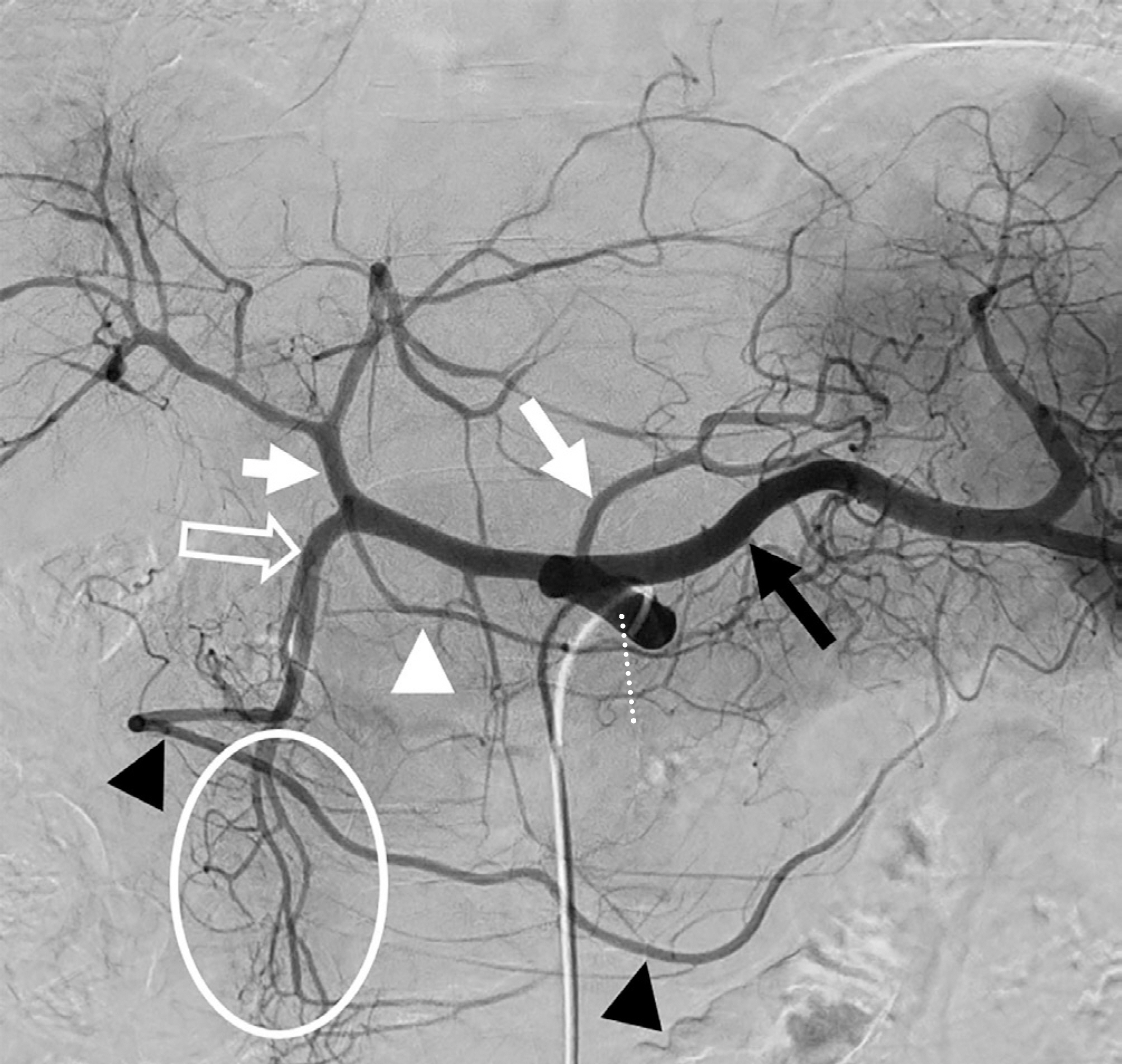
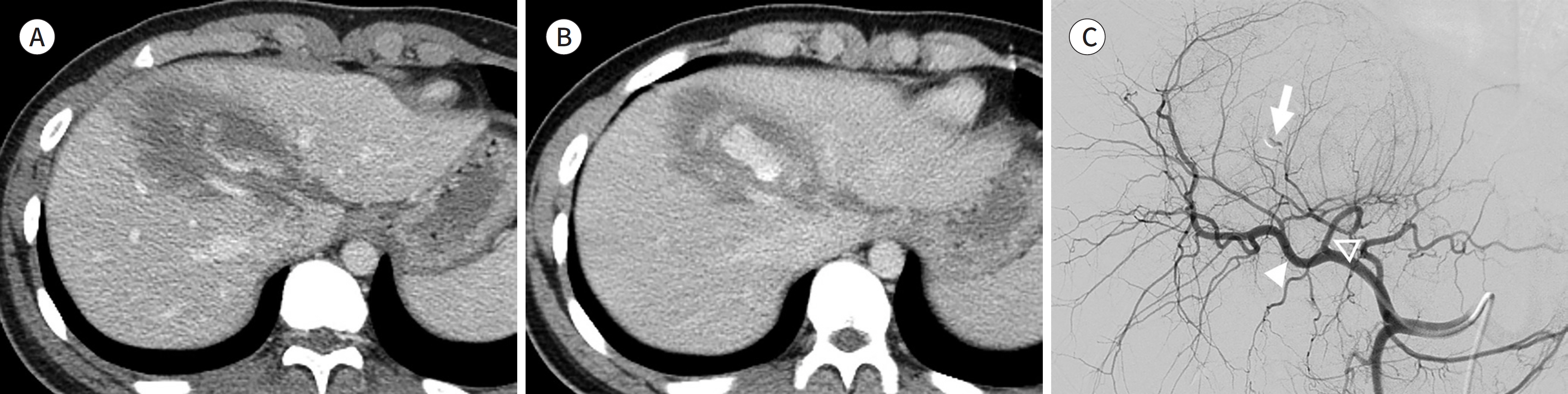
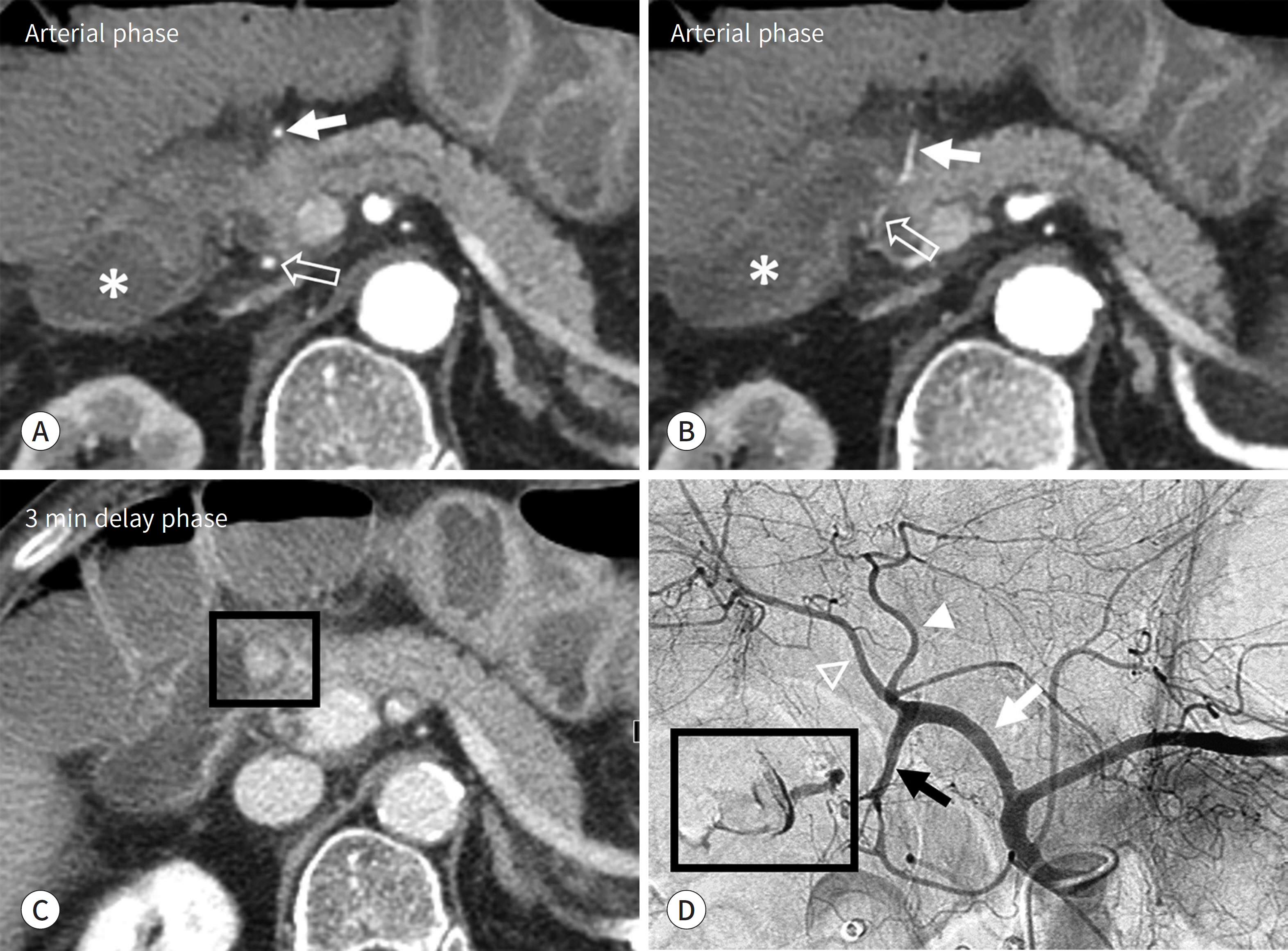
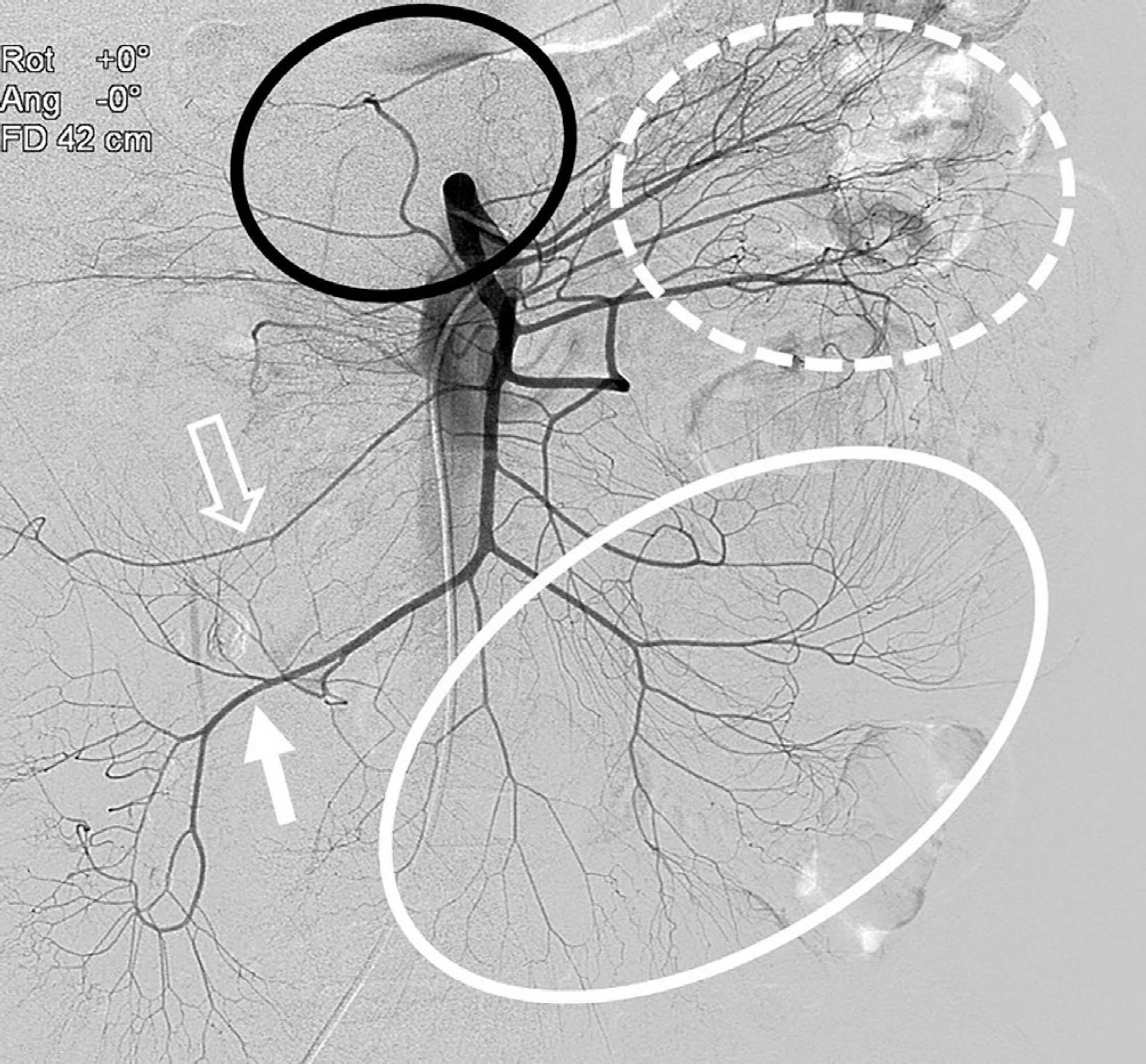
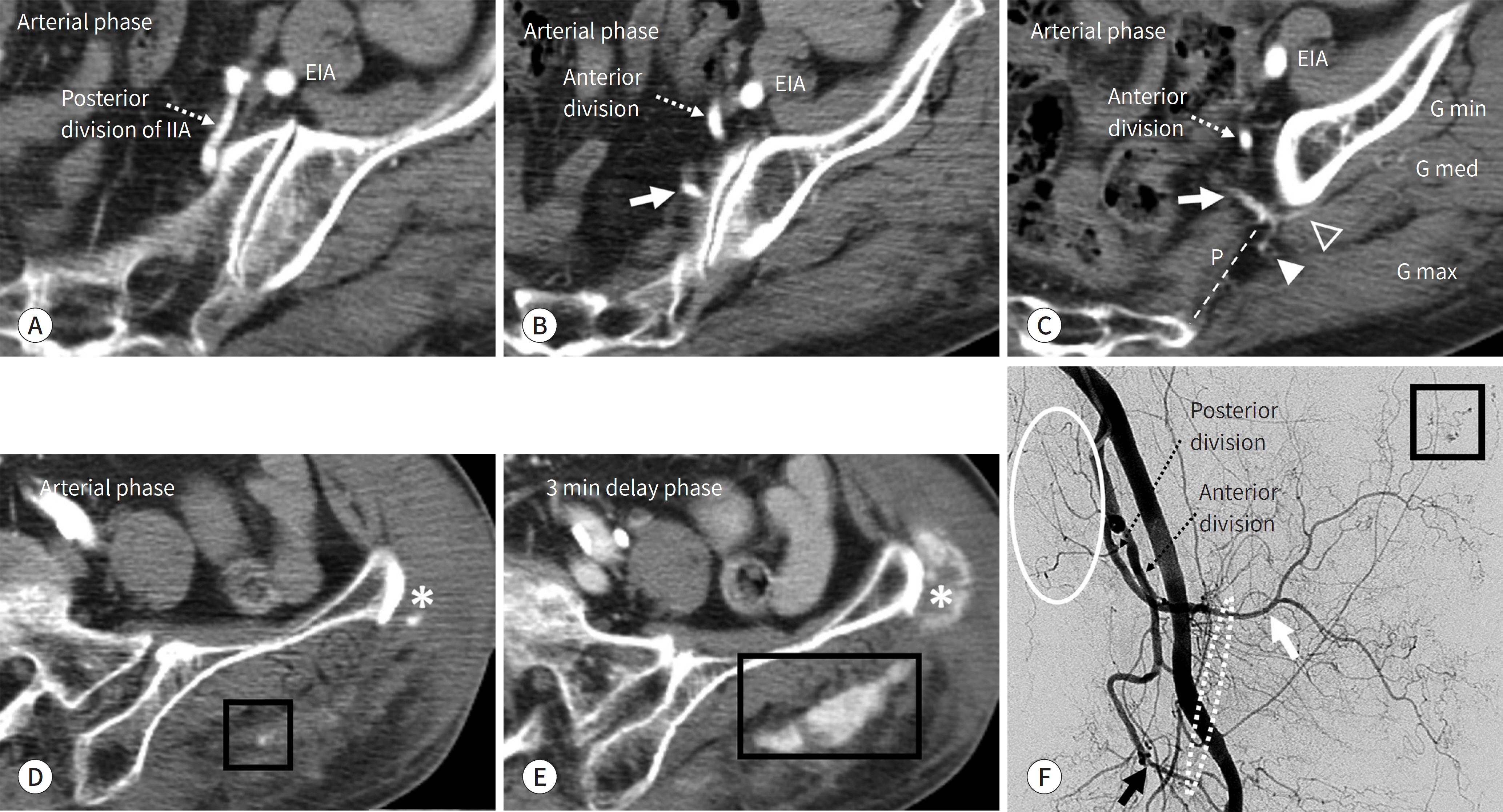
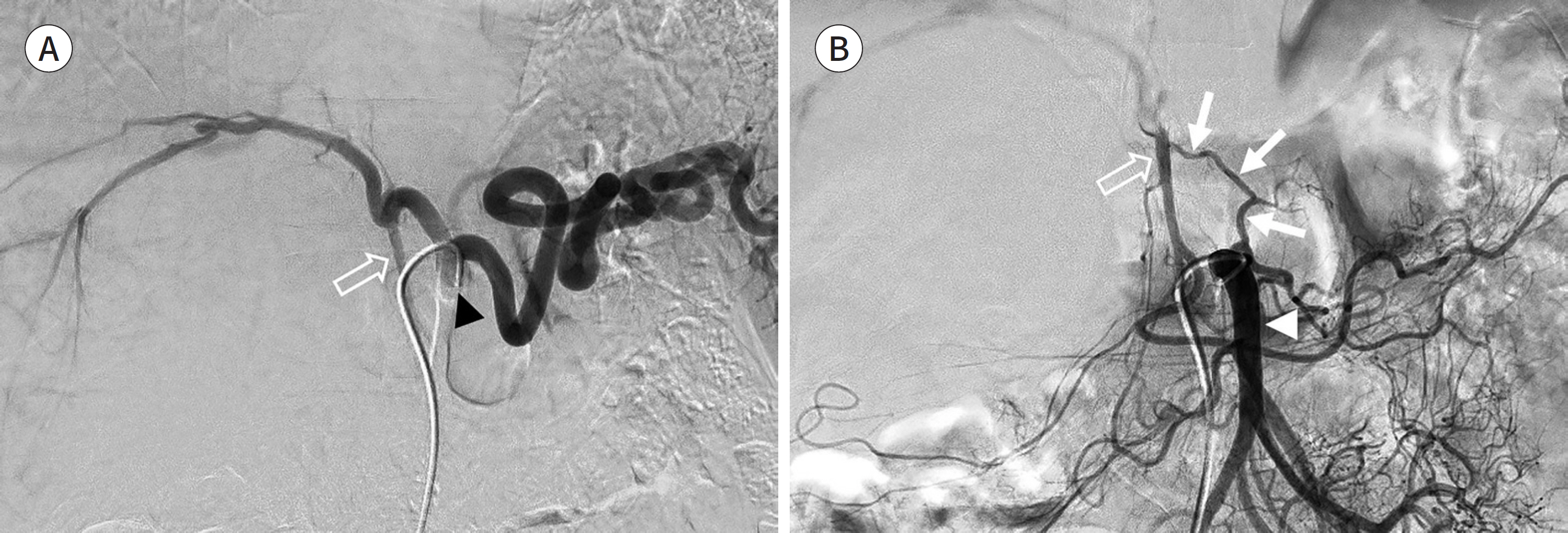
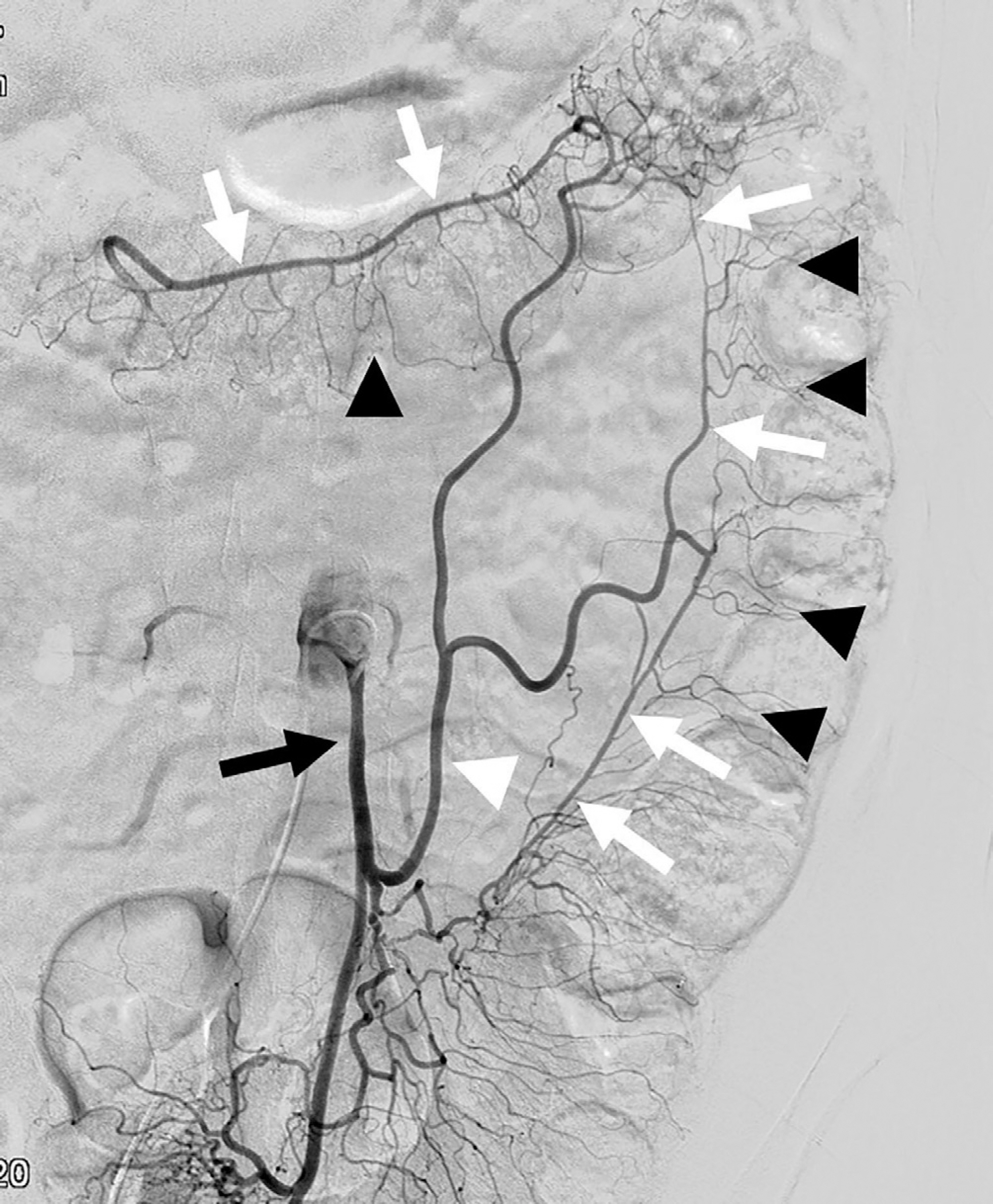
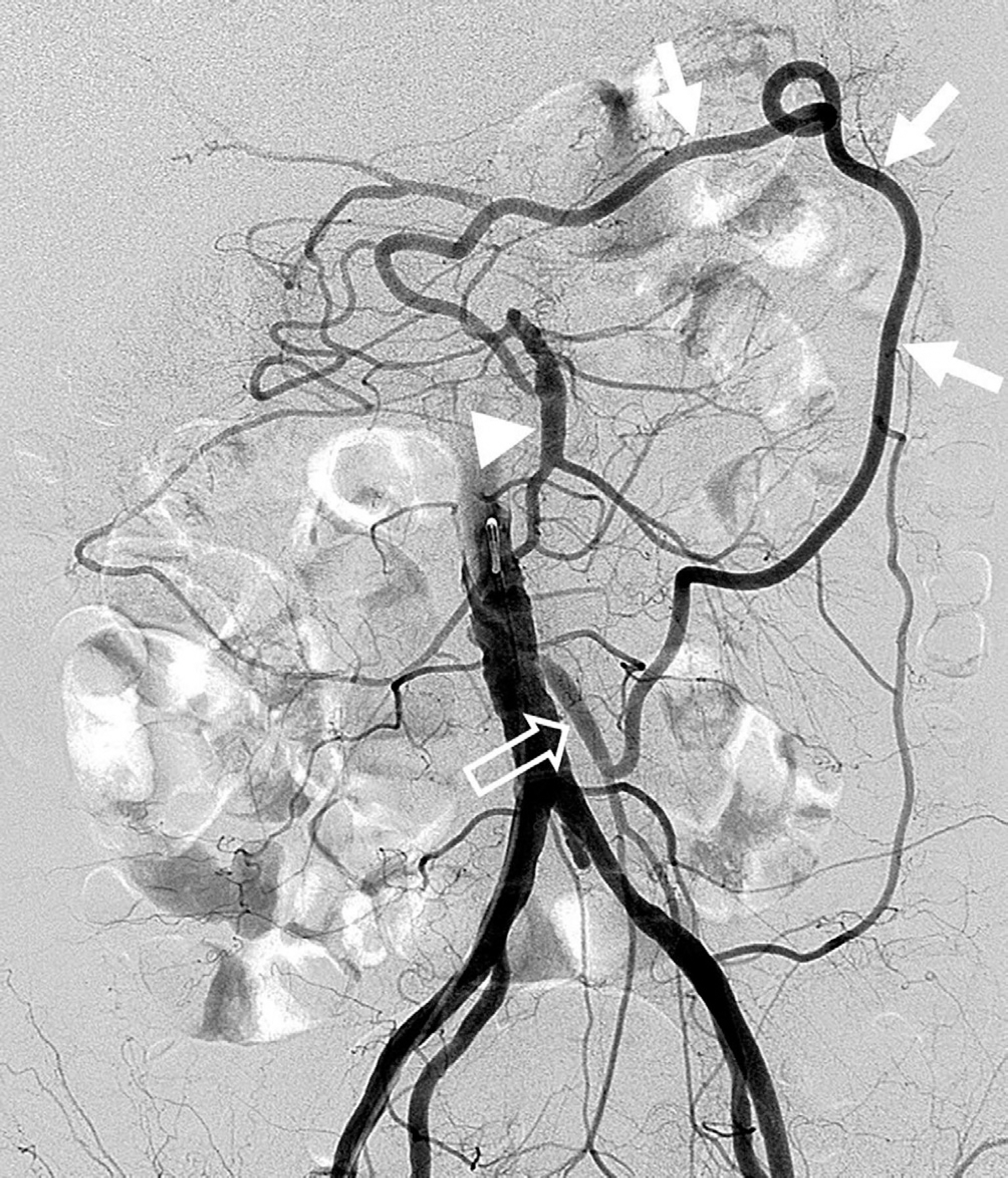
J Korean Soc Radiol.
2020 Jan;81(1):119-134. 10.3348/jksr.2020.81.1.119.
Basic Arterial Anatomy and Interpretation of CT Angiography for Intra-Abdominal or Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Correlation with Conventional Angiographic Findings for Beginners
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Kyung Hee University Medical Center, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. kwon98@khu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2469186
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2020.81.1.119
Abstract
- It is essential to identify the causative artery in case of active intra-abdominal or gastrointestinal bleeding. A thorough understanding of the basic arterial anatomy is required to identify the causative artery on contrast-enhanced CT angiography and conventional catheter angiography. If one is familiar with the basic arterial anatomy, obtaining access to the bleeding artery will be easier, despite the variations in the origin and course of the vessels. We describe the basic arterial anatomy that will help beginners in diagnostic radiology to identify the blood vessels that can cause active intra-abdominal or gastrointestinal bleeding.
MeSH Terms
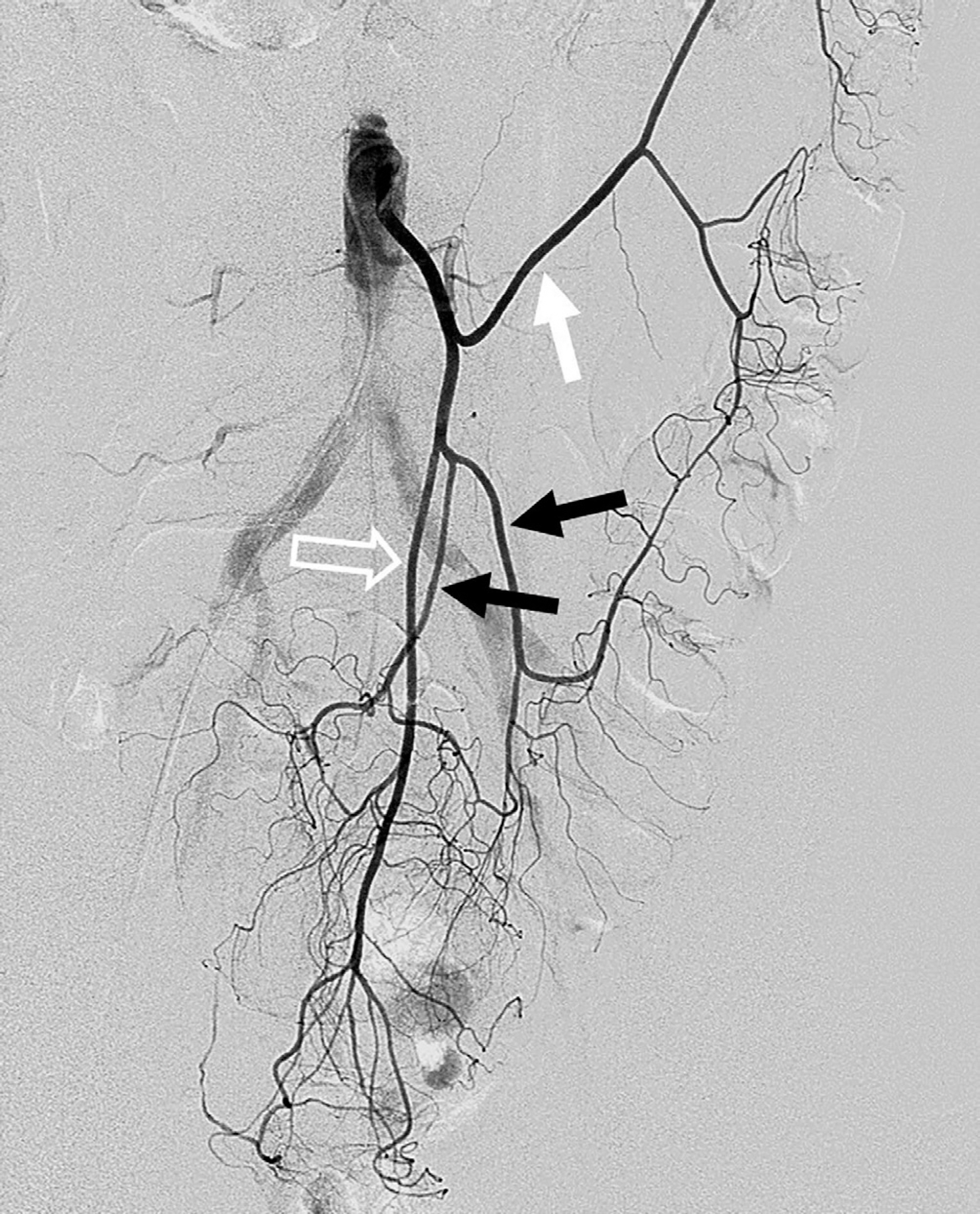
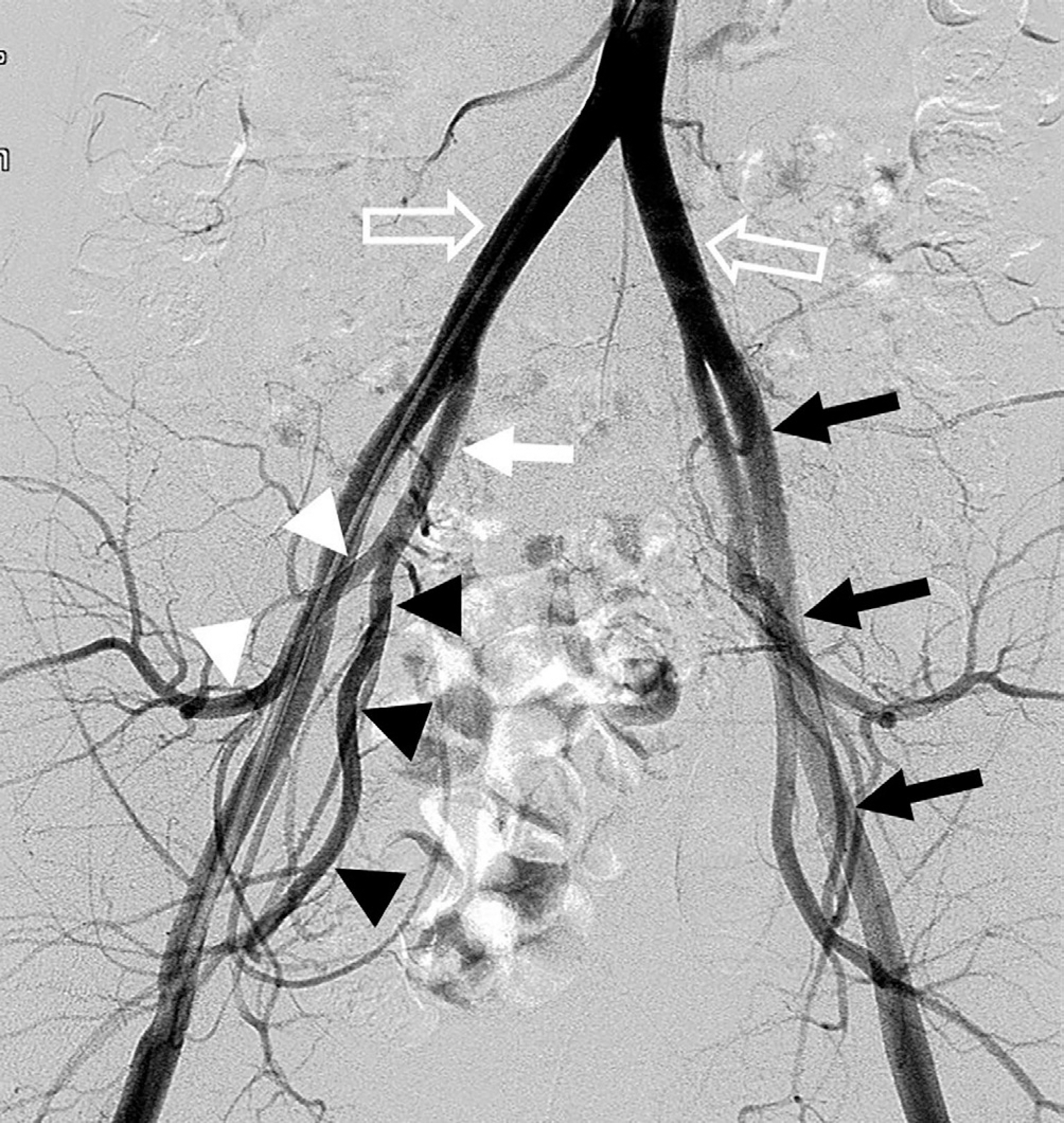
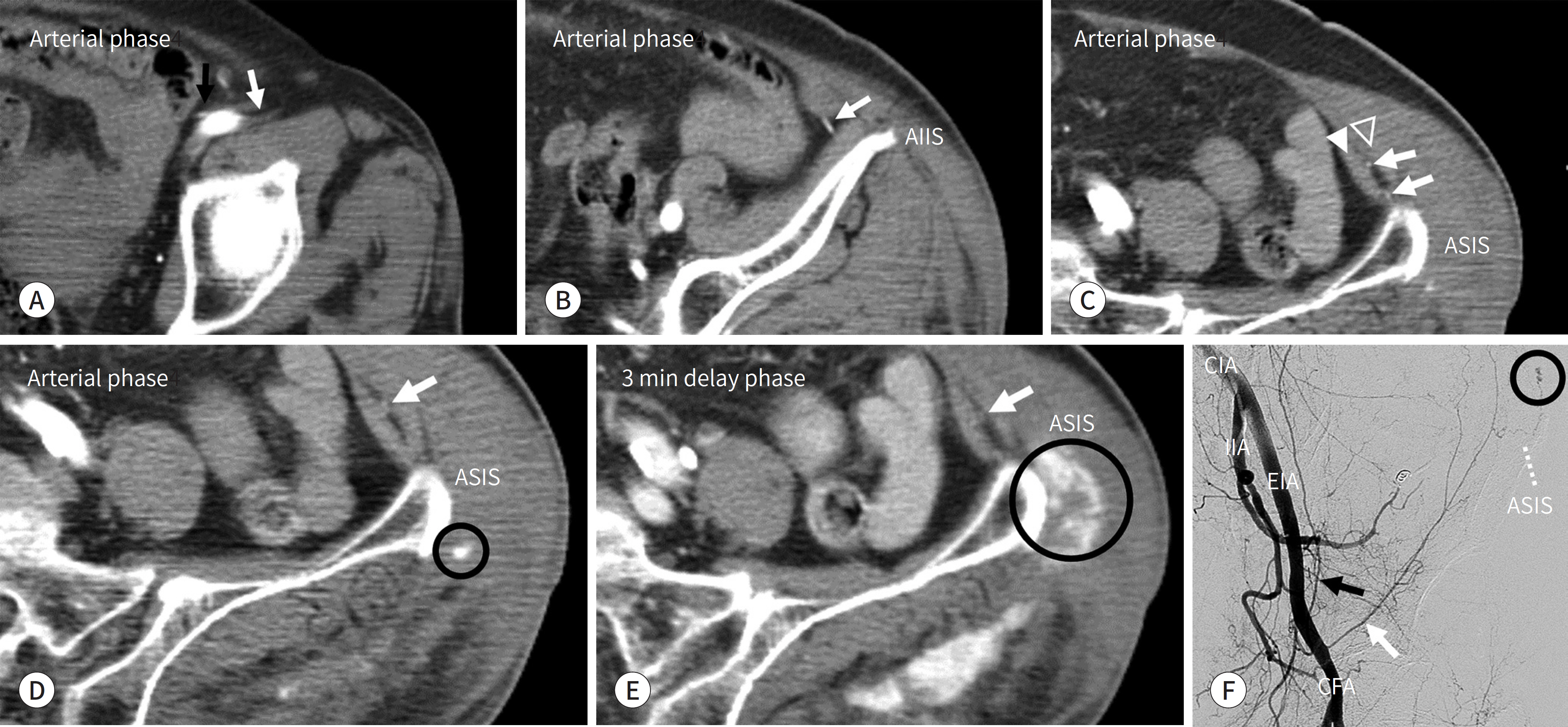
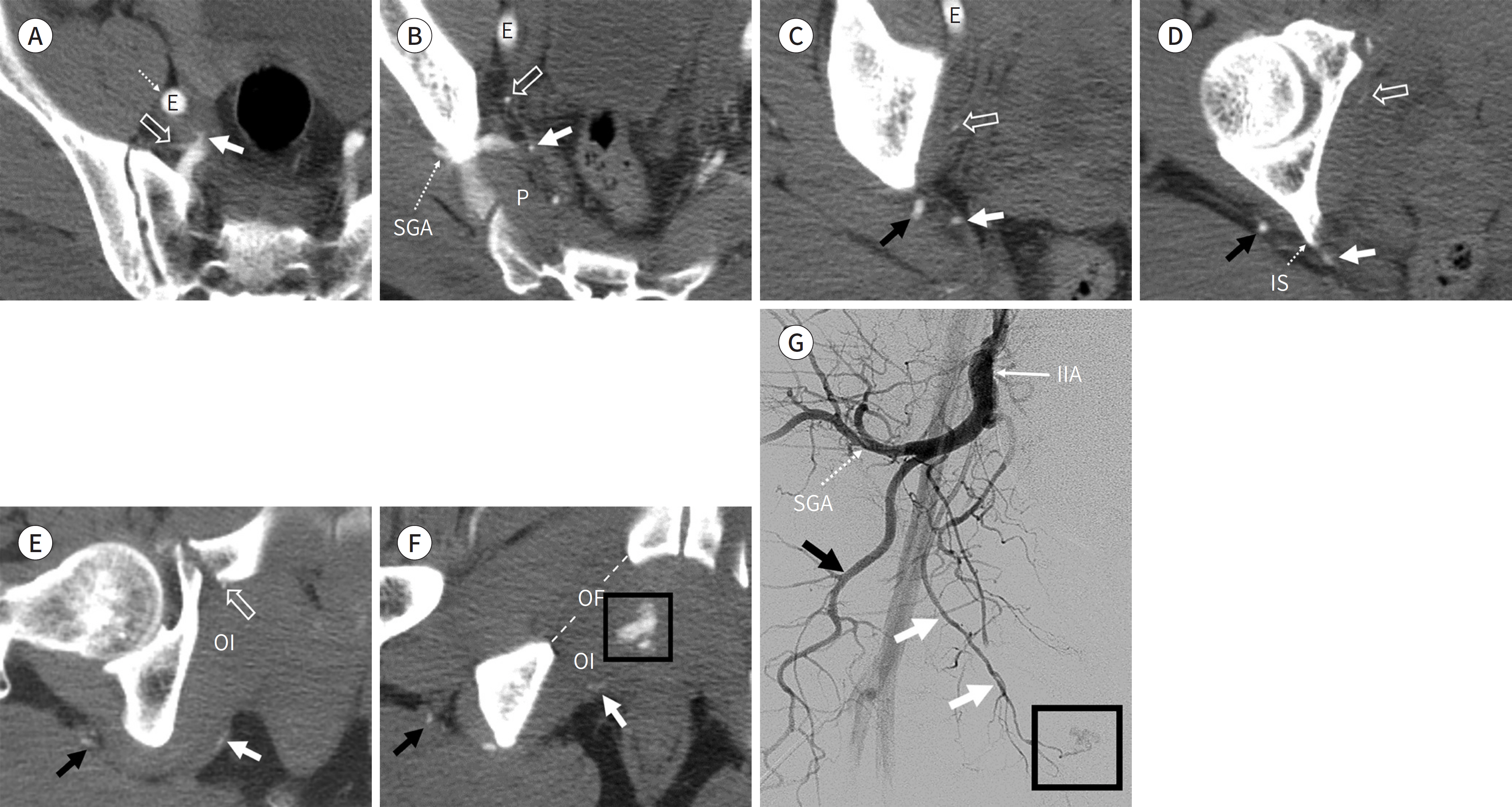
Figure
Reference
-
1. Artigas JM, Martí M, Soto JA, Esteban H, Pinilla I, Guillén E. Multidetector CT angiography for acute gastrointestinal bleeding: technique and findings. Radiographics. 2013; 33:1453–1470.
Article2. Dobritz M, Engels HP, Schneider A, Wieder H, Feussner H, Rummeny EJ, et al. Evaluation of dual-phase multidetector-row CT for detection of intestinal bleeding using an experimental bowel model. Eur Radiol. 2009; 19:875–881.
Article3. Kuhle WG, Sheiman RG. Detection of active colonic hemorrhage with use of helical CT: findings in a swine model. Radiology. 2003; 228:743–752.
Article4. Rimola J, Perendreu J, Falcó J, Fortuño JR, Massuet A, Branera J. Percutaneous arterial embolization in the management of rectus sheath hematoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 188:W497–W502.
Article5. Nakayama T, Ishibashi T, Eguchi D, Yamada K, Tsurumaru D, Sakamoto K, et al. Spontaneous internal oblique hematoma successfully treated by transcatheter arterial embolization. Radiat Med. 2008; 26:446–449.
Article6. Garg A, Gupta AK, Khandelwal N. Diagnostic radiology: chest and cardiovascular imaging. 4th ed. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Pub 2018:2.7. White RD, Weir-McCall JR, Sullivan CM, Mustafa SA, Yeap PM, Budak MJ, et al. The celiac axis revisited: anatomic variants, pathologic features, and implications for modern endovascular management. Radiographics. 2015; 35:879–898.
Article8. Ahluwalia N, Futterman B. Anatomy, abdomen and pelvis, celiac trunk. Treasure Island: StatPearls Publish-ing LLC;2019.9. Korean Society of Interventional Radiology. Interventional radiology. 2nd ed. Seoul: Ilchokak;2014.10. Madoff DC, Denys A, Wallace MJ, Murthy R, Gupta S, Pillsbury EP, et al. Splenic arterial interventions: anatomy, indications, technical considerations, and potential complications. Radiographics. 2005; 25(Suppl 1):S191–S211.
Article11. Oderich GS. Mesenteric vascular disease current therapy. Berlin: Spinger;2015. p. 15.12. Horton KM, Fishman EK. Volume-rendered 3D CT of the mesenteric vasculature: normal anatomy, anatomic variants, and pathologic conditions. Radiographics. 2002; 22:161–172.
Article13. Joy P, Prithishkumar IJ, Isaac B. Clinical anatomy of the inferior epigastric artery with special relevance to invasive procedures of the anterior abdominal wall. J Minim Access Surg. 2017; 13:18–21.14. Selçuk I, Yassa M, Tatar I, Huri E. Anatomic structure of the internal iliac artery and its educative dissection for peripartum and pelvic hemorrhage. Turk J Obstet Gynecol. 2018; 15:126–129.
Article15. Yoon W, Kim JK, Jeong YY, Seo JJ, Park JG, Kang HK. Pelvic arterial hemorrhage in patients with pelvic frac-tures: detection with contrast-enhanced CT. Radiographics. 2004; 24:1591–1605. discussion 1605-1606.
Article16. Tansatit T, Chokrungyaranont P, Sanguansit P, Wanidchaphloi S. Anatomical study of the superior gluteal artery perforator (S-GAP) for free flap harvesting. J Med Assoc Thai. 2008; 91:1244–1249.17. Song SY, Chung JW, Kwon JW, Joh JH, Shin SJ, Kim HB, et al. Collateral pathways in patients with celiac axis stenosis: angiographic-spiral CT correlation. Radiographics. 2002; 22:881–893.
Article18. Kalva SP, Athanasoulis CA, Greenfield AJ, Fan CM, Curvelo M, Waltman AC, et al. Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery aneurysms in association with celiac axis stenosis or occlusion. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2007; 33:670–675.
Article19. Kwon SH, Ahn HJ, Oh JH. Is it the Arc of riolan or meandering mesenteric artery?J Endovasc Ther. 2015; 22:825–826.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multidetector-row CT Angiography of Hepatic Artery: Comparison with Conventional Angiography
- Identifying Small Bowel Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor as the Culprit Lesion in Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Emphasis on Angiographic Findings
- Correlation of CT and angiographic findings in cerebrovascular occlusive disease
- Clinical Progression of Segmental Arterial Mediolysis; Renal Infarction and Intra-abdominal Hemorrhage
- Transcatheter Arterial Embolization of Arterial Esophageal Bleeding with the Use of N-Butyl Cyanoacrylate