J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2020 Mar;24(1):14-18. 10.14193/jkfas.2020.24.1.14.
Correlation between Chronic Ankle Instability and Center of Pressure Using Pedobrarograph
- Affiliations
-
- 1rtment of Orthopedic Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Korea
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, SNU Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2502903
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2020.24.1.14
Abstract
- Purpose
Chronic ankle instability is a very common abnormality of the ankle, but there is still controversy regarding its evaluation criteria. The stress view has difficulties in reflecting the patient’s symptoms and treatment progress. Therefore, this study examined the relationship between the center of pressure (COP) measured by a pedobarograph and the symptoms of the patient.
Materials and Methods
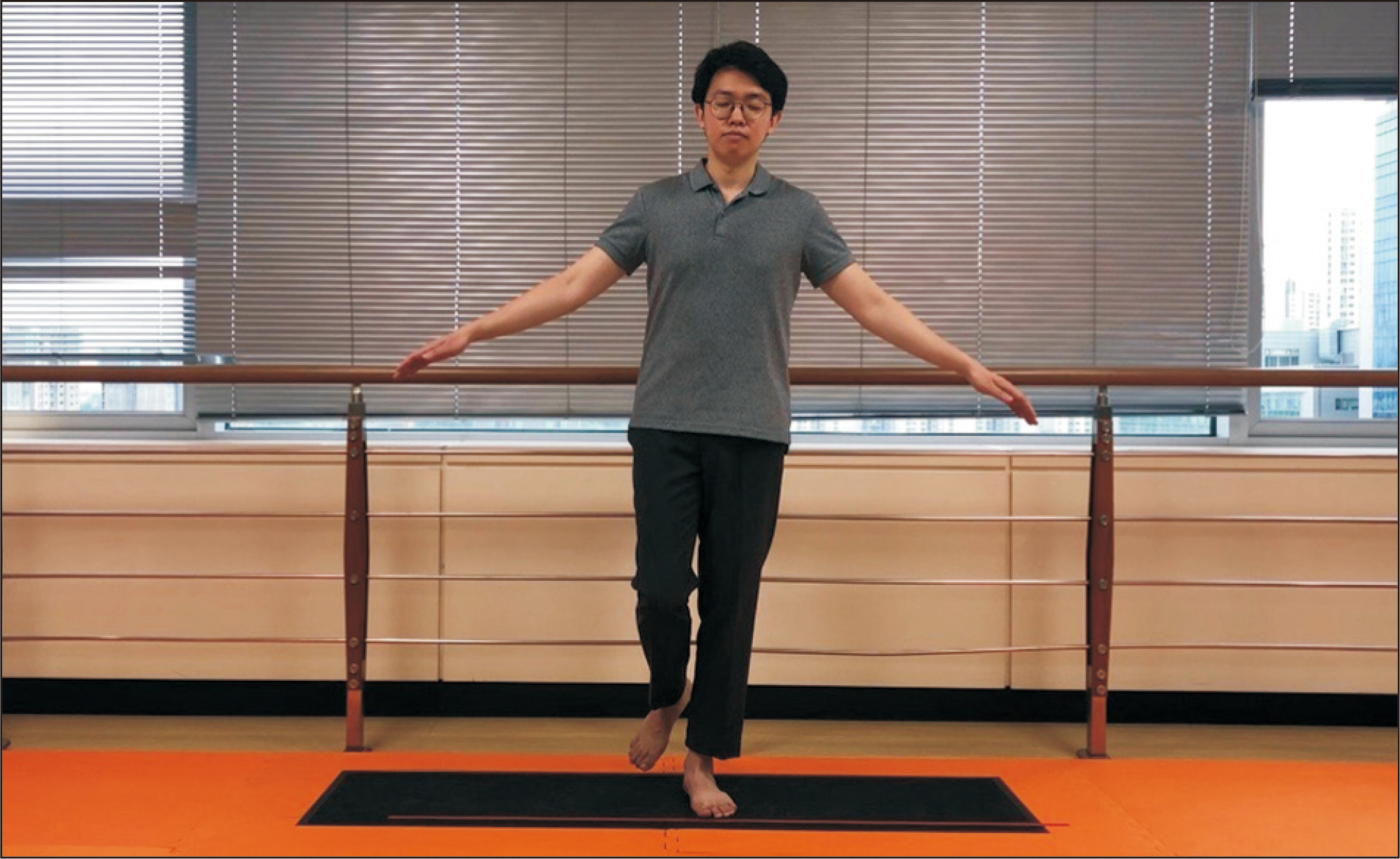
Thirty patients with chronic ankle instability from February to August 2018 were included. Each patient was surveyed with the foot and ankle outcome score (FAOS). The COP was measured with a foot pressure scanner, and the travel distance and ellipse area of the COP were calculated. Each patient was measured on one foot and on two feet with his or her eyes closed and open. The relationship between the COP measurement and FAOS score was analyzed using the Pearson correlation coefficient.
Results
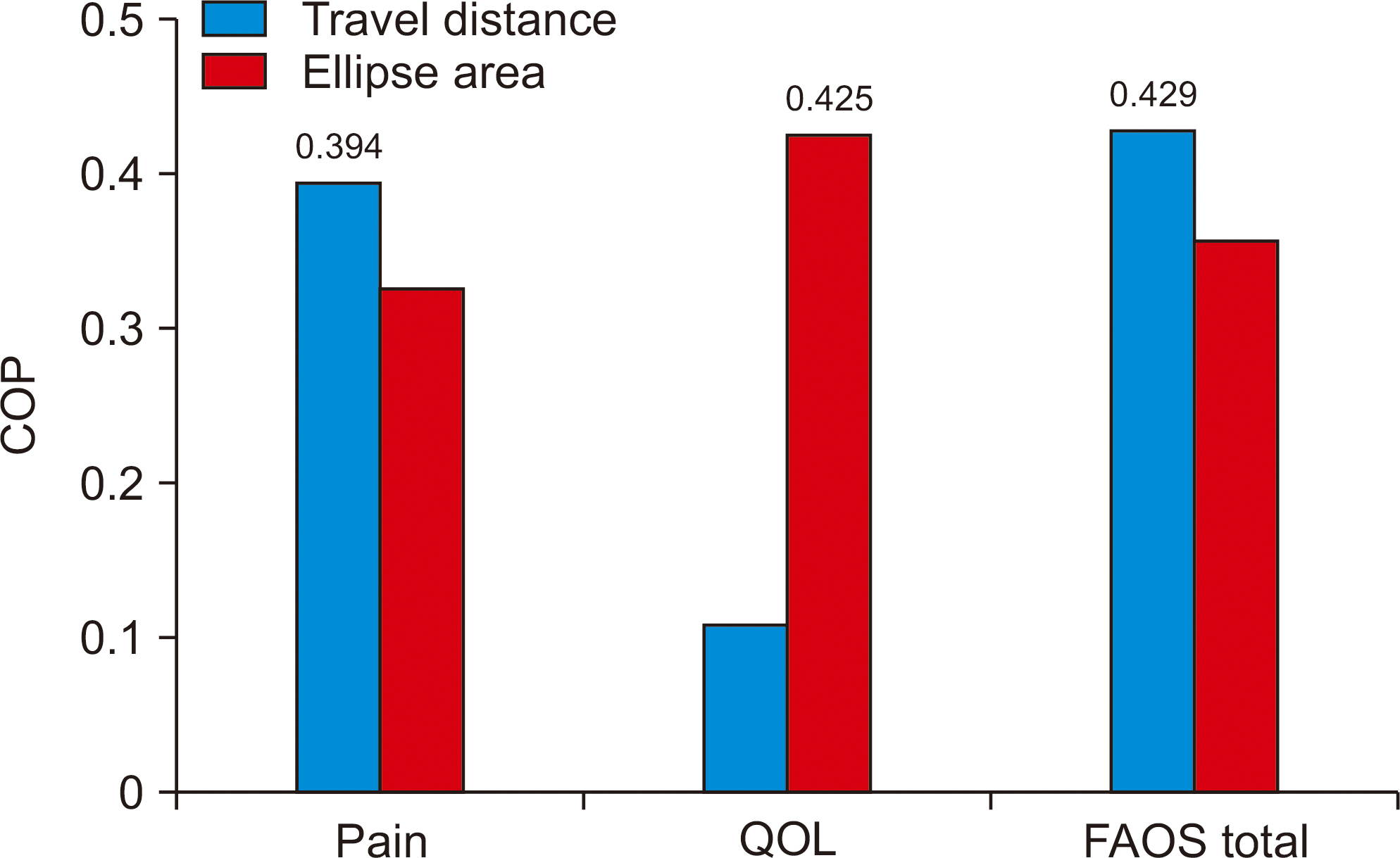
The participants were consisted of 21 male and nine female, with a mean age of 30 years, mean weight of 72 kg, and mean foot size of 259 mm. With the eyes open, the correlation coefficient between the FAOS and travel distance of the affected side was –0.394 (p<0.05) and that between the FAOS and the ellipse area of the affected side was –0.425 (p<0.05). On the other hand, no significant correlations were found between the travel distance and ellipse area of the affected side when patients closed their eyes.
Conclusion
Measurement of the COP using foot pressure scanner could evaluate objectively patients with chronic ankle instability, with measurements in patients with their eyes open being more significant. Based on the findings of this study, an analysis of the COP with the patients with their eyes open and standing on one foot may help determine the management strategy and assess the progress of the patients.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Functional Evaluation Using Center of Pressure between Chronic Ankle Instability and Healthy Control
Dong Wook Lee, Hyung Gyu Jeon, Byung Hun Kim, Sae Yong Lee, Jin Su Kim
Korean J Sports Med. 2022;40(4):217-225. doi: 10.5763/kjsm.2022.40.4.217.
Reference
-
References
1. Olmsted LC, Carcia CR, Hertel J, Shultz SJ. Efficacy of the star excursion balance tests in detecting reach deficits in subjects with chronic ankle instability. J Athl Train. 2002; 37:501–6.2. Freeman MA. Instability of the foot after injuries to the lateral ligament of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1965; 47:669–77. doi:. DOI: 10.1302/0301-620X.47B4.669.3. Kaikkonen A, Kannus P, Järvinen M. A performance test protocol and scoring scale for the evaluation of ankle injuries. Am J Sports Med. 1994; 22:462–9. doi:. DOI: 10.1177/036354659402200405.4. Ji SW, Kim HS, Kwon KW, Shin YO, Kim YJ, Lee JP, et al. The ankle strength, balance and functional ability of the adolescent volleyball players with functional ankle instability. Korean J Phys Educ-Huma-nit Soc Sci. 2004; 43:567–78.5. Lee KM, Chung CY, Kwon SS, Sung KH, Lee SY, Won SH, et al. Transcultural adaptation and testing psychometric properties of the Korean version of the Foot and Ankle Outcome Score (FAOS). Clin Rheumatol. 2013; 32:1443–50. doi:. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-013-2288-1.
Article6. Guillo S, Bauer T, Lee JW, Takao M, Kong SW, Stone JW, et al. Consensus in chronic ankle instability: aetiology, assessment, surgical indications and place for arthroscopy. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013; 99(8 Suppl):): S411-9.doi:. DOI: 10.1016/j.otsr.2013.10.009.
Article7. Lord SR, Murray SM, Chapman K, Munro B, Tiedemann A. Sit-to-stand performance depends on sensation, speed, balance, and psychological status in addition to strength in older people. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2002; 57:M539–43. doi:. DOI: 10.1093/gerona/57.8.m539.
Article8. Plisky PJ, Gorman PP, Butler RJ, Kiesel KB, Underwood FB, Elkins B. The reliability of an instrumented device for measuring components of the star excursion balance test. N Am J Sports Phys Ther. 2009; 4:929.9. Shin SH, Lee JW, Jeong GY, Kwon TK. Assessment of body for dynamic postural balance exercise. Paper presented at: The Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers Spring Conference;. 2011. May; Busan, Korea. p.2718–9.10. Jonsson E, Seiger A, Hirschfeld H. One-leg stance in healthy young and elderly adults: a measure of postural steadiness? Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2004; 19:688–94. doi:. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2004.04.002.
Article11. Bohannon RW, Leary KM. Standing balance and function over the course of acute rehabilitation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1995; 76:994–6. doi:. DOI: 10.1016/s0003-9993 (95)81035-8.
Article12. Frzovic D, Morris ME, Vowels L. Clinical tests of standing balance: performance of persons with multiple sclerosis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2000; 81:215–21. doi:. DOI: 10.1016/s0003-9993 (00)90144-8.
Article13. Tinetti ME. Performance-oriented assessment of mobility problems in elderly patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1986; 34:119–26. doi:. DOI: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1986.tb05480.x.
Article14. Karlsson A, Frykberg G. Correlations between force plate measures for assessment of balance. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2000; 15:365–9. doi:. DOI: 110.1016/s0268-0033 (99)00096-0.
Article15. Franchignoni F, Tesio L, Martino MT, Ricupero C. Reliability of four simple, quantitative tests of balance and mobility in healthy elderly females. Aging (Milano). 1998; 10:26–31. doi:. DOI: 10.1007/bf03339630.
Article16. Coughlan GF, Fullam K, Delahunt E, Gissane C, Caulfield BM. A comparison between performance on selected directions of the star excursion balance test and the Y balance test. J Athl Train. 2012; 47:366–71. doi:. DOI: 10.4085/1062-6050-47.4.03.
Article17. Ruhe A, Fejer R, Walker B. The test-retest reliability of centre of pressure measures in bipedal static task conditions–a systematic review of the literature. Gait Posture. 2010; 32:436–45. doi:. DOI: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2010.09.012.18. Adlerton AK, Moritz U, Moe-Nilssen R. Forceplate and accelerometer measures for evaluating the effect of muscle fatigue on postural control during one-legged stance. Physiother Res Int. 2003; 8:187–99. doi:. DOI: 10.1002/pri.289.
Article19. Goh EK. Clinical application of computerized dynamic posturography. J Korean Balance Soc. 2005; 4:107–18.20. Verhagen E, Bobbert M, Inklaar M, van Kalken M, van der Beek A, Bouter L, et al. The effect of a balance training programme on centre of pressure excursion in one-leg stance. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2005; 20:1094–100. doi:. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2005.07.001.
Article21. Haas G, Diener HC, Rapp H, Dichgans J. Development of feedback and feedforward control of upright stance. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1989; 31:481–8. doi:. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1989.tb04026.x.22. Le Clair K, Riach C. Postural stability measures: what to measure and for how long. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1996; 11:176–8. doi:. DOI: 10.1016/0268-0033 (95)00027-5.
Article23. Mauritz KH, Dietz V. Characteristics of postural instability induced by ischemic blocking of leg afferents. Exp Brain Res. 1980; 38:117–9. doi:. DOI: 10.1007/bf00237939.
Article24. Riach CL, Hayes KC. Maturation of postural sway in young children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1987; 29:6508. doi:. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1987.tb08507.x.
Article25. Schmit JM, Regis DI, Riley MA. Dynamic patterns of postural sway in ballet dancers and track athletes. Exp Brain Res. 2005; 163:370–8. doi:. DOI: 10.1007/s00221-004-2185-6.
Article26. Tsai LC, Yu B, Mercer VS, Gross MT. Comparison of different structural foot types for measures of standing postural control. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2006; 36:942–53. doi:. DOI: 10.2519/jospt.2006.2336.
Article27. Murphy DF, Connolly DA, Beynnon BD. Risk factors for lower extremity injury: a review of the literature. Br J Sports Med. 2003; 37:13–29. doi:. DOI: 10.1136/bjsm.37.1.13.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability
- Ligament Repair in Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability: Efficacy and Technique of Broström Procedures
- Diagnosis of Lateral Ankle Ligament Injury in the Evaluation of Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability
- Diagnosis and Comorbidity of Chronic Ankle Instability
- Arthroscopic Procedure in the Treatment of Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability