J Korean Med Sci.
2020 Jun;35(23):e209. 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e209.
Prognostic Factors for Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Daegu, Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonology and Allergy, Department of Internal Medicine, Regional Center for Respiratory Diseases, Yeungnam University Medical Center, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea
- 2Division of Infection, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University Medical Center, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea
- 3Aging Research Center, Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Daejeon, Korea
- KMID: 2502924
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e209
Abstract
- Background
Since its first detection in December 2019, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection has spread rapidly around the world. Although there have been several studies investigating prognostic factors for severe COVID-19, there have been no such studies in Korea.
Methods
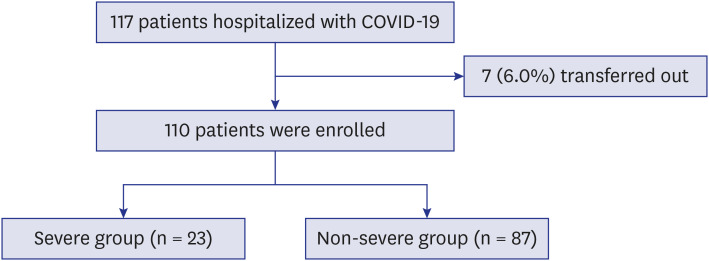
We performed a retrospective observational study of 110 patients with confirmed COVID-19 hospitalized at a tertiary hospital in Daegu, Korea. Demographic, clinical, laboratory, and outcome data were collected and analyzed. Severe disease was defined as a composite outcome of acute respiratory distress syndrome, intensive care unit care, or death.
Results
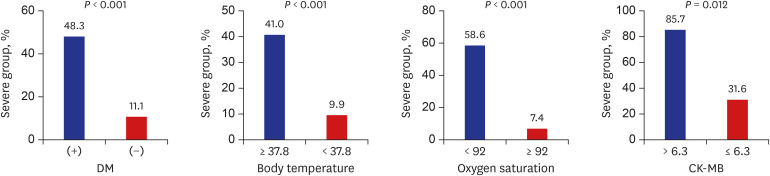
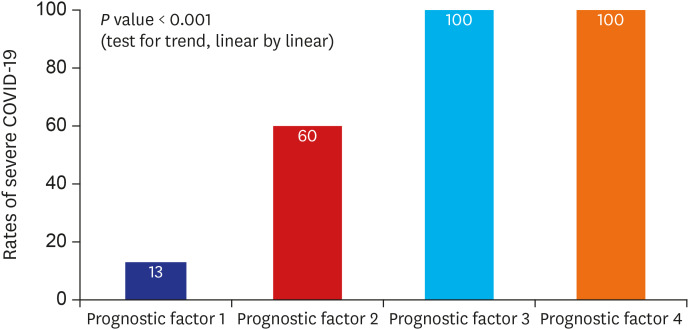
Diabetes mellitus (odds ratio [OR], 19.15; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.90–193.42; P = 0.012), body temperature ≥ 37.8°C (OR, 10.91; 95% CI, 1.35–88.36; P = 0.025), peripheral oxygen saturation < 92% (OR, 33.31; 95% CI, 2.45–452.22; P = 0.008), and creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB) > 6.3 (OR, 56.84; 95% CI, 2.64–1,223.78, P = 0.010) at admission were associated with higher risk of severe COVID-19. The likelihood of development of severe COVID-19 increased with an increasing number of prognostic factors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we found that diabetes mellitus, body temperature ≥ 37.8°C, peripheral oxygen saturation < 92%, and CK-MB > 6.3 are independent predictors of severe disease in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Appropriate assessment of prognostic factors and close monitoring to provide the necessary interventions at the appropriate time in high-risk patients may reduce the case fatality rate of COVID-19.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical Features of COVID-19 in Uzbekistan
KyungHee Kim, Jae Wook Choi, Juyoung Moon, Habibulla Akilov, Laziz Tuychiev, Bakhodir Rakhimov, Kwang Sung Min
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(45):e404. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e404.
Reference
-
1. Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382(18):1708–1720. PMID: 32109013.2. Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020; 323(13):1239.3. Chen T, Dai Z, Mo P, Li X, Ma Z, Song S, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of older patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China (2019): a single-centered, retrospective study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020.4. Wu J, Li W, Shi X, Chen Z, Jiang B, Liu J, et al. Early antiviral treatment contributes to alleviate the severity and improve the prognosis of patients with novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19). J Intern Med. 2020.
Article5. Li X, Xu S, Yu M, Wang K, Tao Y, Zhou Y, et al. Risk factors for severity and mortality in adult COVID-19 inpatients in Wuhan. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020.
Article6. Shi Y, Yu X, Zhao H, Wang H, Zhao R, Sheng J. Host susceptibility to severe COVID-19 and establishment of a host risk score: findings of 487 cases outside Wuhan. Crit Care. 2020; 24(1):108. PMID: 32188484.
Article7. Zhang J, Wang X, Jia X, Li J, Hu K, Chen G, et al. Risk factors for disease severity, unimprovement, and mortality in COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, China. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020; 26(6):767–772. PMID: 32304745.
Article8. Wei YY, Wang RR, Zhang DW, Tu YH, Chen CS, Ji S, et al. Risk factors for severe COVID-19: Evidence from 167 hospitalized patients in Anhui, China. J Infect. 2020.
Article9. ARDS Definition Task Force, Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, Ferguson ND, Caldwell E, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition. JAMA. 2012; 307(23):2526–2533. PMID: 22797452.10. Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019; 157:107843. PMID: 31518657.11. Kornum JB, Thomsen RW, Riis A, Lervang HH, Schønheyder HC, Sørensen HT. Type 2 diabetes and pneumonia outcomes: a population-based cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30(9):2251–2257. PMID: 17595354.
Article12. Yang JK, Feng Y, Yuan MY, Yuan SY, Fu HJ, Wu BY, et al. Plasma glucose levels and diabetes are independent predictors for mortality and morbidity in patients with SARS. Diabet Med. 2006; 23(6):623–628. PMID: 16759303.
Article13. Kulcsar KA, Coleman CM, Beck SE, Frieman MB. Comorbid diabetes results in immune dysregulation and enhanced disease severity following MERS-CoV infection. JCI Insight. 2019; 4(20):e131774.
Article14. Casqueiro J, Casqueiro J, Alves C. Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus: a review of pathogenesis. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 16(Suppl 1):S27–36. PMID: 22701840.15. Guo W, Li M, Dong Y, Zhou H, Zhang Z, Tian C, et al. Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020.16. Fine MJ, Auble TE, Yealy DM, Hanusa BH, Weissfeld LA, Singer DE, et al. A prediction rule to identify low-risk patients with community-acquired pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336(4):243–250. PMID: 8995086.
Article17. Bone RC, Sibbald WJ, Sprung CL. The ACCP-SCCM consensus conference on sepsis and organ failure. Chest. 1992; 101(6):1481–1483. PMID: 1600757.
Article18. Netea MG, Kullberg BJ, Van der Meer JW. Circulating cytokines as mediators of fever. Clin Infect Dis. 2000; 31(Suppl 5):S178–S184. PMID: 11113021.
Article19. Hong KS, Lee KH, Chung JH, Shin KC, Choi EY, Jin HJ, et al. Clinical features and outcomes of 98 patients hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 infection in Daegu, South Korea: a brief descriptive study. Yonsei Med J. 2020; 61(5):431–437. PMID: 32390367.
Article20. Xie J, Tong Z, Guan X, Du B, Qiu H, Slutsky AS. Critical care crisis and some recommendations during the COVID-19 epidemic in China. Intensive Care Med. 2020; 46(5):837–840. PMID: 32123994.
Article21. Li JW, Han TW, Woodward M, Anderson CS, Zhou H, Chen YD, et al. The impact of 2019 novel coronavirus on heart injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2020.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnosis of Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in the Early Stage of Outbreak
- Management of Diabetes in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Prognosis and Practical Issues
- Coronavirus Disease 2019-Liver InjuryLiterature Review and Guidelines Based on the Recommendations of Hepatological Societies
- Obesity and Coronavirus Disease 2019