Perspect Nurs Sci.
2020 Apr;17(1):12-27. 10.16952/pns.2020.17.1.12.
A Systematic Review of School-bullying Interventions for Children andAdolescents in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Graduate Student, College of Nursing, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2500145
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.16952/pns.2020.17.1.12
Abstract
- Purpose
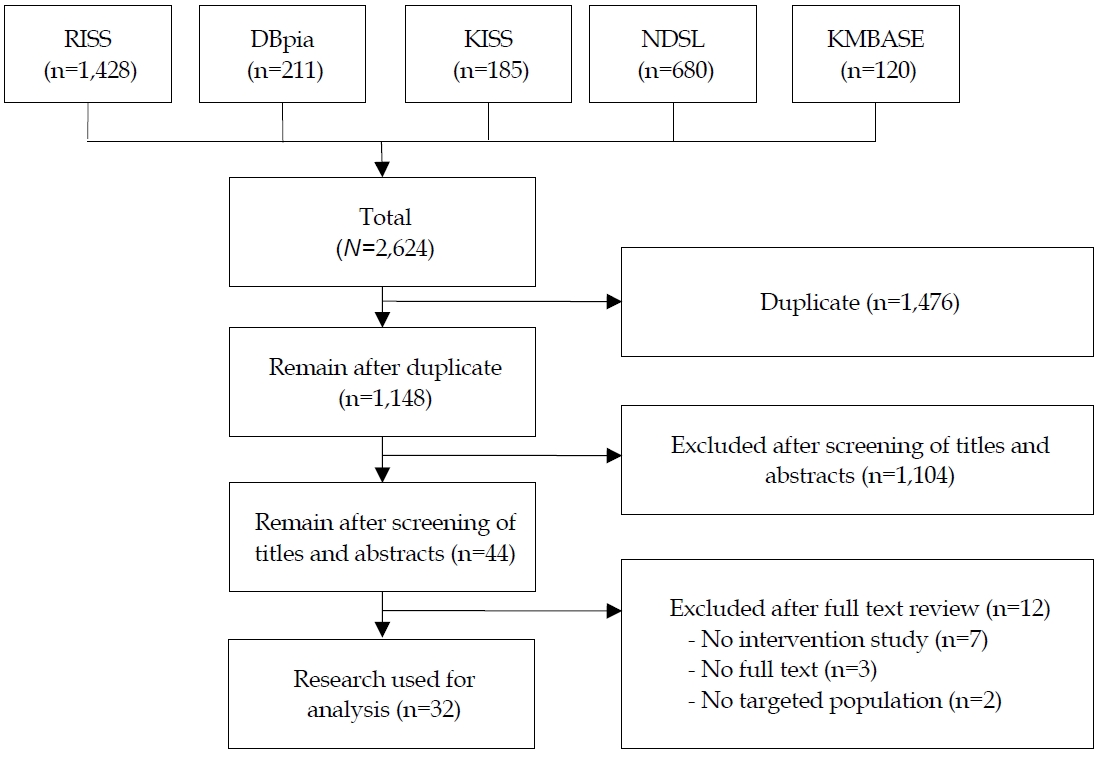
Bullying is a global problem, and various programs are under way to prevent it. The purpose of this study was to review school bullying interventions for Korean school-age children and adolescents. Methods: Online databases such as RISS, KISS, DBpia, NDSL and KMBASE were searched, identifying 32 intervention studies published from January 2009 to November 2018.
Results
Thirty-two intervention studies were identified: 23 included school bullying prevention and 9 included school bullying treatment for victims or youth at high risk for bullying. The main purpose of preventive intervention was to decrease the bystander's attitude toward group bullying and treatment program was to improve the psychosocial adaptation of bullying victims. The school bullying interventions varied from group counseling, social skills training, art therapy, bibliotherapy using role-play, game & activities. Classroom environment variables and self-esteem, peer-related variables improved significantly after the school bullying prevention programs and school bullying treatment programs, respectively.
Conclusion
There is potential for enhancing the outcomes of the behavioral, interpersonal psychological variable. Integrated interventions considering the individuality, gender and physical health of children and adolescents will also be needed. However, a rigorous study design is required to compensate for the methodological limitations.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ministry of Education. [The first school violence survey results in 2019] [Internet]. Sejong (KO): Ministry of Education;[updated 2019 Aug 27, cited 2019 Dec 21]. Korean. Available from: https://www.moe.go.kr/boardCnts/view.do?boardID=294&boardSeq=78346&lev=0&searchType=null&statusYN=W&page=1&s=moe&m=020402&opType=N.2. Ministry of Education. [Announcement of the 4th basic plan for prevention and countermeasures against school violence] [Internet]. Sejong (KO): Ministry of Education;[updated 2020 Jan 15; cited 2020 Apr 3]. Korean. Available from: https://www.moe.go.kr/boardCnts/view.do?boardID=294&boardSeq=79501&lev=0&m=02.3. Olweus D. Aggression in the schools: bullies and whipping boys. Oxford: Hemisphere;1978. p. 218.4. Perry DG, Kusel SJ, Perry LC. Victims of peer aggression. Dev Psychol. 1988; 26(4):807–14. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.24.6.807.
Article5. Heaven PCL. Contemporary adolescence: a social psychological approach. Macmillan Educational Australia. 1994. 265 p.6. Choi MK, Doh HS. Influences of victimization by peers on the self-esteem of adolescents: the role of attachment and friendship. Korean J Child Stud. 2000; 21(3):85–105.7. Asher SR. Peer rejection in childhood. New York: Cambridge University Press; 1990. 1, Recent advances in the study of peer rejection; p. 3-14.8. Teicher MH, Samson JA, Sheu YS, Polcari A, McGreenery CE. Hurtful words: association of exposure to peer verbal abuse with elevated psychiatric symptom scores and corpus callosum abnormalities. Am J Psychiatry. 2010; Dec. 167(12):1464–74. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2010.10010030.
Article9. Maslow AH. A theory of human motivation. Psycholog Rev. 1943; Jul. 1. 50(4):370–96. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0054346.
Article10. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. [Overview of bullying] [Internet]. Cheongju (KO): Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;c2019 [updated 2017 Nov 30; cited 2020 Mar 24]. Korean. Available from: http://health.cdc.go.kr/health/mobileweb/content/group_view.jsp?CID=082BF9B8BB#none.11. Seo MJ. Participation in bullying: bystanders' characteristics and role behaviors. Korean J Child Stud. 2008; Oct. 29(5):79–96.12. Yoon CH, Park SG, Shin IS. A meta-analysis of the effects of school violence prevention programs in Korea. Asian J Educ. 2014; Mar. 15(1):189–215. https://doi.org/10.15753/aje.2014.15.1.009.
Article13. Park JK. A socio-cultural study on peer rejection phenomenon of adolescent group. Korea J Youth Stud. 2000; 7(2):39–71.14. Gaffney H, Ttofi MM, Farrington DP. valuating the effectiveness of school-bullying prevention programs: an updated meta-analytical review. Aggress Violent Behav. 2019; Mar. 45:111–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2018.07.001.
Article15. Nocentini A, Zambuto V, Menesini E. Anti-bullying programs and information and communication technologies (ICTs): a systematic review. Aggress Violent Behav. 2015; Jul. 23:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2015.05.012.
Article16. Espelage DL. An ecological perspective to school-based bullying prevention. Prev Res. 2004; Jan. 9. 11(3):3–6.17. Park SJ, Kim DY. The effect of the preventive education of bullying with the self-assertive training program for elementary school students in higher grade. J Korean Soc child Welf. 2014; Sep. 47:69–91.18. Bahn GH, Choi YS. The role of physicians in preventing school bullying. J Korean Med Assoc. 2013; Jul. 15. 56(7):554–8. https://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2013.56.7.554.
Article19. Lee HM, Kim KS. The effects of peer counseling on the bullying prevention in the elementary school. Korean J Ele Couns. 2013; Sep. 30. 12(3):365–83.20. Kim SH, Park HW, Shin CB. Interactive applications for worries sharing and solution. HCI Soc Korea. 2013; (1):614–7.21. Lee DY, Roh EM, Kim IY, Ko GN, Choi JW, Lee YR, et al. School-based short term mental health awareness and school bullying prevention programs: preliminary report. J Korean Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatr. 2014; 25(4):196–202. https://doi.org/10.5765/jkacap.2014.25.4.196.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effectiveness of Interventions for Workplace Bullying among Nurses: A Systematic Review
- Relationship Between Bullying and Health Problems in Primary School Children
- School Bullying Among Korean Students-Current Status
- Characteristics of the Bullying in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
- The role of the pediatrician in youth violence prevention