J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2020 Mar;22(1):20-25. 10.7461/jcen.2020.22.1.20.
Middle meningeal artery embolizationto treat progressive epidural hematoma:a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Cheju Halla General Hospital, Jeju, Korea
- KMID: 2500070
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2020.22.1.20
Abstract
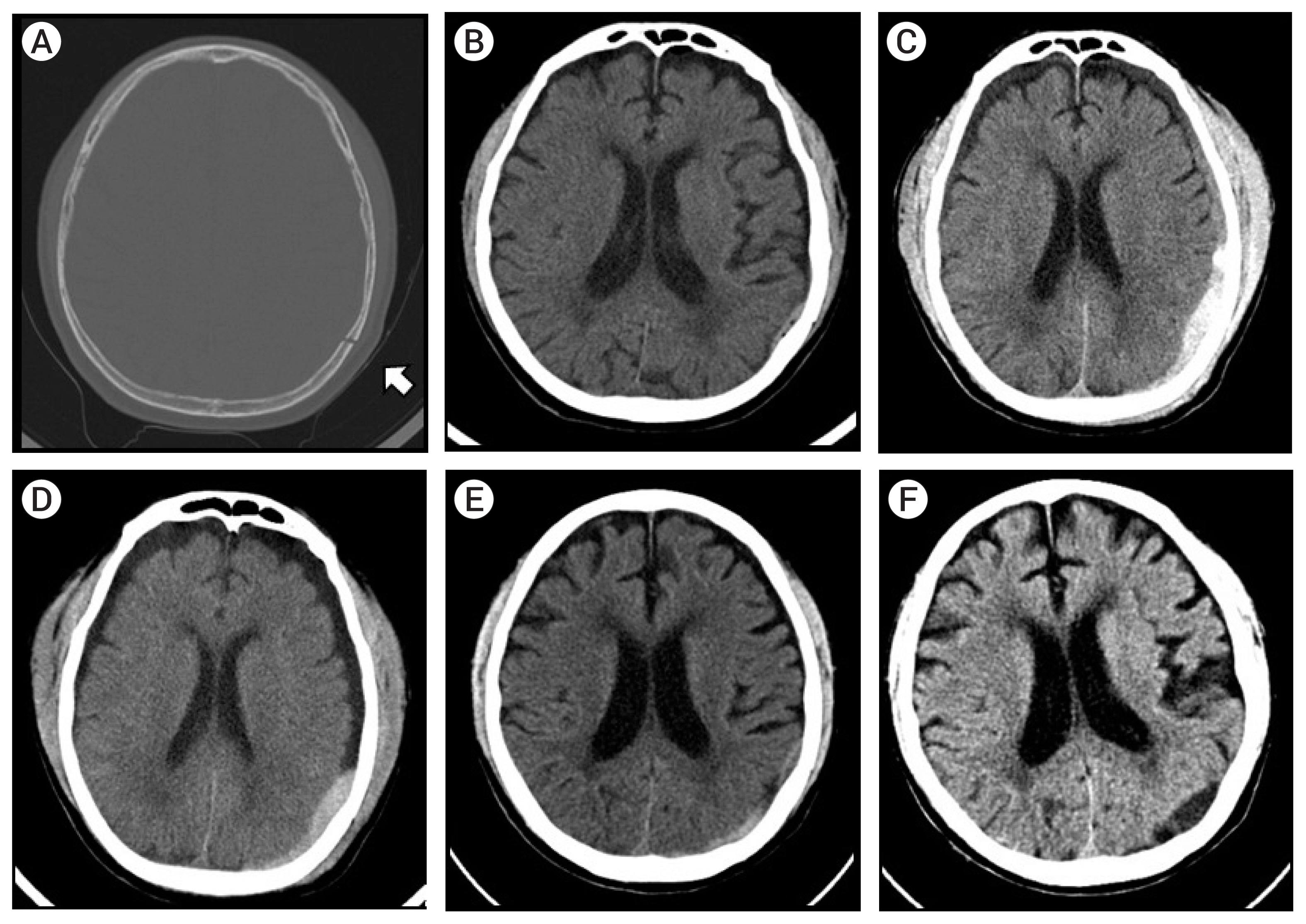
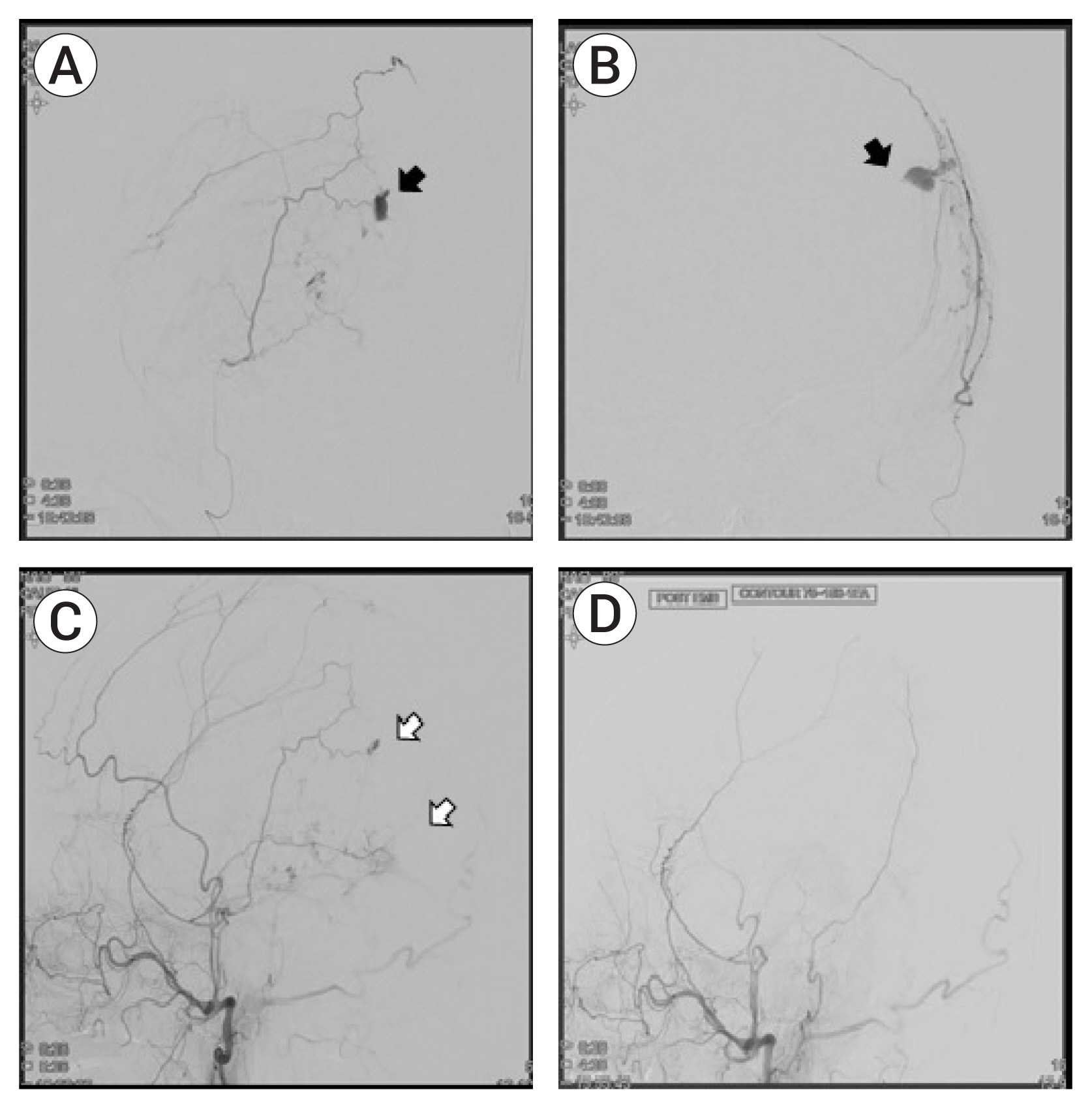
- Progressive epidural hematoma is a form of acute epidural hematoma that gradually expands from a small initial hematoma; in cases that are clinically aggravated due to the presence of a mental illness or neurological condition, patients should be surgically treated for evacuation of the hematoma, but poorer outcomes are expected if the patient has several medical co-morbidities for surgery. We experienced two cases of progressive epidural hematoma which were successfully managed by endovascular treatment: an 85-year-old male with medical co-morbidities and a 51-year-old female with a poor-grade subarachnoid hemorrhage resulting from the rupture of a dissecting aneurysm of the vertebral artery. In both cases, a middle meningeal artery embolization was performed and contrast leakage was observed and controlled using cerebral angiography, halting the progression of their epidural hematomas. Thus, endovascular embolization of a middle meningeal artery may play a useful role in salvage therapy in certain complicated situations that limit treatment of the hematoma by surgical evacuation.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Andrade AF, Figueiredo EG, Caldas JG, Paiva WS, De Amorim RL, Puglia P, et al. Intracranial vascular lesions associated with small epidural hematomas. Neurosurgery. 2008; Feb. 62(2):416–20. discussion 420–1.2. Bortoluzzi M, Pavia M. Endovascular treatment of incoercible epistaxis and epidural cerebral hematoma. A case report. Interv Neuroradiol. 2006; Sep. 12(3):233–6.3. Chen H, Guo Y, Chen SW, Wang G, Cao HL, Chen J, et al. Progressive epidural hematoma in patients with head trauma: incidence, outcome, and risk factors. Emerg Med Int. 2012; 2012:Article ID 134905.
Article4. Kang J, Whang K, Hong SK, Pyen JS, Cho SM, Kim JY, et al. Middle meningeal srtery embolization in recurrent chronic subdural hematoma combined with arachnoid Cyst. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2015; Oct. 11(2):187–90.5. Link TW, Boddu S, Paine SM, Kamel H, Knopman J. Middle meningeal artery embolization for chronic subdural hematoma: A series of 60 cases. Neurosurgery. 2019; Dec. 85(6):801–7.
Article6. Link TW, Rapoport BI, Paine SM, Kamel H, Knopman J. Middle meningeal artery embolization for chronic subdural hematoma: Endovascular technique and radiographic findings. Interv Neuroradiol. 2018; Aug. 24(4):455–62.
Article7. Offner PJ, Pham B, Hawkes A. Nonoperative management of acute epidural hematomas: A no brainer. Am J Surg. 2006; Dec. 192(6):801–5.8. Ordookhanian C, Kaloostian PE. Trauma-induced acute epidural hematoma: The rising sun in a progressively lethargic man. Cureus. 2018; Aug. 10(8):e3162.
Article9. Peres CMA, Caldas JGMP, Puglia P, de Andrade AF, da Silva IAF, Teixeira MJ, et al. Endovascular management of acute epidural hematomas: clinical experience with 80 cases. J Neurosurg. 2018; Apr. 128(4):1044–50.
Article10. Reponen E, Korja M, Niemi T, Silvasti-Lundell M, Hernesniemi J, Tuominen H. Preoperative identification of neurosurgery patients with a high risk of in-hospital complications: a prospective cohort of 418 consecutive elective craniotomy patients. J Neurosurg. 2015; Sep. 123(3):594–604.
Article11. Ross IB. Embolization of the middle meningeal artery for the treatment of epidural hematoma. J Neurosurg. 2009; Jun. 110(6):1247–9.
Article12. Sirh S, Park HR, Park SQ. Usefulness of middle meningeal embolization to prevent recurrent spontaneous chronic subdural hemorrhage. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2018; Mar. 20(1):40–6.
Article13. Sivanaser V, Manninen P. Preoperative assessment of adult patients for intracranial surgery. Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2010; Mar. 2010:Article ID 241307.
Article14. Suzuki S, Endo M, Kurata A, Ohmomo T, Oka H, Kitahara T, et al. Efficacy of endovascular surgery for the treatment of acute epidural hematomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; Aug. 25(7):1177–80.15. Tempaku A, Yamauchi S, Ikeda H, Tsubota N, Furukawa H, Maeda D, et al. Usefulness of interventional embolization of the middle meningeal artery for recurrent chronic subdural hematoma: Five cases and a review of the literature. Interv Neuroradiol. 2015; Jun. 21(3):366–71.
Article16. Winn HR. Youmans & Winn Neurological surgery. 4:7th ed.Elsevier;New York: 2017. p. 2823–913.17. Yu J, Guo Y, Xu B, Xu K. Clinical importance of the middle meningeal artery: A review of the literature. Int J Med Sci. 2016; Oct. 13(10):790–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Angiographically Progressive Change of Traumatic Pseudoaneurysm Arising from the Middle Meningeal Artery
- Angiographic Extravasation
- Radiologic Evaluation of Epidural and subdural Hematoma
- Intracerebral Hematoma Caused by Ruptured Traumatic Pseudoaneurysm of the Middle Meningeal Artery: A Case Report
- The Evaluation of Angiographic Features in Intracranial Epidural and Subdural Hematomas