Yonsei Med J.
2020 Apr;61(4):341-348. 10.3349/ymj.2020.61.4.341.
Surgical Outcomes of Dysphagia Provoked by Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis in the Cervical Spine
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. hyzhang@nhimc.or.kr
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. spinepjy@gmail.com
- KMID: 2471920
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2020.61.4.341
Abstract
- PURPOSE
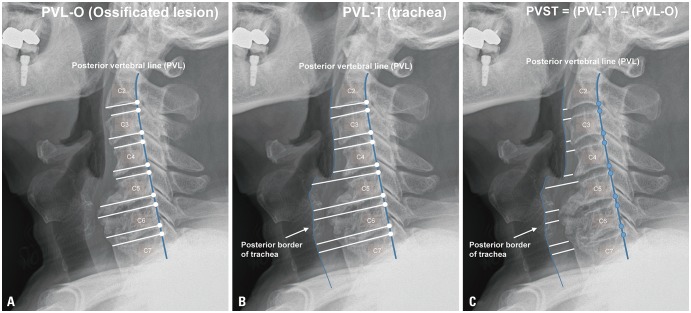
This study aimed to predict the surgical outcomes of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH)-related dysphagia (DISH-phagia) and to evaluate the importance of prevertebral soft tissue thickness (PVST).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In total, 21 surgeries (anterior osteophytectomy or anterior cervical decompression and fixation) were included in this study for DISH-phagia from 2003 to 2019. Clinical outcomes were assessed using the Dysphagia Outcome and Severity Scale (DOSS) preoperatively, at 1 month postoperatively, and last follow up (mean 29.5 months). PVST was measured using lateral plain radiographs. Paired t-test and Spearman's correlation test was used to identify relationships between various PVST indices and DOSS.
RESULTS
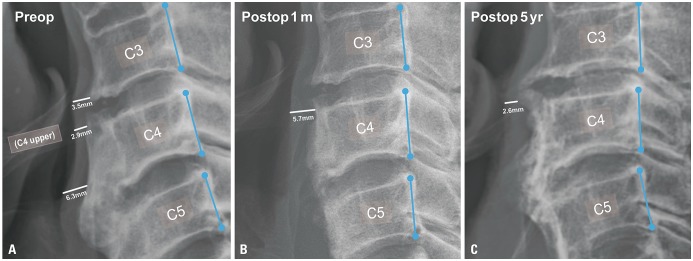
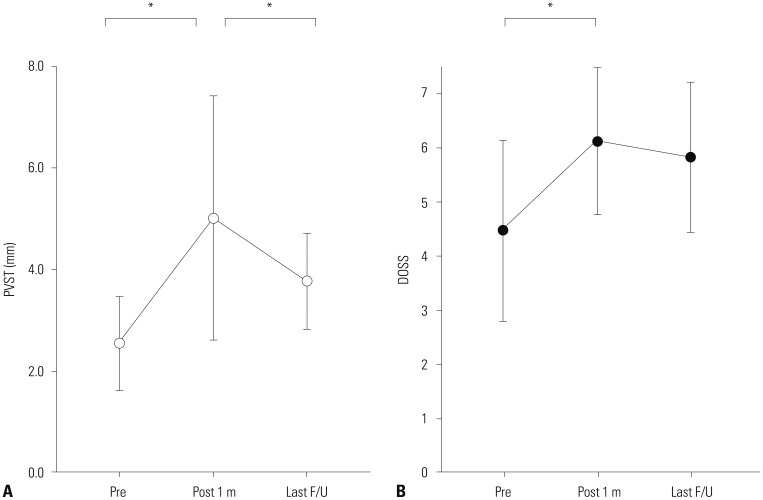
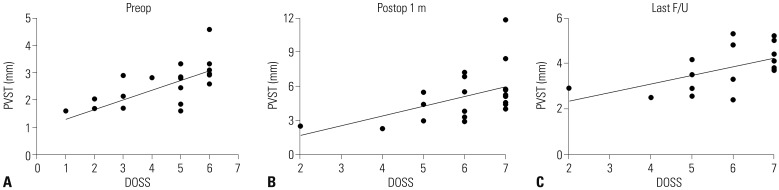
Comparisons were made from 17 patients out of 21, in which the record had all of three measurements. The narrowest PVST preoperatively was 2.55±0.90 mm, with a DOSS score of 4.47±1.61, and that at 1 month after surgery was 5.02±2.33 mm, with a DOSS score of 6.12±1.32. At last follow up, PVST and DOSS values were 3.78±0.92 mm and 5.82±1.34, and three patients experienced symptom relapse. Significant relationships were found between PVST and DOSS at all time points: before surgery (R=0.702, p<0.001), 1 month after surgery (R=0.539, p=0.012), and last follow up (R=0.566, p=0.020).
CONCLUSION
Surgical removal of anterior osteophytes is an effective treatment option for DISH-phagia, and PVST is a useful parameter in DISH-phagia. The goal of DISH surgery should be to remove DISH as much as possible to ensure sufficient PVST postoperatively.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Egerter AC, Kim ES, Lee DJ, Liu JJ, Cadena G, Panchal RR, et al. Dysphagia secondary to anterior osteophytes of the cervical spine. Global Spine J. 2015; 5:e78–e83. PMID: 26430607.
Article2. Mazières B. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (Forestier-Rotes-Querol disease): what's new? Joint Bone Spine. 2013; 80:466–470. PMID: 23566663.
Article3. Yunoki M, Suzuki K, Uneda A, Okubo S, Hirashita K, Yoshino K. The importance of recognizing diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis for neurosurgeons: a review. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2016; 56:510–515. PMID: 27021643.
Article4. Taljanovic MS, Hunter TB, Wisneski RJ, Seeger JF, Friend CJ, Schwartz SA, et al. Imaging characteristics of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis with an emphasis on acute spinal fractures: self-assessment module. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193(3 Suppl):S20–S24. PMID: 19696240.5. Aydin E, Akdogan V, Akkuzu B, Kirbas¸ I, Ozgirgin ON. Six cases of Forestier syndrome, a rare cause of dysphagia. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006; 126:775–778. PMID: 16803720.
Article6. Kmucha ST, Cravens RB Jr. DISH syndrome and its role in dysphagia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1994; 110:431–436. PMID: 8170689.
Article7. Verlaan JJ, Boswijk PF, de Ru JA, Dhert WJ, Oner FC. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis of the cervical spine: an underestimated cause of dysphagia and airway obstruction. Spine J. 2011; 11:1058–1067. PMID: 22015236.
Article8. Curtis JR, Lander PH, Moreland LW. Swallowing difficulties from “DISH-phagia”. J Rheumatol. 2004; 31:2526–2527. PMID: 15570664.9. Carlson ML, Archibald DJ, Graner DE, Kasperbauer JL. Surgical management of dysphagia and airway obstruction in patients with prominent ventral cervical osteophytes. Dysphagia. 2011; 26:34–40. PMID: 20099000.
Article10. Miyamoto K, Sugiyama S, Hosoe H, Iinuma N, Suzuki Y, Shimizu K. Postsurgical recurrence of osteophytes causing dysphagia in patients with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Eur Spine J. 2009; 18:1652–1658. PMID: 19714374.
Article11. Sebaaly A, Boubez G, Sunna T, Wang Z, Alam E, Christopoulos A, et al. Diffuse idiopathic hyperostosis manifesting as dysphagia and bilateral cord paralysis: a case report and literature review. World Neurosurg. 2018; 111:79–85. PMID: 29269071.
Article12. Urrutia J, Bono CM. Long-term results of surgical treatment of dysphagia secondary to cervical diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Spine J. 2009; 9:e13–e17.13. O'Neil KH, Purdy M, Falk J, Gallo L. The Dysphagia Outcome and Severity Scale. Dysphagia. 1999; 14:139–145. PMID: 10341109.14. Resnick D, Niwayama G. Radiographic and pathologic features of spinal involvement in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Radiology. 1976; 119:559–568. PMID: 935390.
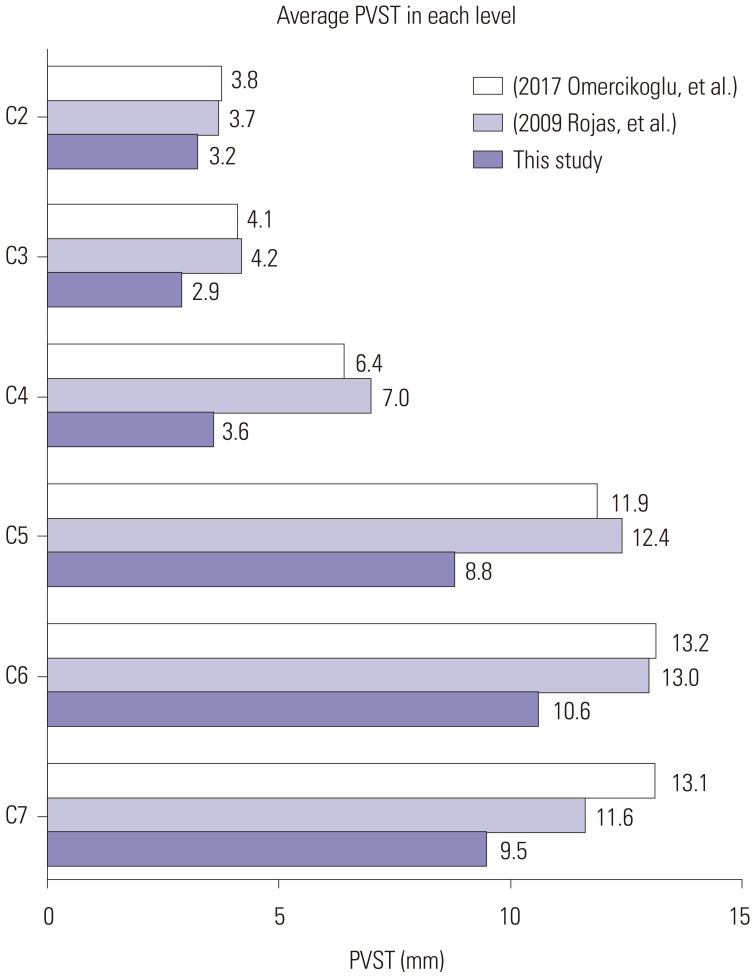
Article15. Omercikoglu S, Altunbas E, Akoglu H, Onur O, Denizbasi A. Normal values of cervical vertebral measurements according to age and sex in CT. Am J Emerg Med. 2017; 35:383–390. PMID: 27863890.
Article16. Rojas CA, Vermess D, Bertozzi JC, Whitlow J, Guidi C, Martinez CR. Normal thickness and appearance of the prevertebral soft tissues on multidetector CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 30:136–141. PMID: 19001541.
Article17. Forestier J, Rotes-Querol J. Senile ankylosing hyperostosis of the spine. Ann Rheum Dis. 1950; 9:321–330. PMID: 14800245.
Article18. Sobol SM, Rigual NR. Anterolateral extrapharyngeal approach for cervical osteophyte-induced dysphagia. Literature review. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1984; 93(5 Pt 1):498–504. PMID: 6388464.19. Yee C, Wong HY, Fewer HD, Rogers AG. Two cases of dysphagia due to cervical spine osteophytes successfully treated surgically. Can Med Assoc J. 1985; 132:810–812. PMID: 3978503.20. Laus M, Malaguti MC, Alfonso C, Ferrari D, Zappoli FA, Giunti A. Dysphagia due to cervical osteophytosis. Chir Organi Mov. 1995; 80:263–271. PMID: 8681676.21. Scholz C, Naseri Y, Hohenhaus M, Hubbe U, Klingler JH. Long-term results after surgical treatment of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) causing dysphagia. J Clin Neurosci. 2019; 67:151–155. PMID: 31221580.
Article22. Jonathan YC, Sayal P, Prezerakos G, Russo V, Choi D, Casey ATH. The surgical management of dysphagia secondary to diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2018; 167:36–42. PMID: 29438856.23. Mader R, Verlaan JJ, Buskila D. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: clinical features and pathogenic mechanisms. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013; 9:741–750. PMID: 24189840.
Article24. Kuperus JS, Waalwijk JF, Regan EA, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, Oner FC, de Jong PA, et al. Simultaneous occurrence of ankylosing spondylitis and diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: a systematic review. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018; 57:2120–2128. PMID: 30060244.
Article25. Tsukahara S, Miyazawa N, Akagawa H, Forejtova S, Pavelka K, Tanaka T, et al. COL6A1, the candidate gene for ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament, is associated with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in Japanese. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:2321–2324. PMID: 16227896.
Article26. Steele CM, Bailey GL, Chau T, Molfenter SM, Oshalla M, Waito AA, et al. The relationship between hyoid and laryngeal displacement and swallowing impairment. Clin Otolaryngol. 2011; 36:30–36. PMID: 21414151.
Article27. von der Hoeh NH, Voelker A, Jarvers JS, Gulow J, Heyde CE. Results after the surgical treatment of anterior cervical hyperostosis causing dysphagia. Eur Spine J. 2015; 24 Suppl 4:S489–S493. PMID: 25108621.
Article28. Shriver MF, Lewis DJ, Kshettry VR, Rosenbaum BP, Benzel EC, Mroz TE. Dysphagia rates after anterior cervical diskectomy and fusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Global Spine J. 2017; 7:95–103. PMID: 28451514.
Article29. Haws BE, Khechen B, Patel DV, Yoo JS, Guntin JA, Cardinal KL, et al. Swallowing function following anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with and without anterior plating: a SWAL-QOL (swallowing-quality of life) and radiographic assessment. Neurospine. 2019; 16:601–607. PMID: 31284338.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dysphagia Due to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis of The Cervical Spine: A Case Report
- Intraoperative Traction May Induce Acute Onset Dysphagia With Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis After Anterior Cervical Discectomy
- A Case of Dysphagia due to Cricopharyngeal Dysfunction and Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis
- Swallowing Difficulty in Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis with Metabolic Syndrome
- Dysphagia due to Cervical Osteophytes: Case Report