J Breast Cancer.
2019 Dec;22(4):613-623. 10.4048/jbc.2019.22.e48.
Oncologic Outcomes of Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy with Immediate Breast Reconstruction in Patients with Tumor–Nipple Distance Less than 2.0 cm
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Breast Surgery, Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. Paojlus@hanmail.com
- 2Division of Breast and Endocrine Surgery, Specialized Surgical Unit, King Abdullah Medical City, Makkah, Saudi Arabia.
- 3Department of Surgery, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2470897
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2019.22.e48
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Although the indications for nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) are expanding, there remains a debate regarding the oncologic outcomes of patients treated with this method, especially those with a short tumor-nipple distance (STND). The aim of this study was to compare the long-term oncologic outcomes between patients with a long tumor-nipple distance (LTND) (≥ 2.0 cm) and those with STND (< 2.0 cm).
METHODS
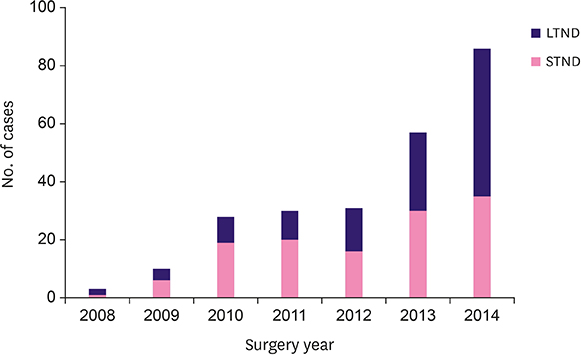
This was a retrospective study in which 266 patients who underwent NSM with immediate breast reconstruction between January 2008 and December 2014 at a single institution were enrolled. Of these patients, 21 were excluded because of loss to follow-up; thus, 245 patients were finally analyzed. All patients underwent preoperative breast magnetic resonance imaging and intraoperative frozen biopsy.
RESULTS
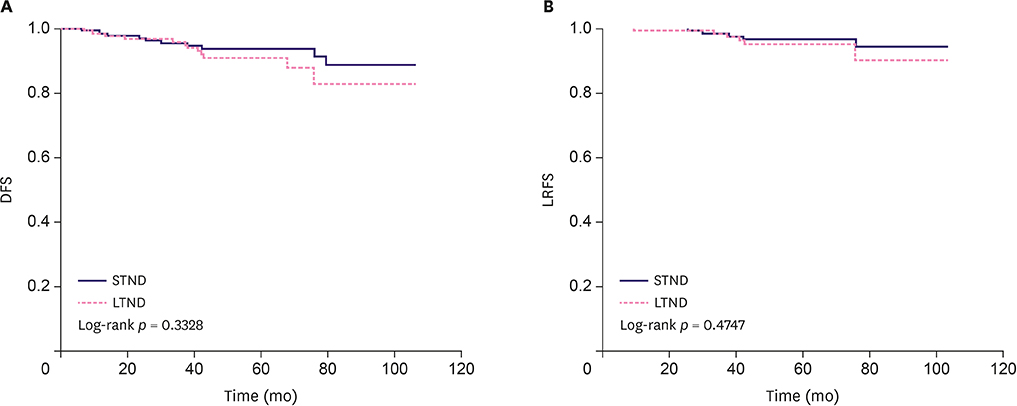
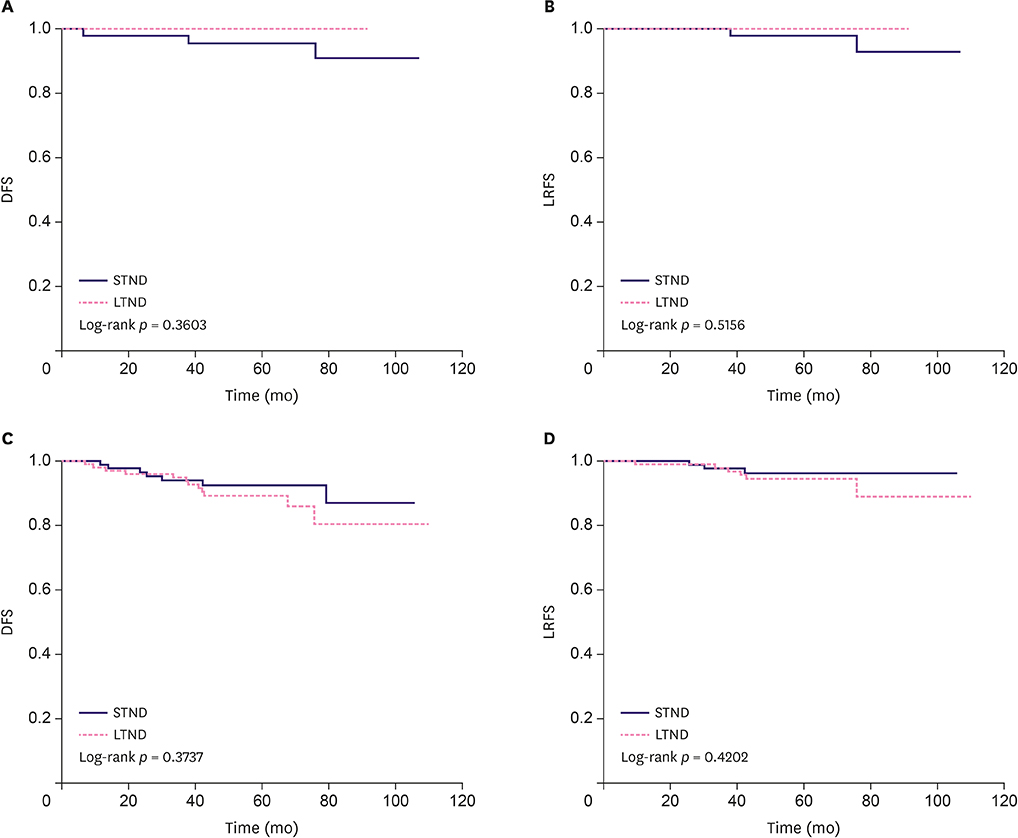
The mean age of the patients was 42.4 years. STND was identified in 128 patients, and LTND in 117 patients. The mean follow-up period was 60.5 months. There were no significant differences between the 2 groups with respect to lymphovascular invasion, nuclear grade, nodal status, and subtype (p = 0.339, 0.372, 0.955, and 0.338, respectively). The STND group had significantly smaller tumors than the LTND group (p = 0.005). The median TND in the STND and LTND groups was 0.7 cm and 3.0 cm, respectively. Locoregional recurrence was reported in 4 patients in the STND group (3.1%) and 6 (5.1%) in the LTND group. A total of 3 patients died (1.2%; 2 in the STND group and one in the LTND group). There was no significant difference between the 2 groups with respect to disease-free survival or local recurrence-free survival (p = 0.334 and p = 0.477, respectively).
CONCLUSION
The long-term oncologic outcomes of patients treated with NSM did not significantly differ according to TND when the intraoperative frozen biopsy was negative for tumor cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gerber B, Krause A, Dieterich M, Kundt G, Reimer T. The oncological safety of skin sparing mastectomy with conservation of the nipple-areola complex and autologous reconstruction: an extended follow-up study. Ann Surg. 2009; 249:461–468.
Article2. Peled AW, Duralde E, Foster RD, Fiscalini AS, Esserman LJ, Hwang ES, et al. Patient-reported outcomes and satisfaction after total skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate expander-implant reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2014; 72:Suppl 1. S48–S52.
Article3. Sosin M, Gulla A, Potdevin L, Cox SE, Bartholomew AJ, Seevaratnam S, et al. Timing of radiation therapy in nipple-sparing mastectomy influences outcomes and patient-reported quality of life. Breast J. 2018; 24:934–939.
Article4. Giannini V, Bianchi V, Carabalona S, Mazzetti S, Maggiorotto F, Kubatzki F, et al. MRI to predict nipple-areola complex (NAC) involvement: an automatic method to compute the 3D distance between the NAC and tumor. J Surg Oncol. 2017; 116:1069–1078.
Article5. Özkurt E, Tükenmez M, Güven E, Çelet Özden B, Öner G, Müslümanoğlu M, et al. Favorable outcome with close margins in patients undergoing nipple/skin sparing mastectomy with immediate breast reconstruction: 5-year follow-up. Balkan Med J. 2018; 35:84–92.
Article6. Chirappapha P, Srichan P, Lertsithichai P, Thaweepworadej P, Sukarayothin T, Leesombatpaiboon M, et al. Nipple-areola complex sensation after nipple-sparing mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2018; 6:e1716.
Article7. Pek WS, Tan BK, Ru Ng YY, Kiak Mien Tan V, Rasheed MZ, Kiat Tee Tan B, et al. Immediate breast reconstruction following nipple-sparing mastectomy in an Asian population: aesthetic outcomes and mitigating nipple-areolar complex necrosis. Arch Plast Surg. 2018; 45:229–238.
Article8. Endara M, Chen D, Verma K, Nahabedian MY, Spear SL. Breast reconstruction following nipple-sparing mastectomy: a systematic review of the literature with pooled analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013; 132:1043–1054.9. Ryu JM, Nam SJ, Kim SW, Lee SK, Bae SY, Yi HW, et al. Feasibility of nipple-sparing mastectomy with immediate breast reconstruction in breast cancer patients with tumor-nipple distance less than 2.0 cm. World J Surg. 2016; 40:2028–2035.
Article10. Moris D, Kontos M. Nipple-sparing mastectomy with immediate breast reconstruction in breast cancer patients with tumour-nipple distance less than 2.0 cm: the jury is still out. World J Surg. 2017; 41:348.
Article11. Caruso F, Ferrara M, Castiglione G, Trombetta G, De Meo L, Catanuto G, et al. Nipple sparing subcutaneous mastectomy: sixty-six months follow-up. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2006; 32:937–940.
Article12. Jensen JA, Orringer JS, Giuliano AE. Nipple-sparing mastectomy in 99 patients with a mean follow-up of 5 years. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011; 18:1665–1670.
Article13. Benediktsson KP, Perbeck L. Survival in breast cancer after nipple-sparing subcutaneous mastectomy and immediate reconstruction with implants: a prospective trial with 13 years median follow-up in 216 patients. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008; 34:143–148.
Article14. Petit JY, Veronesi U, Orecchia R, Curigliano G, Rey PC, Botteri E, et al. Risk factors associated with recurrence after nipple-sparing mastectomy for invasive and intraepithelial neoplasia. Ann Oncol. 2012; 23:2053–2058.
Article15. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Breast cancer, version 1. National Comprehensive Cancer Network (US);2018. Accessed May 1, 2019. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.asp.16. Amara D, Peled AW, Wang F, Ewing CA, Alvarado M, Esserman LJ. Tumor involvement of the nipple in total skin-sparing mastectomy: strategies for management. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015; 22:3803–3808.
Article17. Haslinger ML, Sosin M, Bartholomew AJ, Crocker A, Gulla A, Willey SC, et al. Positive nipple margin after nipple-sparing mastectomy: an alternative and oncologically safe approach to preserving the nipple-areolar complex. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018; 25:2303–2307.
Article18. De La Cruz L, Moody AM, Tappy EE, Blankenship SA, Hecht EM. Overall survival, disease-free survival, local recurrence, and nipple-areolar recurrence in the setting of nipple-sparing mastectomy: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015; 22:3241–3249.
Article19. de Alcantara Filho P, Capko D, Barry JM, Morrow M, Pusic A, Sacchini VS. Nipple-sparing mastectomy for breast cancer and risk-reducing surgery: the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center experience. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011; 18:3117–3122.
Article20. Stolier AJ, Sullivan SK, Dellacroce FJ. Technical considerations in nipple-sparing mastectomy: 82 consecutive cases without necrosis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008; 15:1341–1347.
Article21. Wagner JL, Fearmonti R, Hunt KK, Hwang RF, Meric-Bernstam F, Kuerer HM, et al. Prospective evaluation of the nipple-areola complex sparing mastectomy for risk reduction and for early-stage breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012; 19:1137–1144.
Article22. Warren Peled A, Foster RD, Stover AC, Itakura K, Ewing CA, Alvarado M, et al. Outcomes after total skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate reconstruction in 657 breasts. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012; 19:3402–3409.
Article23. Sacchini V, Pinotti JA, Barros AC, Luini A, Pluchinotta A, Pinotti M, et al. Nipple-sparing mastectomy for breast cancer and risk reduction: oncologic or technical problem? J Am Coll Surg. 2006; 203:704–714.
Article24. D'Alonzo M, Martincich L, Biglia N, Pisacane A, Maggiorotto F, Rosa GD, et al. Clinical and radiological predictors of nipple-areola complex involvement in breast cancer patients. Eur J Cancer. 2012; 48:2311–2318.25. Ponzone R, Maggiorotto F, Carabalona S, Rivolin A, Pisacane A, Kubatzki F, et al. MRI and intraoperative pathology to predict nipple-areola complex (NAC) involvement in patients undergoing NAC-sparing mastectomy. Eur J Cancer. 2015; 51:1882–1889.
Article26. Mariscotti G, Durando M, Houssami N, Berzovini CM, Esposito F, Fasciano M, et al. Preoperative MRI evaluation of lesion-nipple distance in breast cancer patients: thresholds for predicting occult nipple-areola complex involvement. Clin Radiol. 2018; 73:735–743.
Article27. Cense HA, Rutgers EJ, Lopes Cardozo M, Van Lanschot JJ. Nipple-sparing mastectomy in breast cancer: a viable option? Eur J Surg Oncol. 2001; 27:521–526.
Article28. Steen ST, Chung AP, Han SH, Vinstein AL, Yoon JL, Giuliano AE. Predicting nipple-areolar involvement using preoperative breast MRI and primary tumor characteristics. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013; 20:633–639.
Article29. Dent BL, Miller JA, Eden DJ, Swistel A, Talmor M. Tumor-to-nipple distance as a predictor of nipple involvement: expanding the inclusion criteria for nipple-sparing mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017; 140:1e–8e.30. Galimberti V, Vicini E, Corso G, Morigi C, Fontana S, Sacchini V, et al. Nipple-sparing and skin-sparing mastectomy: Review of aims, oncological safety and contraindications. Breast. 2017; 34:Suppl 1. S82–S84.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- One-stage nipple and breast reconstruction using a deep inferior epigastric perforator flap after a skin-sparing mastectomy
- Immediate Breast Reconstruction with TRAM Flap after Nipple-Areolar Sparing Mastectomy
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Clinicopathological Factors for the Detection of Occult Nipple Involvement in Breast Cancer Patients
- Skin-sparing mastectomy with immediate nipple reconstruction during autologous latissimus dorsi breast reconstruction: A review of patient satisfaction
- Skin-sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Nipple Graft for Large, Ptotic Breast