J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2020 Mar;61(3):303-306. 10.3341/jkos.2020.61.3.303.
Case Report of Nodular Fasciitis in the Conjunctiva
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. sara514@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Jalbonun St. Mary's Eye Clinic, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2471773
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2020.61.3.303
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We report a case of nodular fasciitis of the conjunctiva that has not been previously reported in the Republic of Korea.
CASE SUMMARY
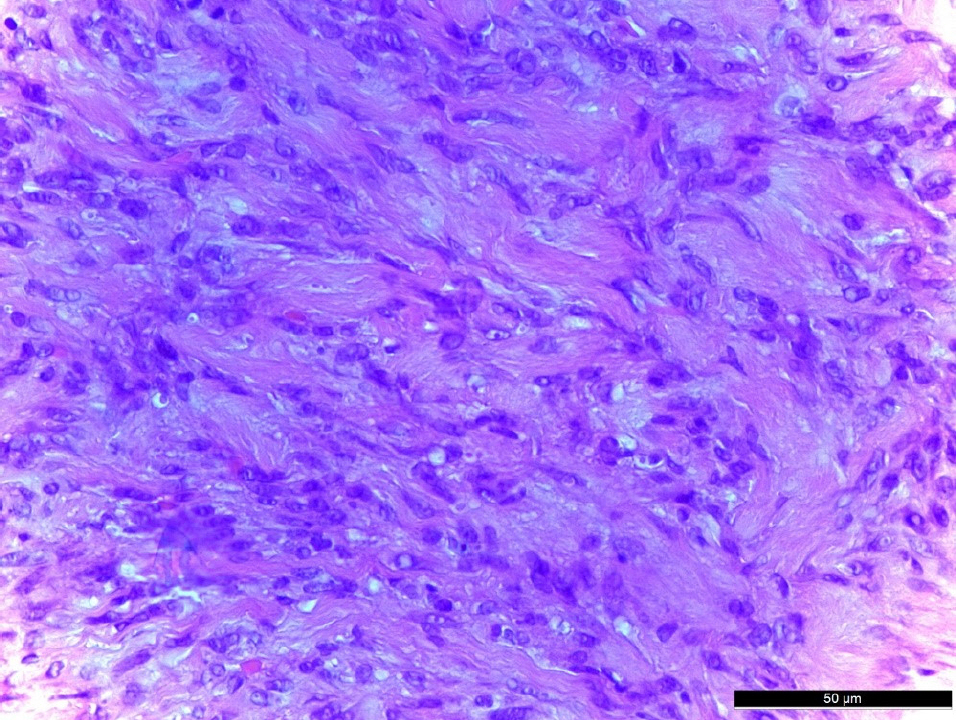
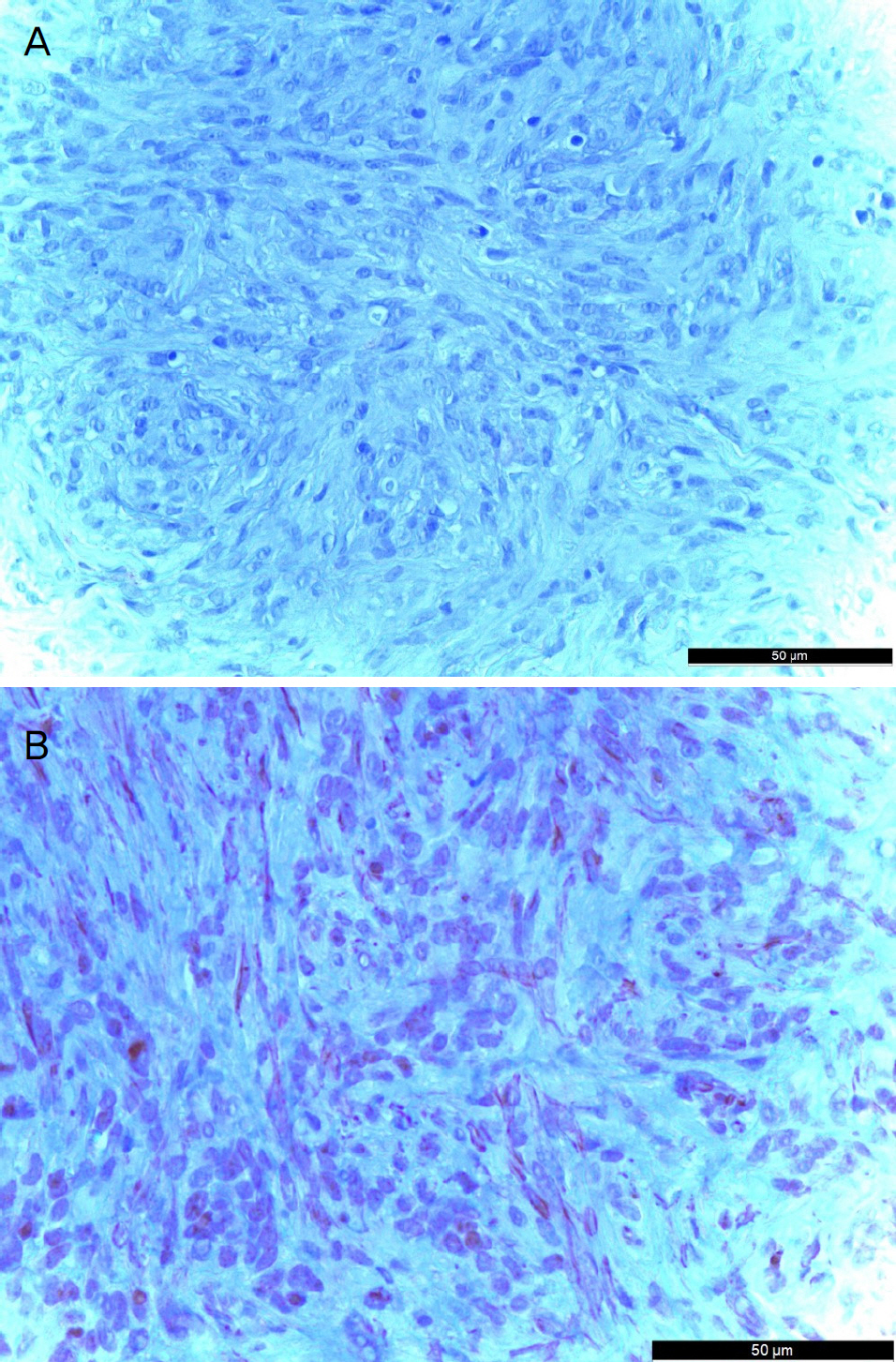
A 18-year-old female patient presented with a left conjunctival mass, which had been enlarging for 1 month. The tumor was located at the corner of the conjunctiva of the left eye. The size of the tumor was 1 mm in width and 1.5 mm in height, and tenderness and redness were not observed. There was no history of trauma, but bilateral upper lid blepharoplasty was performed 2 months prior to her visit. Excision of a conjunctival mass was performed and there was no evidence of involvement of the sclera or peripheral conjunctiva around the mass. We performed immunohistochemistry and PCR for human herpes virus 8 (HHV8). Immunohistochemistry was positive for S-100 and negative for smooth muscle actin and HHV8. The mass was myofibroblastic in nature and the histopathological features and clinical findings of this case were diagnosed as nodular fasciitis with the features as described above. There was no recurrence for 4 months after removal of the mass.
CONCLUSIONS
Because the treatments and prognoses of malignant tumors or other inflammatory diseases such as nodular scleritis and nodular fasciitis are quite different, differentiation from these diseases is considered an important factor in the diagnosis of nodular fasciitis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Riffle JE, Prosser AH, Lee JR, Lynn JJ. Nodular fasciitis of the abdominal: a case report and brief review of the literature. Case Rep Ophthalmol Med. 2011; 2011:235956.2. Konwaler BE, Keasbey L, Kaplan L. Subcutaneous pseudosarcom-atous fibromatosis (fasciitis). Am J Clin Pathol. 1955; 25:241–52.
Article3. Lee YJ, Kim SM, Lee JH, et al. Nodular fasciitis of the periorbital area. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2014; 15:43–6.
Article4. Park MS, Kwon MJ, Lee MJ. Three cases of periorbital nodular fasciitis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2016; 57:1946–52.
Article5. Font RL, Zimmerman LE. Nodular fasciitis of the eye and adnexa. A report of ten cases. Arch Ophthalmol. 1966; 75:475–81.6. Stone DU, Chodosh J. Epibulbar nodular fasciitis associated with floppy eyelids. Cornea. 2005; 24:361–2.
Article7. Massop DJ, Frederick PA, Li HE, Lin A. Epibulbar nodular fasciitis. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2016; 7:262–7.
Article8. Jung SW, Kang NY. A case of nodular fasciitis in the upper eyelid. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:357–61.
Article9. Price EB Jr, Silliphant WM, Shuman R. Nodular fasciitis: a clinicopathological analysis of 65 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1961; 35:122–36.10. Shimizu S, Hashimoto H, Enjoji M. Nodular fasciitis: an analysis of 250 patients. Pathology. 1983; 16:161–6.
Article11. Hseu A, Watters K, Perez-Atayde A, et al. Pediatric nodular abdominal in the head and neck evaluation and management. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015; 141:54–9.12. Pandian TK, Zeidan MM, Ibrahim KA, et al. Nodular fasciitis in the pediatric population: a single center experience. J Pediatr Surg. 2013; 48:1486–9.
Article13. Velagaleti GVN, Tapper JK, Panova NE, et al. Cytogenetic abdominal in a case of nodular fasciitis of subclavicular region. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2003; 141:160–3.14. Silva P, Bruce IA, Malik T, et al. Nodular fasciitis of the head and neck. J Laryngol Otol. 2005; 119:8–11.
Article