Anesth Pain Med.
2020 Jan;15(1):111-119. 10.17085/apm.2020.15.1.111.
The effect of dexmedetomidine and midazolam on combined spinal-epidural anesthesia in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Korea
- 2Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
- KMID: 2500464
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2020.15.1.111
Abstract
- Background
Intravenous dexmedetomidine has been reported to potentiate the anesthetic effect of local anesthetics and improve the quality of postoperative analgesia when used as an adjuvant in neuraxial block. We compared the effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine and midazolam for sedation on combined spinal-epidural (CSE) anesthesia.
Methods
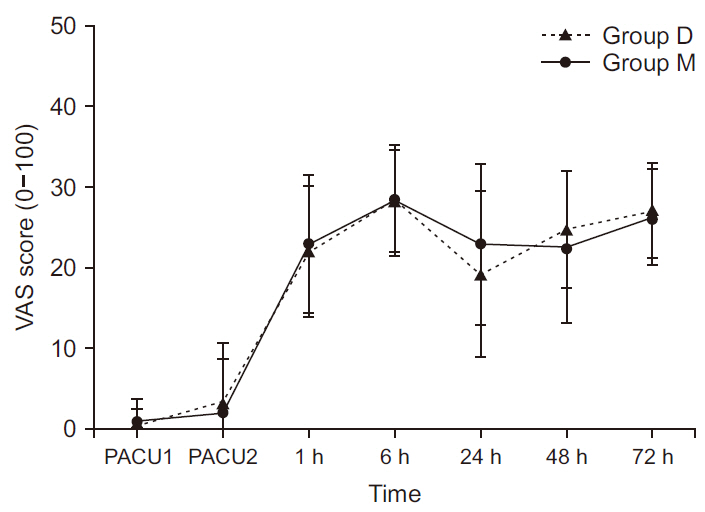
This study included 50 patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. CSE anesthesia was given using 10 mg bupivacaine for all patients. After checking the maximum sensory and motor levels, the patients were randomly allocated into two groups of 25 each to receive intravenous continuous infusion of dexmedetomidine (Group D) or midazolam (Group M) for sedation during surgery. Regression block level, hemodynamic changes, and sedation score were compared between the groups when the patients entered the postanesthetic care unit (PACU). For patient-controlled epidural analgesia, 0.2% levobupivacaine with 650 μg of fentanyl (150 ml in total) was infused at a rate of 1 ml/h, in addition to a 3-ml bolus dose with a 30-min lockout time. The visual analogue scale scores, additional analgesic demand, patient satisfaction, and adverse events between the two groups were also compared postoperatively.
Results
A significant difference was observed in relation to the sensory block level in the PACU (Group D: 6.3 ± 2.1; Group M: 3.2 ± 1.9) (P = 0.002). The motor block level and other outcomes showed no significant intergroup differences.
Conclusions
Intravenous injection of dexmedetomidine, rather than midazolam, for procedural sedation is associated with prolonged sensory block, with comparable incidences of adverse events during CSE anesthesia.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
Johnson RL., Kopp SL., Burkle CM., Duncan CM., Jacob AK., Erwin PJ, et al. 2016. Neuraxial vs general anaesthesia for total hip and total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review of comparative-effectiveness research. Br J Anaesth. 116:163–76. DOI: 10.1093/bja/aev455. PMID: 26787787.Rawal N., Van Zundert A A., Holmström B., Crowhurst JA. 1997. Combined spinal-epidural technique. Reg Anesth. 22:406–23. DOI: 10.1016/S1098-7339(97)80026-0.Höhener D., Blumenthal S., Borgeat A. 2008. Sedation and regional anaesthesia in the adult patient. Br J Anaesth. 100:8–16. DOI: 10.1093/bja/aem342. PMID: 18070783.Virtanen R., Savola JM., Saano V., Nyman L. 1988. Characterization of the selectivity, specificity and potency of medetomidine as an alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 150:9–14. DOI: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90744-3. PMID: 2900154.Grosu I., Lavand’homme P. 2010. Use of dexmedetomidine for pain control. F1000 Med Rep. 2:90. DOI: 10.3410/M2-90. PMID: 21283652. PMCID: PMC3026617.Lee MJ., Koo DJ., Choi YS., Lee KC., Kim HY. 2016. Dexamethasone or dexmedetomidine as local anesthetic adjuvants for ultrasound-guided axillary brachial plexus blocks with nerve stimulation. Korean J Pain. 29:29–33. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.1.29. PMID: 26839668. PMCID: PMC4731548.Ramsay MA., Savege TM., Simpson BR., Goodwin R. 1974. Controlled sedation with alphaxalone-alphadolone. Br Med J. 2:656–9. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.2.5920.656. PMID: 4835444. PMCID: PMC1613102.Dawson C., Ma D., Chow A., Maze M. 2004. Dexmedetomidine enhances analgesic action of nitrous oxide: mechanisms of action. Anesthesiology. 100:894–904. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-200404000-00020. PMID: 15087625.Ware JE Jr., Hays RD. 1988. Methods for measuring patient satisfaction with specific medical encounters. Med Care. 26:393–402. DOI: 10.1097/00005650-198804000-00008. PMID: 3352332.Elcicek K., Tekin M., Kati I. 2010. The effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine on spinal hyperbaric ropivacaine anesthesia. J Anesth. 24:544–8. DOI: 10.1007/s00540-010-0939-9. PMID: 20467879.Hussain N., Grzywacz VP., Ferreri CA., Atrey A., Banfield L., Shaparin N, et al. 2017. Investigating the efficacy of dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to local anesthesia in brachial plexus block: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 18 randomized controlled trials. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 42:184–96. DOI: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000564. PMID: 28178091.Zhang X., Wang D., Shi M., Luo Y. 2017. Efficacy and safety of dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant in epidural analgesia and anesthesia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Drug Investig. 37:343–54. DOI: 10.1007/s40261-016-0477-9. PMID: 27812971.Al-Mustafa MM., Badran IZ., Abu-Ali HM., Al-Barazangi BA., Massad IM., Al-Ghanem SM. 2009. Intravenous dexmedetomidine prolongs bupivacaine spinal analgesia. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 20:225–31. PMID: 19583070.Hong JY., Kim WO., Yoon Y., Choi Y., Kim SH., Kil HK. 2012. Effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine on low-dose bupivacaine spinal anaesthesia in elderly patients. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 56:382–7. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2011.02614.x. PMID: 22220945.Kaya FN., Yavascaoglu B., Turker G., Yildirim A., Gurbet A., Mogol EB, et al. 2010. Intravenous dexmedetomidine, but not midazolam, prolongs bupivacaine spinal anesthesia. Can J Anaesth. 57:39–45. DOI: 10.1007/s12630-009-9231-6. PMID: 20039221.Jorm CM., Stamford JA. 1993. Actions of the hypnotic anaesthetic, dexmedetomidine, on noradrenaline release and cell firing in rat locus coeruleus slices. Br J Anaesth. 71:447–9. DOI: 10.1093/bja/71.3.447. PMID: 8104450.Dinesh CN., Sai Tej NA NA., Yatish B., Pujari VS., Mohan Kumar RM RM., Mohan CV. 2014. Effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine on hyperbaric bupivacaine spinal anesthesia: a randomized study. Saudi J Anaesth. 8:202–8. DOI: 10.4103/1658-354X.130719. PMID: 24843333. PMCID: PMC4024677.Li A., Yuen VM., Goulay-Dufay S., Kwok PC. 2016. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dexmedetomidine. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 42:1917–1927. DOI: 10.1080/03639045.2016.1232727. PMID: 27595299.Ganesh M., Krishnamurthy D. 2018. A comparative study of dexmedetomidine and clonidine as an adjuvant to intrathecal bupivacaine in lower abdominal surgeries. Anesth Essays Res. 12:539–45. DOI: 10.4103/aer.AER_54_18. PMID: 29962631. PMCID: PMC6020565.Rhee K., Kang K., Kim J., Jeon Y. 2003. Intravenous clonidine prolongs bupivacaine spinal anesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 47:1001–5. DOI: 10.1034/j.1399-6576.2003.00158.x. PMID: 12904193.Abdallah FW., Abrishami A., Brull R. 2013. The facilitatory effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine on the duration of spinal anesthesia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anesth Analg. 117:271–8. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e318290c566. PMID: 23632057.Arain SR., Ebert TJ. 2002. The efficacy, side effects, and recovery characteristics of dexmedetomidine versus propofol when used for intraoperative sedation. Anesth Analg. 95:461–6. DOI: 10.1213/00000539-200208000-00042. PMID: 12145072.Cortinez LI., Hsu YW., Sum-Ping ST., Young C., Keifer JC., Macleod D, et al. 2004. Dexmedetomidine pharmacodynamics: part II: crossover comparison of the analgesic effect of dexmedetomidine and remifentanil in healthy volunteers. Anesthesiology. 101:1077–83. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-200411000-00006. PMID: 15505442.Kim KH. 2014. Safe sedation and hypnosis using dexmedetomidine for minimally invasive spine surgery in a prone position. Korean J Pain. 27:313–20. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.4.313. PMID: 25317279. PMCID: PMC4196495.Alhashemi JA. 2006. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam for monitored anaesthesia care during cataract surgery. Br J Anaesth. 96:722–6. DOI: 10.1093/bja/ael080. PMID: 16595611.Aun C., Flynn PJ., Richards J., Major E. 1984. A comparison of midazolam and diazepam for intravenous sedation in dentistry. Anaesthesia. 39:589–93. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1984.tb07370.x. PMID: 6742394.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effect of combined spinal-epidural anesthesia on stress responses during total knee replacement
- Dexmedetomidine combined with midazolam vs. dexmedetomidine alone for sedation during spinal anesthesia
- Spinal epidural hematoma after epidural anesthesia in a patient receiving enoxaparin: A case report
- Dexmedetomidine Sedation in an Old Patient for Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Epidural hematoma after total knee arthroplasty in a patient receiving rivaroxaban: A case report