Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 3Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2502416
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0091
Abstract
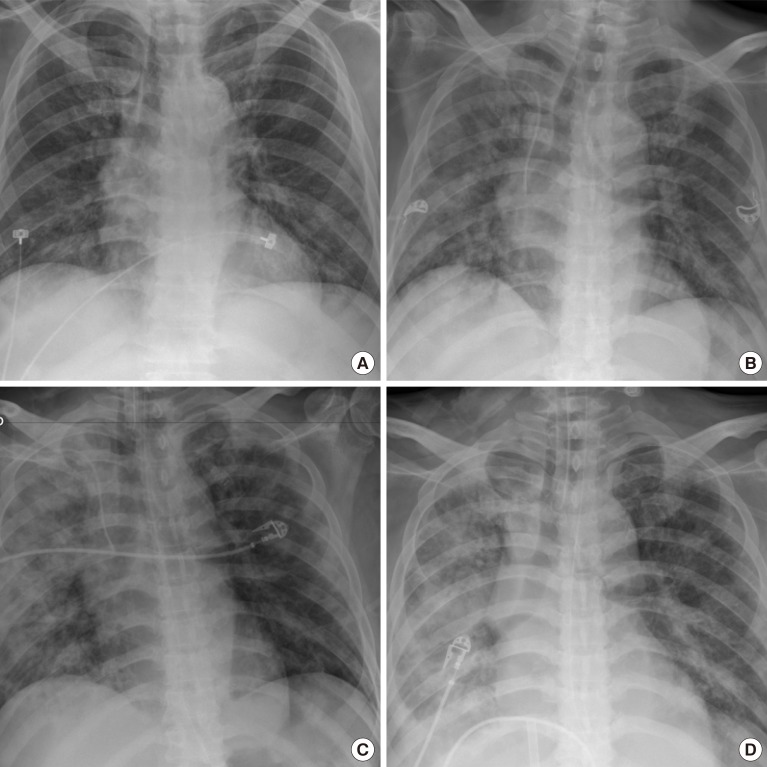
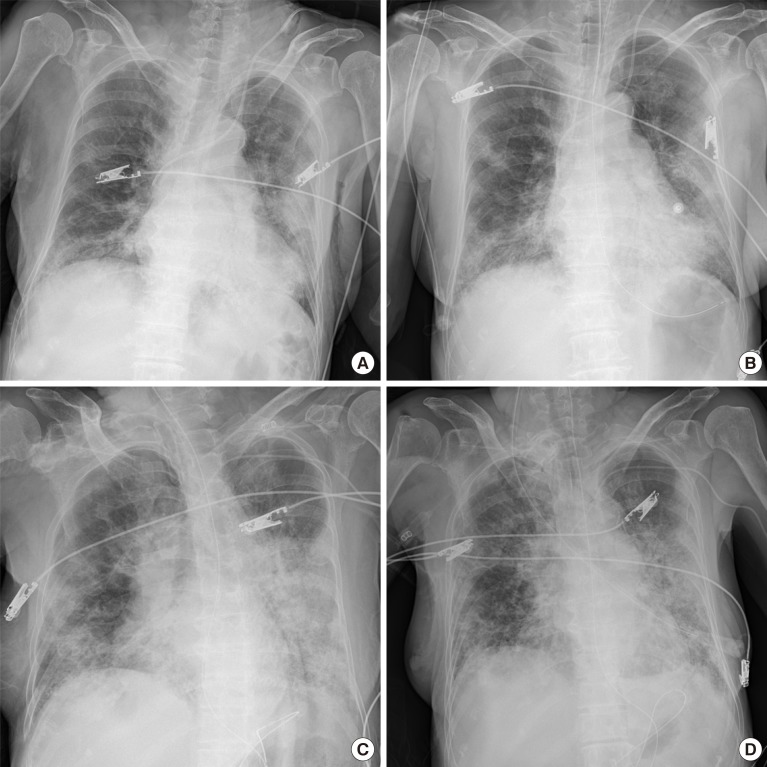
- Since the first case was contracted by coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) in Daegu, Korea in February 2020, about 6,800 cases and 130 deaths have been reported on April 9, 2020. Recent studies have reported that patients with diabetes showed higher mortality and they had a worse prognosis than the group without diabetes. In poorly controlled patients with diabetes, acute hyperglycemic crises such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) also might be precipitated by COVID- 19. Thus, intensive monitoring and aggressive supportive care should be needed to inadequately controlled patients with diabetes and COVID-19 infection. Here, we report two cases of severe COVID-19 patients with acute hyperglycemic crises in Korea.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Diabetes: The Epidemic and the Korean Diabetes Association Perspective
Junghyun Noh, Hyun-Ha Chang, In-Kyung Jeong, Kun Ho Yoon
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):372-381. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0138.Letter: Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports (
Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:349–53)
Ja Young Jeon
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):480-481. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0121.Response: Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports (
Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:349–53)
Na-young Kim, Eunyeong Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Yong-Hoon Lee, Eun Young Choi
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):484-485. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0129.Management of Diabetes in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Prognosis and Practical Issues
Hye Soon Kim
J Korean Diabetes. 2020;21(3):120-125. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2020.21.3.120.A Case of COVID-19 with Acute Myocardial Infarction and Cardiogenic Shock
Hong Nyun Kim, Jang Hoon Lee, Hun Sik Park, Dong Heon Yang, Se Yong Jang, Myung Hwan Bae, Yongkeun Cho, Shung Chull Chae, Yong-Hoon Lee
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(27):e258. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e258.
Reference
-
1. Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, Xiang J, Wang Y, Song B, Gu X, Guan L, Wei Y, Li H, Wu X, Xu J, Tu S, Zhang Y, Chen H, Cao B. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020; 395:1054–1062. PMID: 32171076.
Article2. Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, Shu H, Xia J, Liu H, Wu Y, Zhang L, Yu Z, Fang M, Yu T, Wang Y, Pan S, Zou X, Yuan S, Shang Y. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020; 2. 24. DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5. [Epub].
Article3. Guo W, Li M, Dong Y, Zhou H, Zhang Z, Tian C, Qin R, Wang H, Shen Y, Du K, Zhao L, Fan H, Luo S, Hu D. Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020; 3. 31. DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.3319. [Epub].4. Kim KJ, Kwon TY, Yu S, Seo JA, Kim NH, Choi KM, Baik SH, Choi DS, Kim SG, Park Y, Kim NH. Ten-year mortality trends for adults with and without diabetes mellitus in south Korea, 2003 to 2013. Diabetes Metab J. 2018; 42:394–401. PMID: 29885109.
Article5. You JH, Song SO, Park SH, Park KH, Nam JY, Kim DW, Kim HM, Kim DJ, Lee YH, Lee BW. Trends in hyperglycemic crisis hospitalizations and in- and out-of-hospital mortality in the last decade based on Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2019; 34:275–281. PMID: 31565880.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Letter: Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports (
Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:349–53) - Obesity and 30-day case fatality after hyperglycemic crisis hospitalizations in Korea: a national cohort study
- Response: Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports (
Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:349–53) - Management of Diabetes in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Prognosis and Practical Issues
- Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in the Early Stage of Outbreak
- Letter: Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports (