Endocrinol Metab.
2020 Mar;35(1):188-191. 10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.188.
Novel ABCD1 Gene Mutation in a Korean Patient with X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy Presenting with Addison's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. sangwookkim@kangwon.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2471735
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.188
Abstract
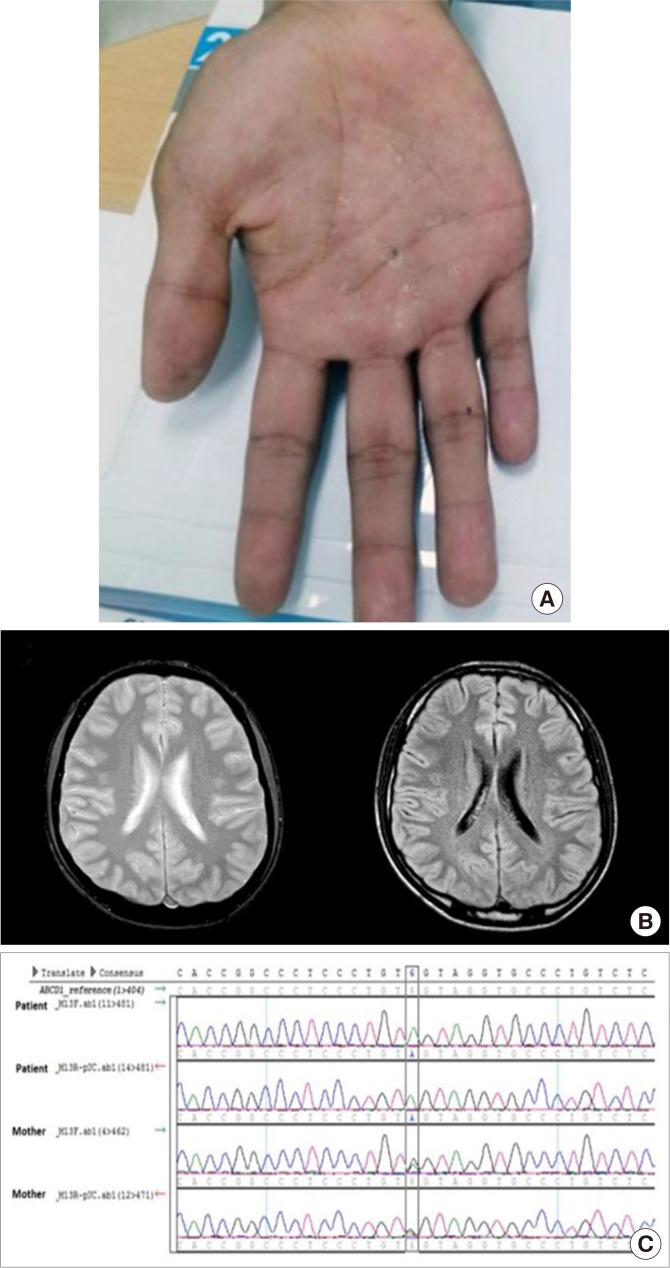
- X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) occurs due to mutations in the ABCD1 gene that encodes the peroxisomal membrane protein peroxisomal transporter ATP-binding cassette sub-family D member 1 (ABCD1). Degradation of very long-chain fatty acids in peroxisomes is impaired owing to ABCD dysfunction, subsequently leading to adrenomyeloneuropathy, cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy, and adrenal insufficiency. X-ALD frequently induces idiopathic Addison's disease in young male patients. Here, we confirmed the diagnosis of X-ALD in a young male patient with primary adrenal insufficiency, and identified a novel ABCD1 gene mutation (p.Trp664*, c.1991 G>A).
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kemp S, Huffnagel IC, Linthorst GE, Wanders RJ, Engelen M. Adrenoleukodystrophy: neuroendocrine pathogenesis and redefinition of natural history. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016; 12:606–615. PMID: 27312864.2. Huffnagel IC, Laheji FK, Aziz-Bose R, Tritos NA, Marino R, Linthorst GE, et al. The natural history of adrenal insufficiency in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: an international collaboration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019; 104:118–126. PMID: 30252065.
Article3. ACMG Board of Directors. Points to consider for informed consent for genome/exome sequencing. Genet Med. 2013; 15:748–749. PMID: 23970068.4. Salsano E, Tabano S, Sirchia SM, Colapietro P, Castellotti B, Gellera C, et al. Preferential expression of mutant ABCD1 allele is common in adrenoleukodystrophy female carriers but unrelated to clinical symptoms. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012; 7:10. PMID: 22280810.
Article5. Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015; 17:405–424. PMID: 25741868.
Article6. Moser HW, Moser AB, Naidu S, Bergin A. Clinical aspects of adrenoleukodystrophy and adrenomyeloneuropathy. Dev Neurosci. 1991; 13:254–261. PMID: 1817030.
Article7. Dubey P, Raymond GV, Moser AB, Kharkar S, Bezman L, Moser HW. Adrenal insufficiency in asymptomatic adrenoleukodystrophy patients identified by very long-chain fatty acid screening. J Pediatr. 2005; 146:528–532. PMID: 15812458.
Article8. Hong AR, Ryu OH, Kim SY, Kim SW. Korean Adrenal Gland and Endocrine Hypertension Study Group. Korean Endocrine Society. Characteristics of Korean patients with primary adrenal insufficiency: a registry-based nationwide survey in Korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2017; 32:466–474. PMID: 29271619.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An Incidentally Identified Sporadic Case with Adrenoleukodystrophy with the ABCD1 Mutation
- Cerebral Adrenomyeloneuropathy with Trp77-Leu82del Mutation in ABCD1 Gene
- A Korean boy with atypical X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy confirmed by an unpublished mutation of ABCD1
- Isolated Cerebellar Variant of Adrenoleukodystrophy with a de novo Adenosine Triphosphate-Binding Cassette D1 (ABCD1) Gene Mutation
- Adrenomyeloneuropathy with cerebral involvement due to a novel frameshift variant in ABCD1 gene