J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2020 Feb;55(1):71-77. 10.4055/jkoa.2020.55.1.71.
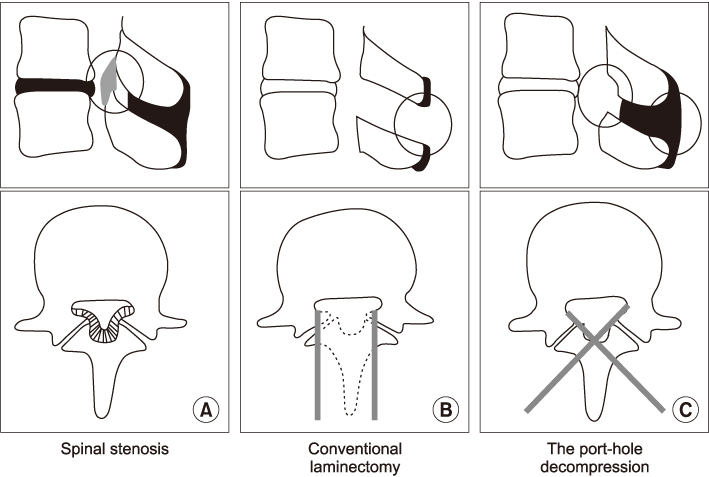
Preservation of the Posterior Ligaments for Preventing Postoperative Spinal Instability in Posterior Decompression of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Comparative Study between Port-Hole Decompression and Subtotal Laminectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Bundang Jeasaeng General Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. hynaspin@naver.com
- KMID: 2470771
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2020.55.1.71
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To determine if sparing the interspinous and supraspinous ligaments during posterior decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis is significant in preventing postoperative spinal instability.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 83 patients who underwent posterior decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis between March 2014 and March 2017 with a minimum one-year follow-up period, were studied retrospectively. The subjects were divided into two groups according to the type of surgery. Fifty-six patients who underwent posterior decompression by the port-hole technique were grouped as A, while 27 patients who underwent posterior decompression by a subtotal laminectomy grouped as B. To evaluate the clinical results, the Oswestry disability index (ODI), visual analogue scale (VAS) for both back pain (VAS-B) and radiating pain (VAS-R), and the walking distance of neurogenic intermittent claudication (NIC) were checked pre- and postoperatively, while simple radiographs of the lateral and flexion-extension view in the standing position were taken preoperatively and then every six months after to measure anteroposterior slippage (slip percentage), the difference in anteroposterior slippage between flexion and extension (dynamic slip percentage), angular displacement, and the difference in angular displacement between flexion and extension (dynamic angular displacement) to evaluate the radiological results.
RESULTS
The ODI (from 28.1 to 12.8 in group A, from 27.3 to 12.3 in group B), VAS-B (from 7.0 to 2.6 in group A, from 7.7 to 3.2 in group B), VAS-R (from 8.5 to 2.8 in group A, from 8.7 to 2.9 in group B), and walking distance of NIC (from 118.4 m to 1,496.2 m in group A, from 127.6 m to 1,481.6 m in group B) were improved in both groups. On the other hand, while the other radiologic results showed no differences, the dynamic angular displacement between both groups showed a significant difference postoperatively (group A from 6.2° to 6.7°, group B from 6.5° to 8.4°, p-value=0.019).
CONCLUSION
Removal of the posterior ligaments, including the interspinous and supraspinous ligaments, during posterior decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis can cause a postoperative increase in dynamic angular displacement, which can be prevented by the port-hole technique, which spares these posterior ligaments.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kleeman TJ, Hiscoe AC, Berg EE. Patient outcomes after minimally destabilizing lumbar stenosis decompression: the “Port-Hole” technique. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:865–870.2. Chatani K. A novel surgical approach to the lumbar spine involving hemilateral split-off of the spinous process to preserve the multifidus muscle: technical note. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016; 24:694–699.
Article3. Reinshagen C, Ruess D, Molcanyi M, et al. A novel translaminar crossover approach for pathologies in the lumbar hidden zone. J Clin Neurosci. 2015; 22:1030–1035.
Article4. Kakiuchi M, Fukushima W. Impact of spinous process integrity on ten to twelve-year outcomes after posterior decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: study of open-door laminoplasty using a spinous process-splitting approach. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015; 97:1667–1677.5. Jalil Y, Carvalho C, Becker R. Long-term clinical and radiological postoperative outcomes after an interspinous microdecompression of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014; 39:368–373.
Article6. Adachi K, Futami T, Ebihara A, et al. Spinal canal enlargement procedure by restorative laminoplasty for the treatment of lumbar canal stenosis. Spine J. 2003; 3:471–478.
Article7. Iguchi T, Kurihara A, Nakayama J, Sato K, Kurosaka M, Yamasaki K. Minimum 10-year outcome of decompressive laminectomy for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:1754–1759.
Article8. Aizawa T, Ozawa H, Kusakabe T, et al. Reoperation rates after fenestration for lumbar spinal canal stenosis: a 20-year period survival function method analysis. Eur Spine J. 2015; 24:381–387.
Article9. Henky J, Yasuda M, Arifin MZ, Takayasu M, Faried A. Trumpet laminectomy microdecompression for lumbal canal stenosis. Asian Spine J. 2014; 8:667–674.
Article10. Thomé C, Zevgaridis D, Leheta O, et al. Outcome after less-invasive decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis: a randomized comparison of unilateral laminotomy, bilateral laminotomy, and laminectomy. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005; 3:129–141.
Article11. Song WS, Na HY, Son EY, Choe S, Lee JH. The clinical results after posterior ligaments preserving fenestration in lumbar spinal stenosis: the port-hole decompression. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2018; 53:44–50.
Article12. Schizas C, Theumann N, Burn A, et al. Qualitative grading of severity of lumbar spinal stenosis based on the morphology of the dural sac on magnetic resonance images. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35:1919–1924.
Article13. Abumi K, Panjabi MM, Kramer KM, Duranceau J, Oxland T, Crisco JJ. Biomechanical evaluation of lumbar spinal stability after graded facetectomies. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1990; 15:1142–1147.
Article14. Natarajan RN, Andersson GB, Patwardhan AG, Andriacchi TP. Study on effect of graded facetectomy on change in lumbar motion segment torsional flexibility using three-dimensional continuum contact representation for facet joints. J Biomech Eng. 1999; 121:215–221.
Article15. Mullin BB, Rea GL, Irsik R, Catton M, Miner ME. The effect of postlaminectomy spinal instability on the outcome of lumbar spinal stenosis patients. J Spinal Disord. 1996; 9:107–116.
Article16. Sharma M, Langrana NA, Rodriguez J. Role of ligaments and facets in lumbar spinal stability. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20:887–900.
Article17. Gillespie KA, Dickey JP. Biomechanical role of lumbar spine ligaments in flexion and extension: determination using a parallel linkage robot and a porcine model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29:1208–1216.
Article18. Yang JC, Kim SG, Kim TW, Park KH. Analysis of factors contributing to postoperative spinal instability after lumbar decompression for spinal stenosis. Korean J Spine. 2013; 10:149–154.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Clinical Results after Posterior Ligaments Preserving Fenestration in Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: The Port-Hole Decompression
- Treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis after fracture of posterior ring apophysis by anterior decompression
- Clinical study on the posterior decompression and posterolateral fusion with instrumentation in lumbar spinal stenosis
- Clinical Analysis of Less Extensive Microsurgical Decompression for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- Clinical Comparison between Decompression and Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Chronic Lower Back Pain Involving Degenerative Disc Disease and Spinal Stenosis