Korean J Leg Med.
2020 Feb;44(1):37-40. 10.7580/kjlm.2020.44.1.37.
Lung Pathology in Septic Shock with Leukopenia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Forensic Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea. gyhuh@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2471743
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7580/kjlm.2020.44.1.37
Abstract
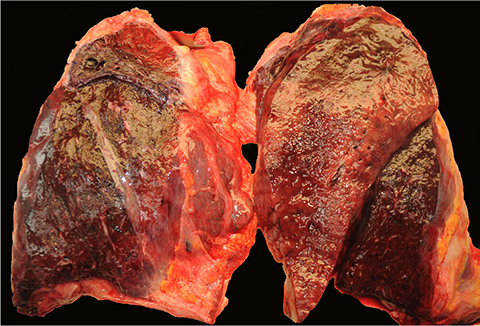
- Sepsis-related deaths are occasionally encountered in forensic practice. However, forensic pathologists are reluctant to use the terminology "sepsis" or "septic shock" as a cause of death because of the lack of definite morphological evidence. When sepsis is considered a cause of death, pathologic assessment is essential to identify the foci of infection or consequences of sepsis, such as diffuse alveolar damage (DAD). Pneumonia is known to be a common source of sepsis and can develop into DAD with progression of sepsis. The histology of DAD varies according to the immunologic status. An autopsy of a 55-year-old man who died of septic shock with leukopenia revealed only abundant gram-negative bacilli in the alveoli without typical DAD pathology.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016; 315:801–810.2. Lucas S. The autopsy pathology of sepsis-related death. Curr Diagn Pathol. 2007; 13:375–388.
Article3. Morris JA, Harrison LM, Partridge SM. Postmortem bacteriology: a re-evaluation. J Clin Pathol. 2006; 59:1–9.
Article4. Laufe MD, Simon RH, Flint A, et al. Adult respiratory distress syndrome in neutropenic patients. Am J Med. 1986; 80:1022–1026.
Article5. Altaf E, Mitchel EK, Berry C, et al. Death due to pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2017; 38:11–13.
Article6. Warny M, Helby J, Nordestgaard BG, et al. Lymphopenia and risk of infection and infection-related death in 98,344 individuals from a prospective Danish population-based study. PLoS Med. 2018; 15:e1002685.
Article7. Schiel X, Hebart H, Kern WV, et al. Sepsis in neutropenia: guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Working Party (AGIHO) of the German Society of Hematology and Oncology (DGHO). Ann Hematol. 2003; 82 Suppl 2:S158–S166.8. Gyawali B, Ramakrishna K, Dhamoon AS. Sepsis: the evolution in definition, pathophysiology, and management. SAGE Open Med. 2019; 7:2050312119835043.
Article9. Drewry AM, Samra N, Skrupky LP, et al. Persistent lymphopenia after diagnosis of sepsis predicts mortality. Shock. 2014; 42:383–391.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Prognostic Factors of Pneumonia with Septic Shock in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department
- Septic Shock due to Vibrio alginolyticus in a Cirrhotic Patient: The First Case in Korea
- Treatment Guidelines of Sepsis and Septic Shock
- Prognostic Factors in Septic Shock Patients on Arrival at Emergency Department
- Septic Shock