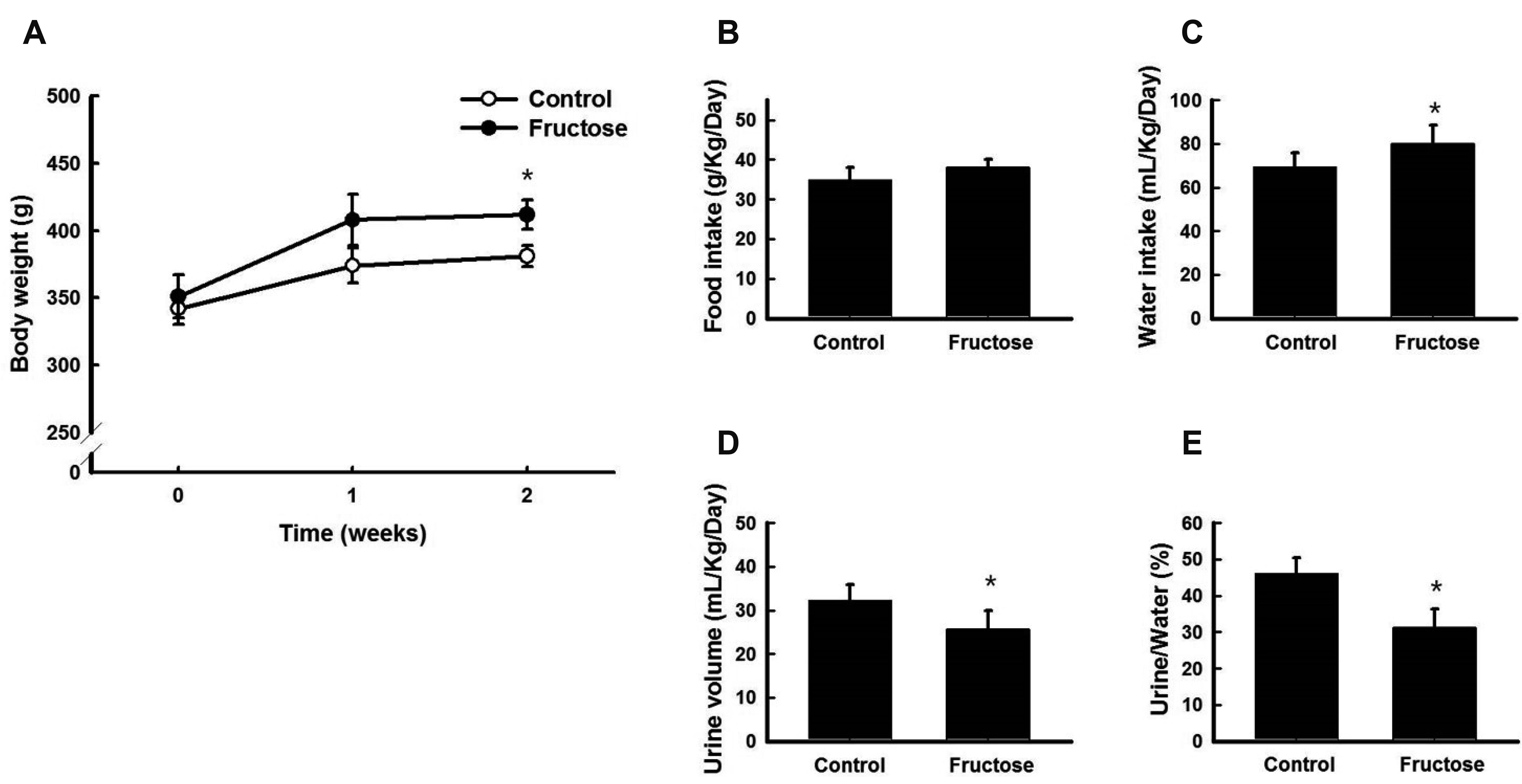
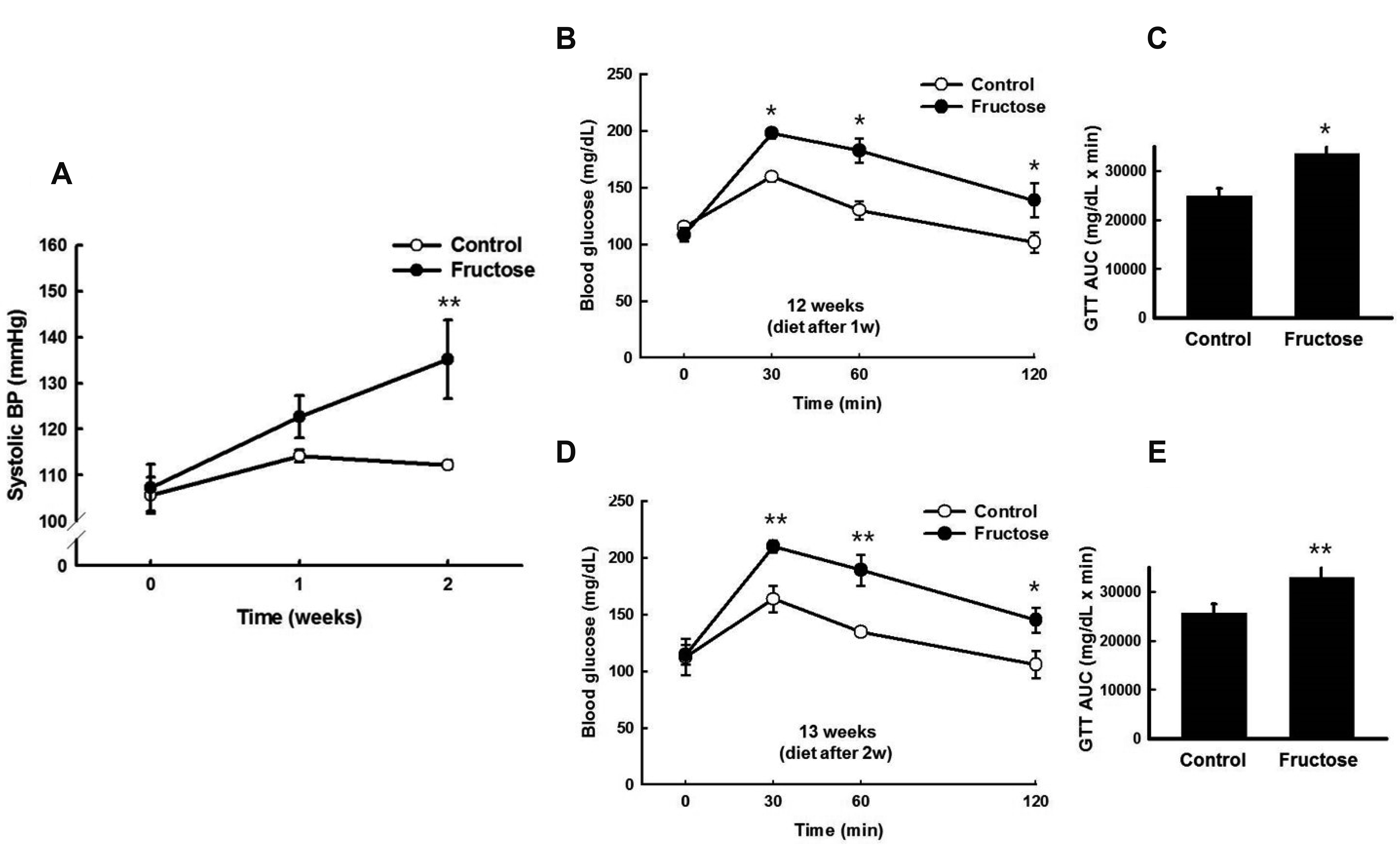
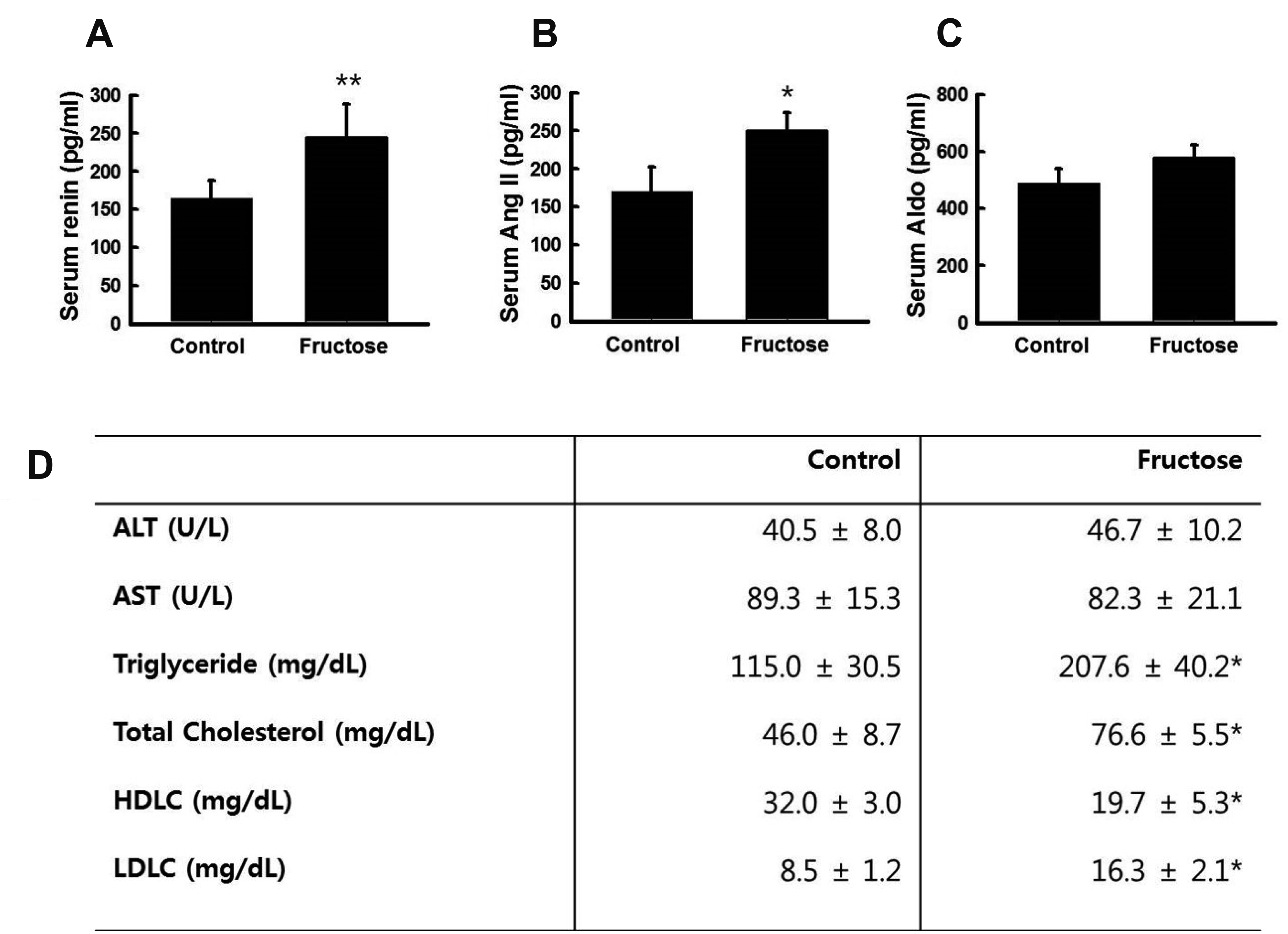
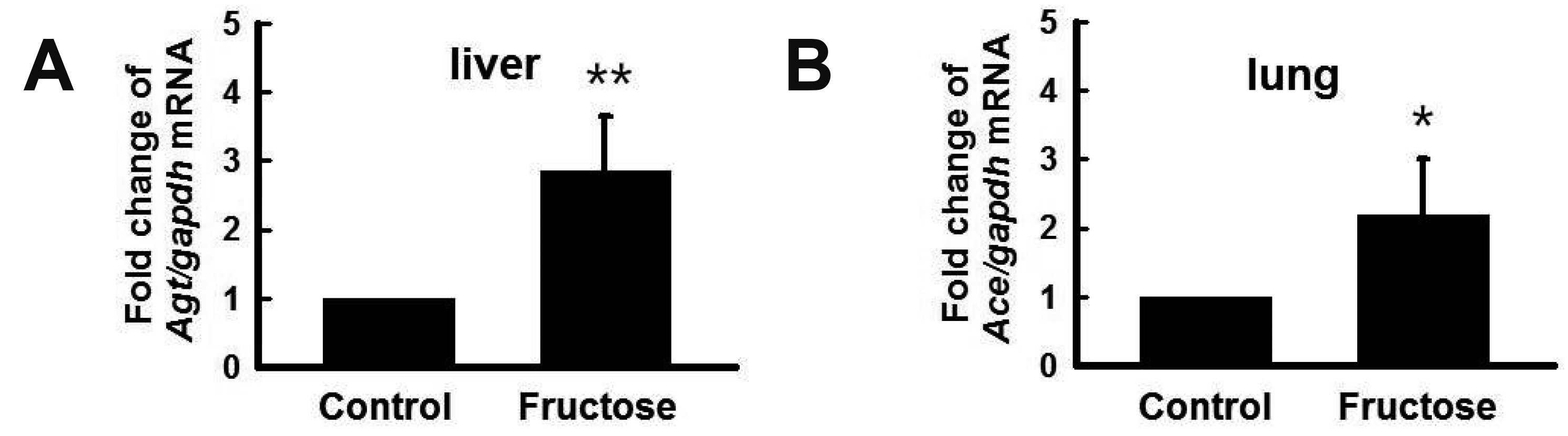
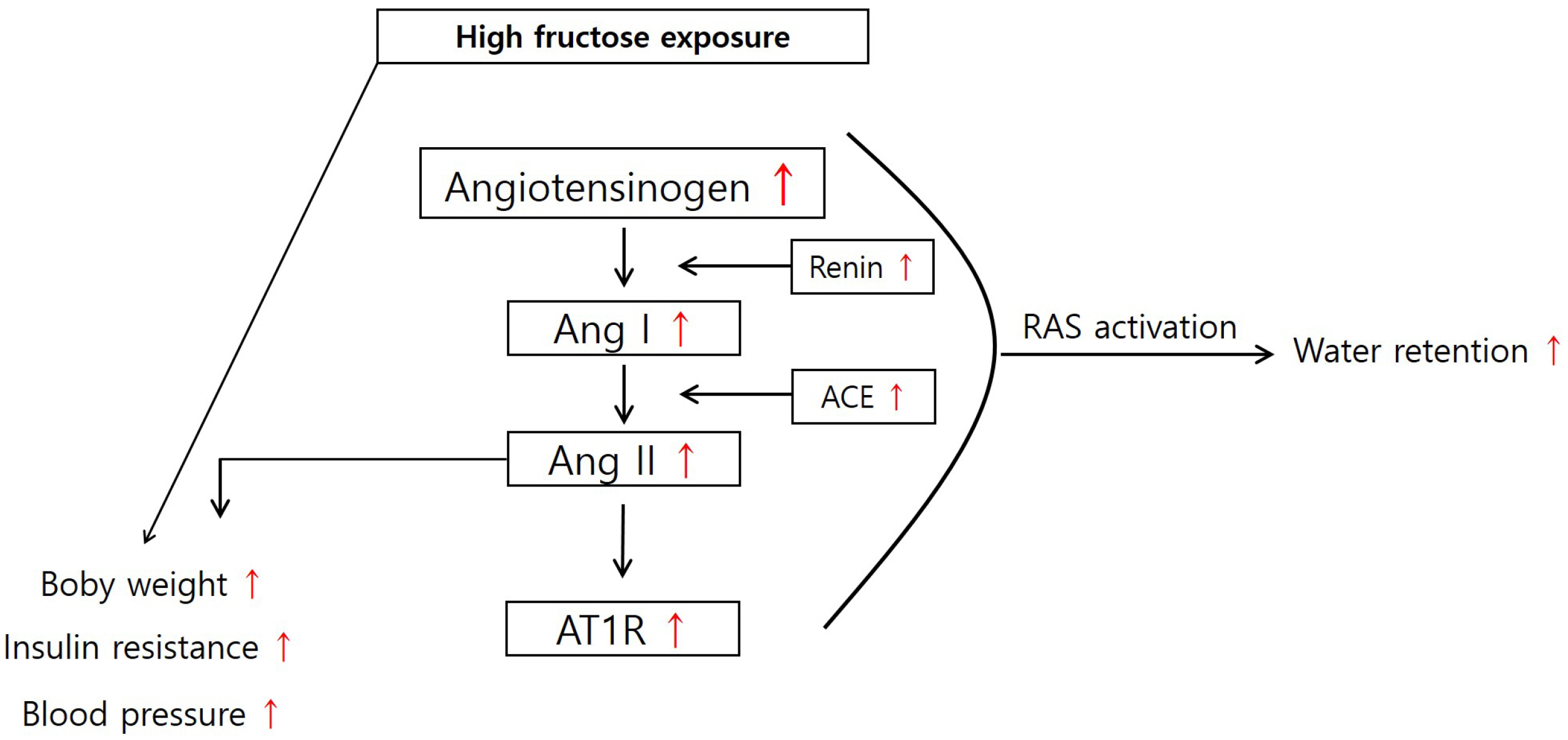
- High fructose intake induces hyperglycemia and hypertension. However, the mechanism by which fructose induces metabolic syndrome is largely unknown. We hypothesized that high fructose intake induces activation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), resulting in hypertension and metabolic syndrome. We provided 11-week-old Sprague–Dawley rats with drinking water, with or without 20% fructose, for two weeks. We measured serum renin, angiotensin II (Ang II), and aldosterone (Aldo) using ELISA kits. The expression of RAS genes was determined by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. High fructose intake increased body weight and water retention, regardless of food intake or urine volume. After two weeks, fructose intake induced glucose intolerance and hypertension. High fructose intake increased serum renin, Ang II, triglyceride, and cholesterol levels, but not Aldo levels. High fructose intake increased the expression of angiotensinogen in the liver; angiotensin-converting enzyme in the lungs; and renin, angiotensin II type 1a receptor (AT1aR), and angiotensin II type 1b receptor (AT1bR) in the kidneys. However, expression of AT1aR and AT1bR in the adrenal glands did not increase in rats given fructose. Taken together, these results indicate that high fructose intake induces activation of RAS, resulting in hypertension and metabolic syndrome.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Ovariectomy, but not orchiectomy, exacerbates metabolic syndrome after maternal high-fructose intake in adult offspring
Mina Kim, Inkyeom Kim
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021;25(1):39-49. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2021.25.1.39.
Reference
-
1. Bray GA. 2008; Fructose: should we worry? Int J Obes (Lond). 32(Suppl 7):S127–S131. DOI: 10.1038/ijo.2008.248. PMID: 19136981.
Article2. Tappy L, Lê KA. 2010; Metabolic effects of fructose and the worldwide increase in obesity. Physiol Rev. 90:23–46. DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00019.2009. PMID: 20086073.
Article3. Ferder L, Ferder MD, Inserra F. 2010; The role of high-fructose corn syrup in metabolic syndrome and hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. 12:105–112. DOI: 10.1007/s11906-010-0097-3. PMID: 20424937.
Article4. Bizeau ME, Pagliassotti MJ. 2005; Hepatic adaptations to sucrose and fructose. Metabolism. 54:1189–1201. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2005.04.004. PMID: 16125531.
Article5. Lê KA, Tappy L. 2006; Metabolic effects of fructose. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 9:469–475. DOI: 10.1097/01.mco.0000232910.61612.4d. PMID: 16778579.6. Tappy L, Lê KA, Tran C, Paquot N. 2010; Fructose and metabolic diseases: new findings, new questions. Nutrition. 26:1044–1049. DOI: 10.1016/j.nut.2010.02.014. PMID: 20471804.
Article7. Wolf G, Butzmann U, Wenzel UO. 2003; The renin-angiotensin system and progression of renal disease: from hemodynamics to cell biology. Nephron Physiol. 93:P3–P13. DOI: 10.1159/000066656. PMID: 12411725.
Article8. Ichihara A, Kobori H, Nishiyama A, Navar LG. 2004; Renal renin-angiotensin system. Contrib Nephrol. 143:117–130. DOI: 10.1159/000078716. PMID: 15248360. PMCID: PMC2575669.
Article9. Timmermans PB, Benfield P, Chiu AT, Herblin WF, Wong PC, Smith RD. 1992; Angiotensin II receptors and functional correlates. Am J Hypertens. 5(12 Pt 2):221S–235S. DOI: 10.1093/ajh/5.12.221S. PMID: 1290617.
Article10. Wang DH, Du Y, Yao A, Hu Z. 1996; Regulation of type 1 angiotensin II receptor and its subtype gene expression in kidney by sodium loading and angiotensin II infusion. J Hypertens. 14:1409–1415. DOI: 10.1097/00004872-199612000-00004. PMID: 8986922.
Article11. Kamide K, Rakugi H, Higaki J, Okamura A, Nagai M, Moriguchi K, Ohishi M, Satoh N, Tuck ML, Ogihara T. 2002; The renin-angiotensin and adrenergic nervous system in cardiac hypertrophy in fructose-fed rats. Am J Hypertens. 15(1 Pt 1):66–71. DOI: 10.1016/S0895-7061(01)02232-4. PMID: 11824863.
Article12. Ito M, Oliverio MI, Mannon PJ, Best CF, Maeda N, Smithies O, Coffman TM. 1995; Regulation of blood pressure by the type 1A angiotensin II receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 92:3521–3525. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3521. PMID: 7724593. PMCID: PMC42199.
Article13. Sugaya T, Nishimatsu S, Tanimoto K, Takimoto E, Yamagishi T, Imamura K, Goto S, Imaizumi K, Hisada Y, Otsuka A, Uchida H, Sugiura M, Fukuta K, Fukamizu A, Murakami K. 1995; Angiotensin II type 1a receptor-deficient mice with hypotension and hyperreninemia. J Biol Chem. 270:18719–18722. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.270.32.18719. PMID: 7642517.
Article14. Chen X, Li W, Yoshida H, Tsuchida S, Nishimura H, Takemoto F, Okubo S, Fogo A, Matsusaka T, Ichikawa I. 1997; Targeting deletion of angiotensin type 1B receptor gene in the mouse. Am J Physiol. 272(3 Pt 2):F299–F304. DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.1997.272.3.F299. PMID: 9087671.
Article15. Hauger RL, Aguilera G, Catt KJ. 1978; Angiotensin II regulates its receptor sites in the adrenal glomerulosa zone. Nature. 271:176–178. DOI: 10.1038/271176a0. PMID: 202874.
Article16. Yee AH, Burns JD, Wijdicks EF. 2010; Cerebral salt wasting: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 21:339–352. DOI: 10.1016/j.nec.2009.10.011. PMID: 20380974.
Article17. Te Riet L, van Esch JH, Roks AJ, van den Meiracker AH, Danser AH. 2015; Hypertension: renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system alterations. Circ Res. 116:960–975. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303587. PMID: 25767283.18. Kakar SS, Sellers JC, Devor DC, Musgrove LC, Neill JD. 1992; Angiotensin II type-1 receptor subtype cDNAs: differential tissue expression and hormonal regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 183:1090–1096. DOI: 10.1016/S0006-291X(05)80302-X. PMID: 1567388.
Article19. Lee HA, Lee DY, Cho HM, Kim SY, Iwasaki Y, Kim IK. 2013; Histone deacetylase inhibition attenuates transcriptional activity of mineralocorticoid receptor through its acetylation and prevents development of hypertension. Circ Res. 112:1004–1012. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301071. PMID: 23421989.
Article20. Dupas J, Feray A, Goanvec C, Guernec A, Samson N, Bougaran P, Guerrero F, Mansourati J. 2017; Metabolic syndrome and hypertension resulting from fructose enriched diet in Wistar rats. Biomed Res Int. 2017:2494067. DOI: 10.1155/2017/2494067. PMID: 28497040. PMCID: PMC5405603.
Article21. Gambaro SE, Zubiría MG, Portales AE, Rey MA, Rumbo M, Giovambattista A. 2018; M1 macrophage subtypes activation and adipocyte dysfunction worsen during prolonged consumption of a fructose-rich diet. J Nutr Biochem. 61:173–182. DOI: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.08.004. PMID: 30245336.
Article22. Gligorovska L, Bursać B, Kovačević S, Veličković N, Matić G, Djordjevic A. 2019; Mif deficiency promotes adiposity in fructose-fed mice. J Endocrinol. 240:133–145. DOI: 10.1530/JOE-18-0333. PMID: 30400058.
Article23. Seong HY, Cho HM, Kim M, Kim I. 2019; Maternal high-fructose intake induces multigenerational activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Hypertension. 74:518–525. DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.12941. PMID: 31327271.
Article24. Reaven GM, Chang H. 1991; Relationship between blood pressure, plasma insulin and triglyceride concentration, and insulin action in spontaneous hypertensive and Wistar-Kyoto rats. Am J Hypertens. 4(1 Pt 1):34–38. DOI: 10.1093/ajh/4.1.34. PMID: 2006995.25. Takagi Y, Kashiwagi A, Tanaka Y, Asahina T, Kikkawa R, Shigeta Y. 1995; Significance of fructose-induced protein oxidation and formation of advanced glycation end product. J Diabetes Complications. 9:87–91. DOI: 10.1016/1056-8727(94)00022-G. PMID: 7599353.
Article26. Johnson RJ, Segal MS, Sautin Y, Nakagawa T, Feig DI, Kang DH, Gersch MS, Benner S, Sánchez-Lozada LG. 2007; Potential role of sugar (fructose) in the epidemic of hypertension, obesity and the metabolic syndrome, diabetes, kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 86:899–906.27. Noelting J, DiBaise JK. 2015; Mechanisms of fructose absorption. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 6:e120. DOI: 10.1038/ctg.2015.50. PMCID: PMC4817407.
Article28. Wang X, Jia X, Chang T, Desai K, Wu L. 2008; Attenuation of hypertension development by scavenging methylglyoxal in fructose-treated rats. J Hypertens. 26:765–772. DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e3282f4a13c. PMID: 18327087.
Article29. Hwang IS, Ho H, Hoffman BB, Reaven GM. 1987; Fructose-induced insulin resistance and hypertension in rats. Hypertension. 10:512–516. DOI: 10.1161/01.HYP.10.5.512. PMID: 3311990.
Article30. Kolderup A, Svihus B. 2015; Fructose metabolism and relation to atherosclerosis, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. J Nutr Metab. 2015:823081. DOI: 10.1155/2015/823081. PMID: 26199742. PMCID: PMC4496653.
Article31. Connell JM, Davies E. 2005; The new biology of aldosterone. J Endocrinol. 186:1–20. DOI: 10.1677/joe.1.06017. PMID: 16002531.
Article32. Sherajee SJ, Rafiq K, Nakano D, Mori H, Kobara H, Hitomi H, Fujisawa Y, Kobori H, Masaki T, Nishiyama A. 2013; Aldosterone aggravates glucose intolerance induced by high fructose. Eur J Pharmacol. 720:63–68. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.10.051. PMID: 24201309. PMCID: PMC3879420.
Article33. Marcus Y, Shefer G, Sasson K, Kohen F, Limor R, Pappo O, Nevo N, Biton I, Bach M, Berkutzki T, Fridkin M, Benayahu D, Shechter Y, Stern N. 2013; Angiotensin 1-7 as means to prevent the metabolic syndrome: lessons from the fructose-fed rat model. Diabetes. 62:1121–1130. DOI: 10.2337/db12-0792. PMID: 23250359. PMCID: PMC3609575.
Article34. Bundalo MM, Zivkovic MD, Romic SD, Tepavcevic SN, Koricanac GB, Djuric TM, Stankovic AD. 2016; Fructose-rich diet induces gender-specific changes in expression of the renin-angiotensin system in rat heart and upregulates the ACE/AT1R axis in the male rat aorta. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 17:1470320316642915. DOI: 10.1177/1470320316642915. PMID: 27121972. PMCID: PMC5843877.
Article35. Wharton J, Morgan K, Rutherford RA, Catravas JD, Chester A, Whitehead BF, De Leval MR, Yacoub MH, Polak JM. 1998; Differential distribution of angiotensin AT2 receptors in the normal and failing human heart. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 284:323–336.36. Utsunomiya H, Nakamura M, Kakudo K, Inagami T, Tamura M. 2005; Angiotensin II AT2 receptor localization in cardiovascular tissues by its antibody developed in AT2 gene-deleted mice. Regul Pept. 126:155–161. DOI: 10.1016/j.regpep.2004.09.004. PMID: 15664662.
Article37. Xu J, Sun Y, Carretero OA, Zhu L, Harding P, Shesely EG, Dai X, Rhaleb NE, Peterson E, Yang XP. 2014; Effects of cardiac overexpression of the angiotensin II type 2 receptor on remodeling and dysfunction in mice post-myocardial infarction. Hypertension. 63:1251–1259. DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.03247. PMID: 24732892. PMCID: PMC4031246.
Article38. Masaki H, Kurihara T, Yamaki A, Inomata N, Nozawa Y, Mori Y, Murasawa S, Kizima K, Maruyama K, Horiuchi M, Dzau VJ, Takahashi H, Iwasaka T, Inada M, Matsubara H. 1998; Cardiac-specific overexpression of angiotensin II AT2 receptor causes attenuated response to AT1 receptor-mediated pressor and chronotropic effects. J Clin Invest. 101:527–535. DOI: 10.1172/JCI1885. PMID: 9449684. PMCID: PMC508594.
Article39. Sánchez-Lozada LG, Tapia E, Jiménez A, Bautista P, Cristóbal M, Nepomuceno T, Soto V, Avila-Casado C, Nakagawa T, Johnson RJ, Herrera-Acosta J, Franco M. 2007; Fructose-induced metabolic syndrome is associated with glomerular hypertension and renal microvascular damage in rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 292:F423–F429. DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00124.2006. PMID: 16940562.
Article40. Cirillo P, Gersch MS, Mu W, Scherer PM, Kim KM, Gesualdo L, Henderson GN, Johnson RJ, Sautin YY. 2009; Ketohexokinase-dependent metabolism of fructose induces proinflammatory mediators in proximal tubular cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:545–553. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008060576. PMID: 19158351. PMCID: PMC2653686.
Article41. Xu C, Lu A, Lu X, Zhang L, Fang H, Zhou L, Yang T. 2017; Activation of renal (pro)renin receptor contributes to high fructose-induced salt sensitivity. Hypertension. 69:339–348. DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08240. PMID: 27993957. PMCID: PMC5556690.
Article42. Ares GR, Kassem KM, Ortiz PA. 2019; Fructose acutely stimulates NKCC2 activity in rat thick ascending limbs by increasing surface NKCC2 expression. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 316:F550–F557. DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00136.2018. PMID: 30516424. PMCID: PMC6459307.
Article43. Cabral PD, Hong NJ, Hye Khan MA, Ortiz PA, Beierwaltes WH, Imig JD, Garvin JL. 2014; Fructose stimulates Na/H exchange activity and sensitizes the proximal tubule to angiotensin II. Hypertension. 63:e68–e73. DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.02564. PMID: 24379189.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Renin Angiotensin System in Rabbit Corpus Cavernosum: Functional Characterization of Angiotensin II Receptors
- Inhibition of indoxyl sulfate-induced intrarenal renin-angiotensin system activation: targeting the aryl hydrocarbon receptor
- Renal Interstitial Fibrosis and Renin Angiotensin System Inhibition
- Role of Renin Angiotensin System in Clitoral avernosum Smooth Muscle
- Effect of Pinealectomy on the Renin-Angiotensin System in Sprague-Dawley Rats