Ann Rehabil Med.
2020 Feb;44(1):48-57. 10.5535/arm.2020.44.1.48.
Determining the Most Appropriate Assistive Walking Device Using the Inertial Measurement Unit-Based Gait Analysis System in Disabled Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Ewha Womans University Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2501045
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2020.44.1.48
Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the gait pattern of patients with gait disturbances without consideration of defilades due to assistive devices. This study focuses on gait analysis using the inertial measurement unit (IMU) system, which can also be used to determine the most appropriate assistive device for patients with gait disturbances.
Methods
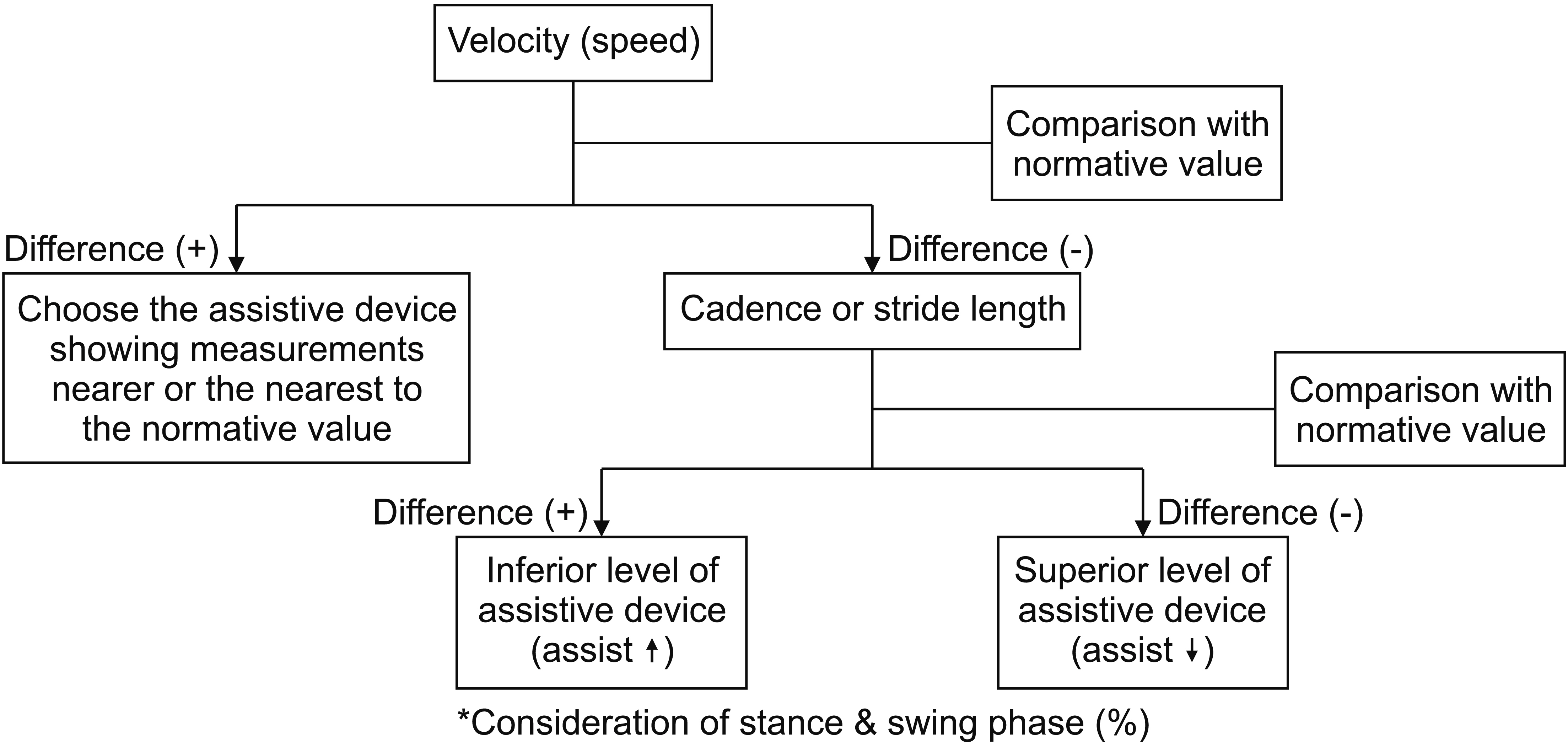
Records of 18 disabled patients who visited the Department of Rehabilitation from May 2018 to June 2018 were selected. Patients’ gait patterns were analyzed using the IMU system with different assistive devices to determine the most appropriate device depending on the patient’s condition. Evaluation was performed using two or more devices, and the appropriate device was selected by comparing the 14 parameters of gait evaluation. The device showing measurements nearer or the nearest to the normative value was selected for rehabilitation.
Results
The result of the gait evaluation in all 18 patients was analyzed using the IMU system. According to the records, the patients were evaluated using various assistive devices without consideration of defilades. Moreover, this gait analysis was effective in determining the most appropriate device for each patient. Increased gait cycle time and swing phase and decreased stance phase were observed in devices requiring significant assistance.
Conclusion
The IMU-based gait analysis system is beneficial in evaluating gait in clinical fields. Specifically, it is useful in evaluating patients with gait disturbances who require assistive devices. Furthermore, it allows the establishment of an evidence-based decision for the most appropriate assistive walking devices for patients with gait disturbances.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sharif Bidabadi S, Murray I, Lee GYF. The application of inertial measurements unit for the clinical evaluation and assessment of gait events. J Med Eng Technol. 2017; 41:612–22.
Article2. Vargas-Valencia LS, Elias A, Rocon E, Bastos-Filho T, Frizera A. An IMU-to-body alignment method applied to human gait analysis. Sensors (Basel). 2016; 16:E2090.
Article3. World Health Organization, World Bank. World report on disability. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization;2011.4. Lee JH, Park SW, Kim DA, Jang SJ, Kim YH. Gait analysis using accelerometer in stroke patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2004; 28:488–93.5. Cho YS, Jang SH, Cho JS, Kim MJ, Lee HD, Lee SY, et al. Evaluation of validity and reliability of inertial measurement unit-based gait analysis systems. Ann Rehabil Med. 2018; 42:872–83.
Article6. Favre J, Jolles BM, Aissaoui R, Aminian K. Ambulatory measurement of 3D knee joint angle. J Biomech. 2008; 41:1029–35.
Article7. Watanabe T, Saito H. Tests of wireless wearable sensor system in joint angle measurement of lower limbs. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2011; 2011:5469–72.
Article8. van Acht V, Bongers E, Lambert N, Verberne R. Miniature wireless inertial sensor for measuring human motions. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2007; 2007:6279–82.
Article9. Luinge HJ, Veltink PH. Measuring orientation of human body segments using miniature gyroscopes and accelerometers. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2005; 43:273–82.
Article10. Zhu R, Zhou Z. A real-time articulated human motion tracking using tri-axis inertial/magnetic sensors package. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2004; 12:295–302.11. Kim MS, Yu SB, Lee KS. Development of a high-precision calibration method for inertial measurement unit. Int J Precis Eng Manuf. 2014; 15:567–75.
Article12. Lee D, Lee S, Park S, Ko S. Test and error parameter estimation for MEMS: based low cost IMU calibration. Int J Precis Eng Manuf. 2011; 12:597–603.13. Madgwick S. An efficient orientation filter for inertial and inertial/magnetic sensor arrays [Internet]. Bristol, UK: X-IO Technologies;2010. [cited 2020 Jan 15]. Available from: http://x-io.co.uk/res/doc/madgwick_internal_report.pdf.14. Vienne A, Barrois RP, Buffat S, Ricard D, Vidal PP. Inertial sensors to assess gait quality in patients with neurological disorders: a systematic review of technical and analytical challenges. Front Psychol. 2017; 8:817.
Article15. Maetzler W, Domingos J, Srulijes K, Ferreira JJ, Bloem BR. Quantitative wearable sensors for objective assessment of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2013; 28:1628–37.
Article16. Caldas R, Mundt M, Potthast W, Buarque de Lima Neto F, Markert B. A systematic review of gait analysis methods based on inertial sensors and adaptive algorithms. Gait Posture. 2017; 57:204–10.
Article17. Muro-de-la-Herran A, Garcia-Zapirain B, MendezZorrilla A. Gait analysis methods: an overview of wearable and non-wearable systems, highlighting clinical applications. Sensors (Basel). 2014; 14:3362–94.18. Sant’Anna A, Wickstrom N, Eklund H, Zugner R, Tranberg R. Assessment of gait symmetry and gait normality using inertial sensors: in-lab and in-situ evaluation. In : Gabriel J, Schier J, Van Huffel S, Conchon E, Correia C, Fred A, Gamboa H, editors. Biomedical engineering systems and technologies. Heidelberg: Springer;2013. p. 239–54.19. Ferrari A, Rocchi L, van den Noort J, Harlaar J. Toward the use of wearable inertial sensors to train gait in subjects with movement disorders. In : Pons J, Torricelli D, Pajaro M, editors. Converging clinical and engineering research on neurorehabilitation. Heidelberg: Springer;2013. p. 937–40.20. Petraglia F, Scarcella L, Pedrazzi G, Brancato L, Puers R, Costantino C. Inertial sensors versus standard systems in gait analysis: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2019; 55:265–80.
Article21. Washabaugh EP, Kalyanaraman T, Adamczyk PG, Claflin ES, Krishnan C. Validity and repeatability of inertial measurement units for measuring gait parameters. Gait Posture. 2017; 55:87–93.
Article22. Brognara L, Palumbo P, Grimm B, Palmerini L. Assessing gait in Parkinson’s disease using wearable motion sensors: a systematic review. Diseases. 2019; 7:E18.
Article23. Zago M, Sforza C, Pacifici I, Cimolin V, Camerota F, Celletti C, et al. Gait evaluation using inertial measurement units in subjects with Parkinson’s disease. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2018; 42:44–8.
Article24. Vienne-Jumeau A, Quijoux F, Vidal PP, Ricard D. Value of gait analysis for measuring disease severity using inertial sensors in patients with multiple sclerosis: protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev. 2019; 8:15.
Article25. Cho JS, Cho YS, Moon SB, Kim MJ, Lee HD, Lee SY, et al. Scoliosis screening through a machine learning based gait analysis test. Int J Precis Eng Manuf. 2018; 19:1861–72.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Validation of foot pitch angle estimation using inertial measurement unit against marker-based optical 3D motion capture system
- Comparison of Gait Parameters during Forward Walking under Different Visual Conditions Using Inertial Motion Sensors
- Evaluation of Validity and Reliability of Inertial Measurement Unit-Based Gait Analysis Systems
- Effects of Gait Training Using a Shoulder-Back Orthosis on Balance and Gait in Patients with Stroke
- Shoe-Type Wearable Sensors Measure Gait Parameters in Vestibular Neuritis: A Preliminary Study