Anesth Pain Med.
2020 Jan;15(1):124-128. 10.17085/apm.2020.15.1.124.
Life-threatening tension pneumothorax after unsuccessful tracheostomy tube exchange in a trauma patient - A case report -
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Dankook University Hospital, Cheonan, Korea
- KMID: 2500466
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2020.15.1.124
Abstract
- Background
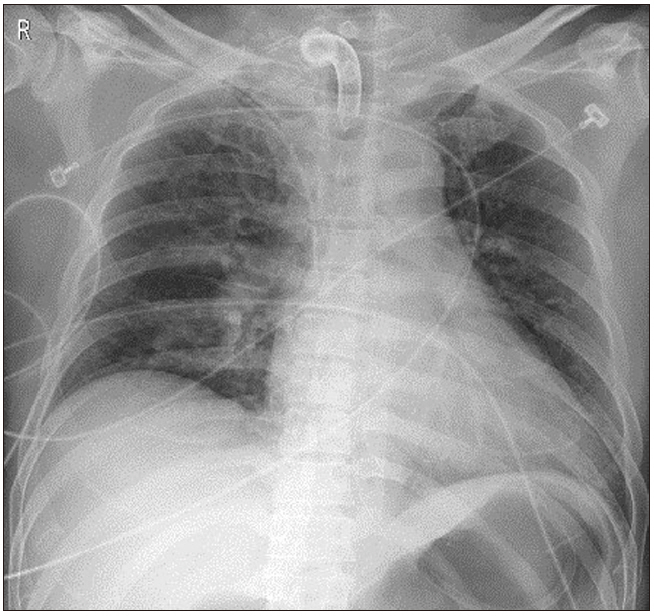
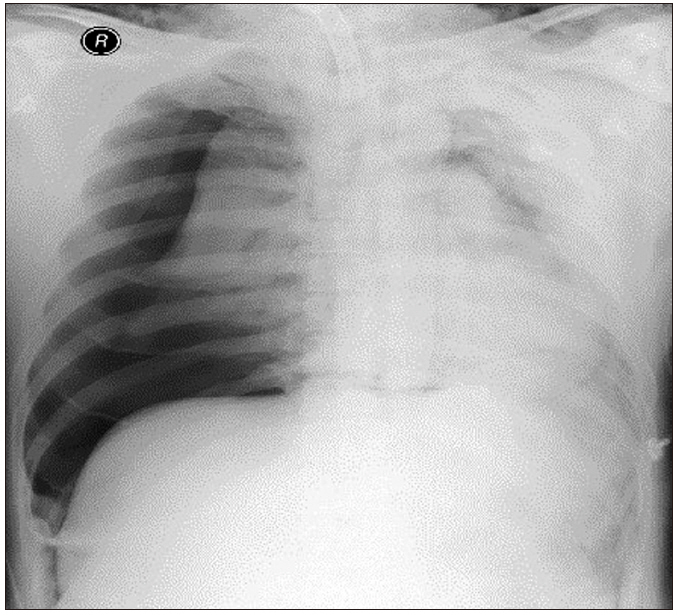
Tracheostomy tube exchange is a common and safe procedure. However, when the tracheocutaneous tract is not completely mature, cannula exchange or endotracheal tube insertion via the tracheostomy site can rarely induce life-threatening complications, including subcutaneous emphysema, loss of airway, tension pneumothorax, and pneumoperitoneum. Case: We report a case of life-threatening tension pneumothorax developed during tracheostomy tube exchange with a reinforced endotracheal tube for a planned facial surgery after recent tracheostomy in a trauma patient.
Conclusions
Understanding of the pathogenesis and the use of preventive strategies based on it are expected to provide safer and more effective anesthetic management to patients with tracheostomy.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
Heyrosa MG., Melniczek DM., Rovito P., Nicholas GG. 2006. Percutaneous tracheostomy: a safe procedure in the morbidly obese. J Am Coll Surg. 202:618–22. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2005.12.009. PMID: 16571432.Engels PT., Bagshaw SM., Meier M., Brindley PG. 2009. Tracheostomy: from insertion to decannulation. Can J Surg. 52:427–33. PMID: 19865580. PMCID: 2769112.Fikkers BG., Briedé IS., Verwiel JM., Van Den Hoogen FJ FJ. 2002. Percutaneous tracheostomy with the Blue Rhino trade mark technique: presentation of 100 consecutive patients. Anaesthesia. 57:1094–7. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2044.2002.02834.x. PMID: 12392457.El Solh AA AA., Jaafar W. 2007. A comparative study of the complications of surgical tracheostomy in morbidly obese critically ill patients. Crit Care. 11:R3. DOI: 10.1186/cc5147. PMID: 17222333. PMCID: PMC2151852.Simon M., Metschke M., Braune SA., Püschel K., Kluge S. 2013. Death after percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy: a systematic review and analysis of risk factors. Crit Care. 17:R258. DOI: 10.1186/cc13085. PMID: 24168826. PMCID: PMC4056379.Fikkers BG., van Veen JA JA., Kooloos JG., Pickkers P., van den Hoogen FJ FJ., Hillen B, et al. 2004. Emphysema and pneumothorax after percutaneous tracheostomy: case reports and an anatomic study. Chest. 125:1805–14. DOI: 10.1378/chest.125.5.1805. PMID: 15136394.Escarment J., Suppini A., Sallaberry M., Kaiser E., Cantais E., Palmier B, et al. 2000. Percutaneous tracheostomy by forceps dilation: report of 162 cases. Anaesthesia. 55:125–30. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2044.2000.055002125.x. PMID: 10651672.Hwang SM., Jang JS., Yoo JI., Kwon HK., Lee SK., Lee JJ, et al. 2011. Difficult tracheostomy tube placement in an obese patient with a short neck -a case report-. Korean J Anesthesiol. 60:434–6. DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2011.60.6.434. PMID: 21738847. PMCID: PMC3121091.Tabaee A., Lando T., Rickert S., Stewart MG., Kuhel WI. 2007. Practice patterns, safety, and rationale for tracheostomy tube changes: a survey of otolaryngology training programs. Laryngoscope. 117:573–6. DOI: 10.1097/MLG.0b013e318030455a. PMID: 17415123.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Tracheostomy Induced Bilateral Tension Pneumothorax
- Emergency Management of Thoracic Trauma
- Tension pneumothorax after arthroscopic shoulder surgery: A case report
- Cardiac arrest caused by contralateral tension pneumothorax during one-lung ventilation - A case report –
- Contralateral Tension Pneumothorax during One Lung Ventilation by a Univent(R) Tube